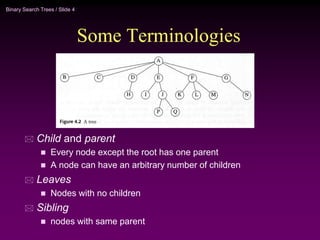
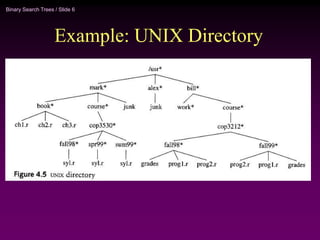
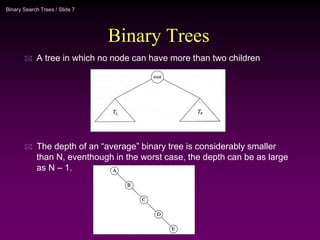
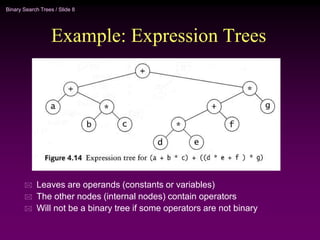
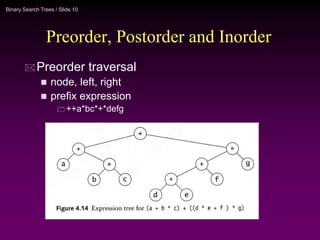
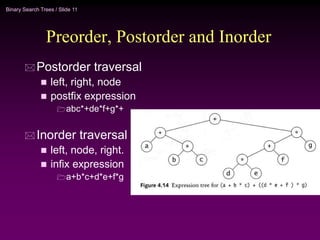
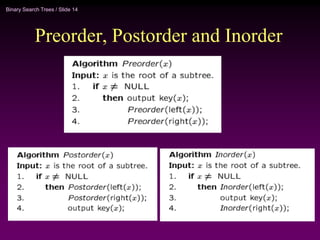
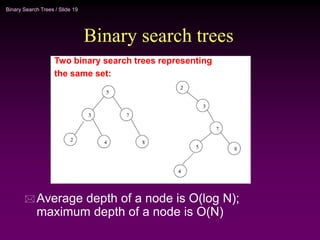
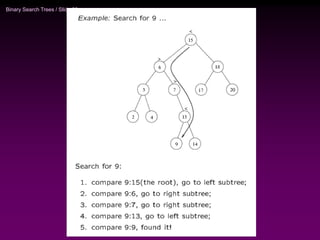
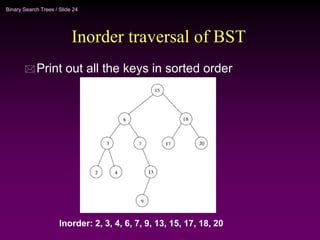
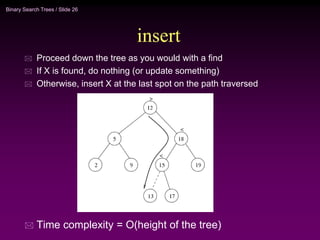
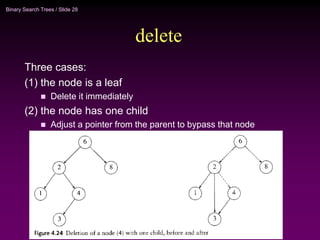
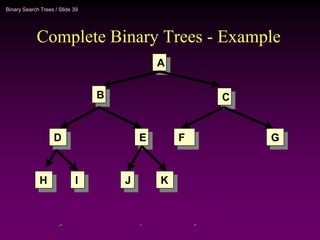
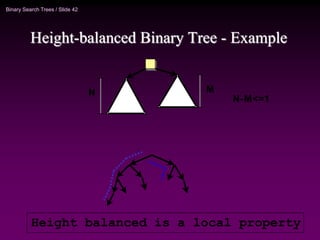
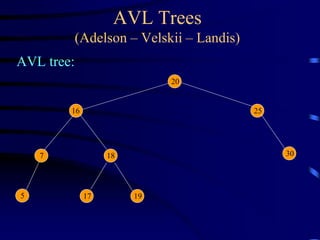
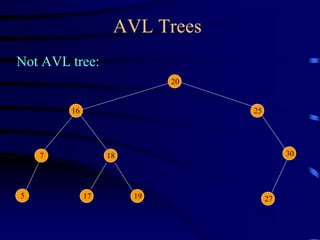
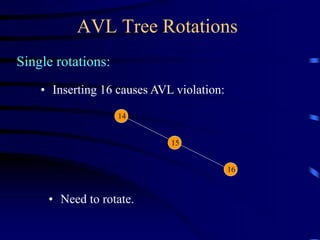
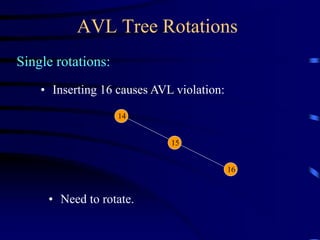
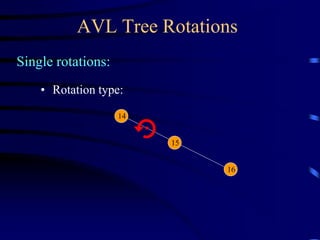
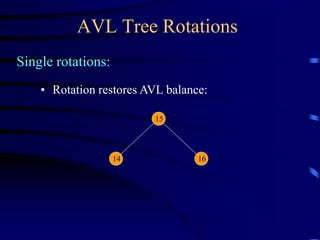
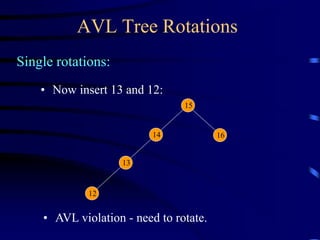
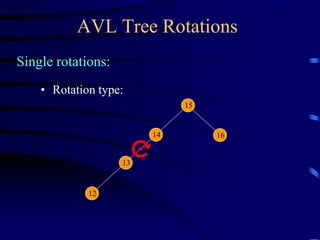
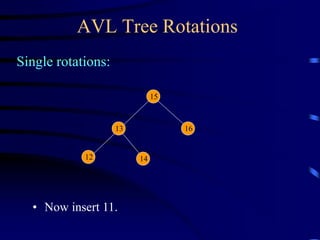
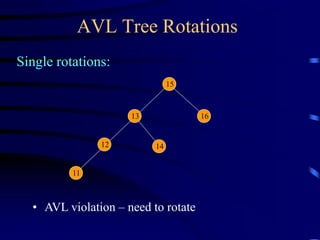
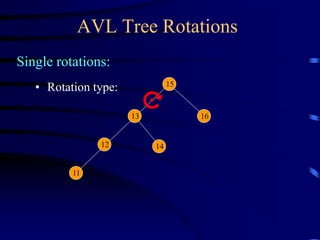
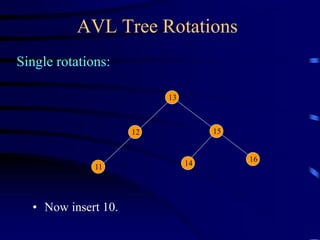
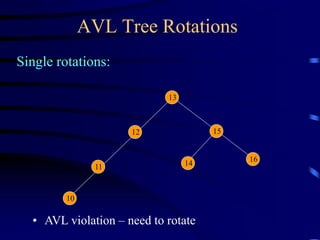
