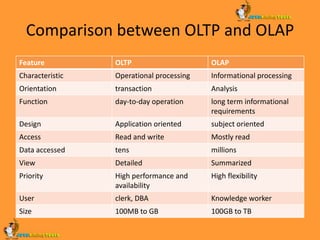
This document discusses data warehousing and online analytical processing (OLAP) technology. It defines a data warehouse, compares it to operational databases, and explains how OLAP systems organize and present data for analysis. The document also describes multidimensional data models, common OLAP operations, and the steps to design and construct a data warehouse. Finally, it discusses applications of data warehouses and efficient processing of OLAP queries.