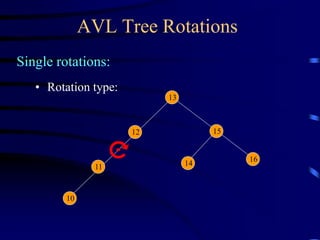
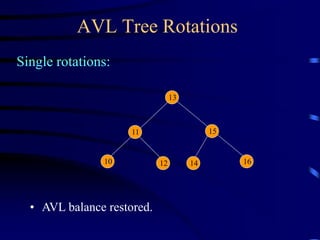
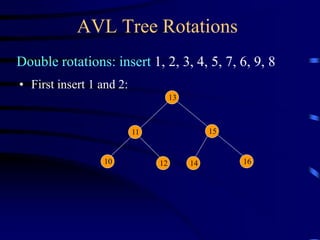
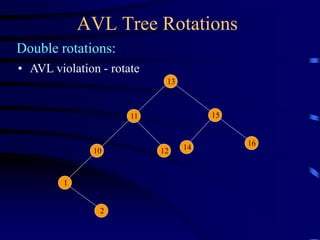
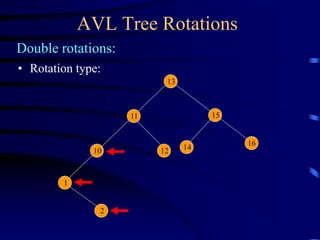
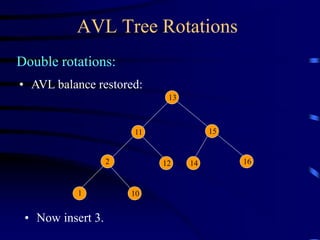
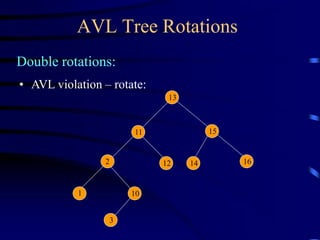
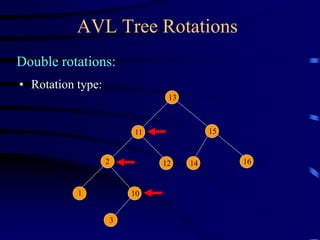
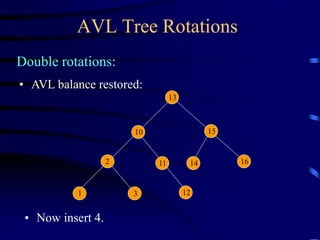
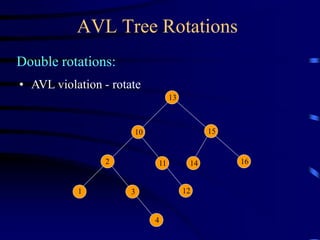
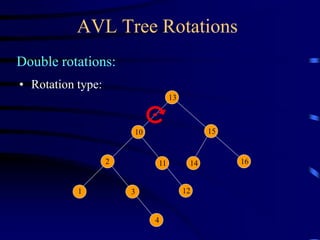
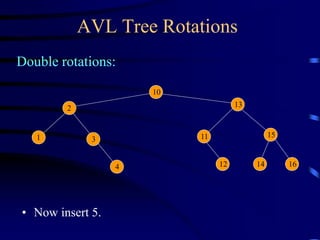
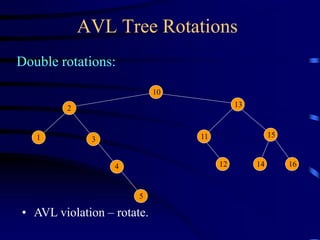
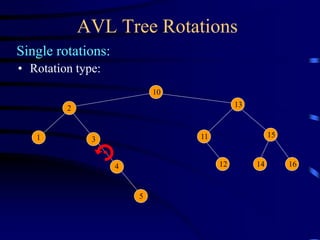
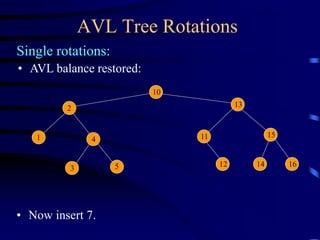
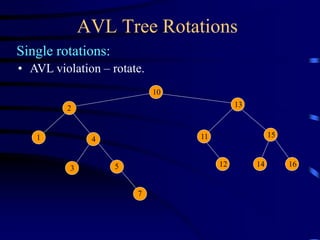
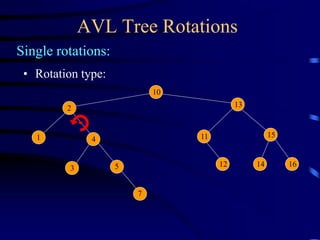
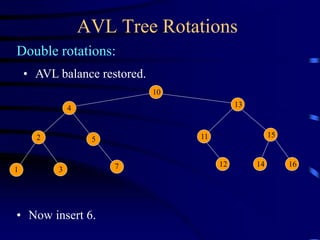
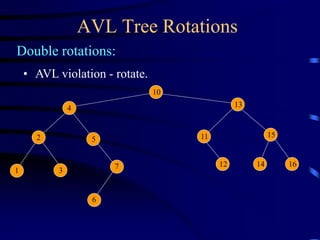
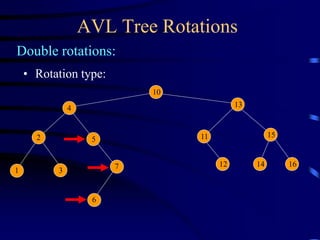
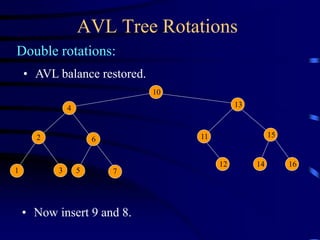
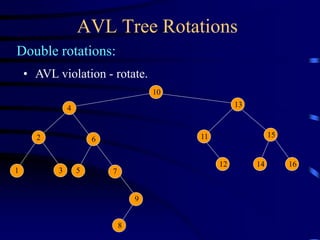
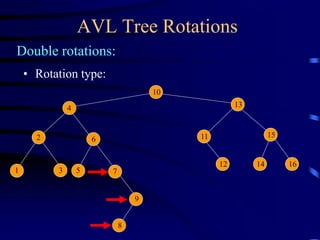
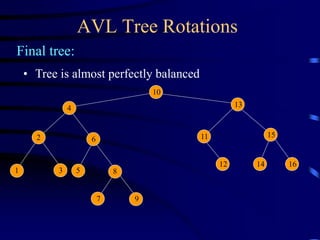
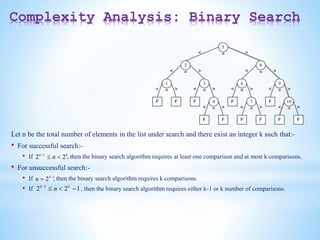
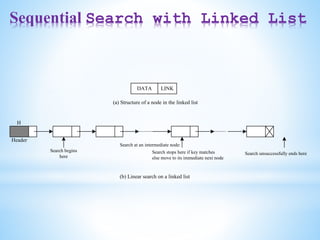
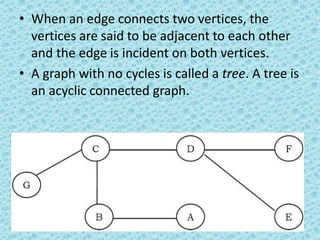
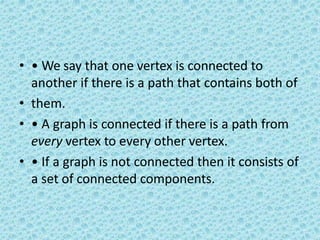
Binary trees and binary search trees are discussed. Binary trees have nodes with at most two children, while binary search trees have the additional property that for every node, all keys in its left subtree are smaller than the node's key and all keys in its right subtree are larger. Common tree operations like searching, insertion, and deletion can be performed in O(log n) time on balanced binary search trees. AVL trees are discussed as one way to balance binary search trees through rotations.































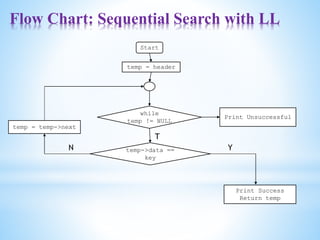
![Flowchart: Sequential Search with Array
Start
i = 0
K = A[i]?
Print "Successful"
Print "Unsuccessful"
i = i+1
i ≥ n
Stop
Yes
Yes
No
No](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructuresmoduleiiiiv-231118053936-965279fd/85/data-structures-module-III-IV-pptx-89-320.jpg)
![Example: Sequential Search with Array
int main()
{
int A[10], i, n, K, flag = 0;
printf("Enter the size of an array: ");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("Enter the elements of the array: ");
for(i=0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%d",&A[i]);
printf("Enter the number to be searched: ");
scanf("%d",&K);
for(i=0;i<n;i++){
if(a[i] == K){
flag = 1; break;
}
}
if(flag == 0)
printf("The number is not in the list");
else
printf("The number is found at index %d",i);
return 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructuresmoduleiiiiv-231118053936-965279fd/85/data-structures-module-III-IV-pptx-90-320.jpg)


![l u
mid = (l+u)/2
(a) An ordered array of elemnets with index values l, u and mid
l u
mid
(b) Search the entire list turns into the searching of left-half only
u = mid-1
Serach this half the same way
if K < A[mid]
l u
mid
l = mid+1 Serach this half the same way
if K > A[mid]
(c) Search the entire list turns into the searching of right-half only
The Technique](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructuresmoduleiiiiv-231118053936-965279fd/85/data-structures-module-III-IV-pptx-94-320.jpg)
![Flowchart: Binary Search with Array
mid = (l+u)/2
K = A[mid]?
Start
Search is successful
YES NO
K < A[mid]?
YES
u = mid-1 l = mid+1
NO
Stop
(l>u)?
Start
Search is unsuccessful
YES
NO](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructuresmoduleiiiiv-231118053936-965279fd/85/data-structures-module-III-IV-pptx-95-320.jpg)
![Binary Search (with Iteration)
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i, l, u, mid, n, K, data[100];
printf("Enter number of elementsn");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("Enter %d integers in sorted ordern", n);
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%d",&array[i]);
printf("Enter value to findn");
scanf("%d", &K);
l = 0;
u = n - 1;
mid = (l+u)/2;
Contd…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructuresmoduleiiiiv-231118053936-965279fd/85/data-structures-module-III-IV-pptx-96-320.jpg)
![Binary Search (with Iteration)
while (l <= u) {
if (data[mid] < K)
l = mid + 1;
else if (data[mid] == K) {
printf("%d found at location %d.n", search, mid+1);
break;
}
else
u = mid - 1;
mid = (l + u)/2;
}
if (l > u)
printf("Not found! %d is not present in the list.n", K);
return 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructuresmoduleiiiiv-231118053936-965279fd/85/data-structures-module-III-IV-pptx-97-320.jpg)
![Binary Search (with Recursion)
#include<stdio.h>
int main(){
int data[100],i, n, K, flag, l, u;
printf("Enter the size of an array: ");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("Enter the elements of the array in sorted order: " );
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
printf("Enter the number to be search: ");
scanf("%d",&K);
l=0,u=n-1;
flag = binarySearch(data,n,K,l,u);
if(flag==0)
printf("Number is not found.");
else
printf("Number is found.");
return 0;
}
Contd…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructuresmoduleiiiiv-231118053936-965279fd/85/data-structures-module-III-IV-pptx-98-320.jpg)
![Binary Search (with Recursion)
int binary(int a[],int n,int K,int l,int u){
int mid;
if(l<=u){
mid=(l+u)/2;
if(K==a[mid]){
return(1);
}
else if(m<a[mid]){
return binarySearch(a,n,K,l,mid-1);
}
else
return binarySearch(a,n,m,mid+1,u);
}
else return(0);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructuresmoduleiiiiv-231118053936-965279fd/85/data-structures-module-III-IV-pptx-99-320.jpg)



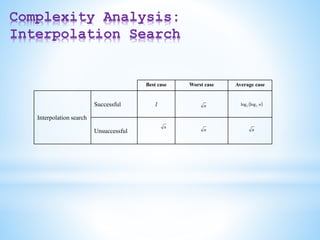
![Interpolation Search
1. l = 1, u = n // Initialization: Range of searching
2. flag = FALSE // Hold the status of searching
3. While (flag = FALSE) do
4. l
l
u
l
A
u
A
l
A
K
loc
]
[
]
[
]
[
5. If ( )
u
loc
l
then // If loc is within the range of the list
6. Case: K < A[loc]
7. u = loc -1
8. Case: K = A[loc]
9. flag = TRUE
10. Case: K > A[loc]
11. l = loc +1
12. Else
13. Exit()
14. EndIf
15. EndWhile
16. If (flag) then
17. Print “Successful at” loc
18. Else
19. Print “Unsuccessful”
20. EndIf
21. Stop](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructuresmoduleiiiiv-231118053936-965279fd/85/data-structures-module-III-IV-pptx-105-320.jpg)
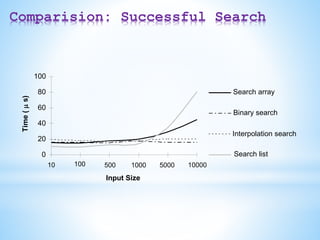
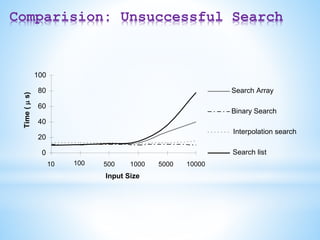



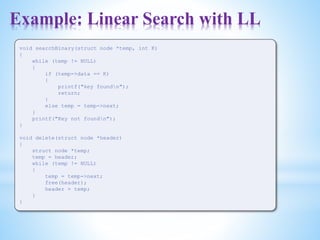

![Sorting
• Sorting means arranging the elements of an array so that they
some relevant order which may be either ascending or descen
• That is, if A is an array, then the elements of A are arrange
order (ascending order) in such a way that A[0] < A[1] < A[2] <
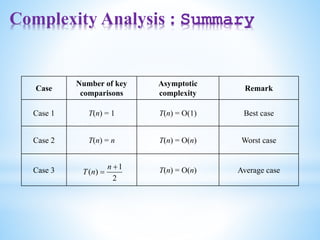
• The practical considerations for different sorting techniques w
• Number of sort key comparisons that will be performed.
• Number of times the records in the list will be moved.
• Best, average and worst case performance.
• Stability of the sorting algorithm where stability means that equival
records retain their relative positions even after sorting is done.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructuresmoduleiiiiv-231118053936-965279fd/85/data-structures-module-III-IV-pptx-117-320.jpg)


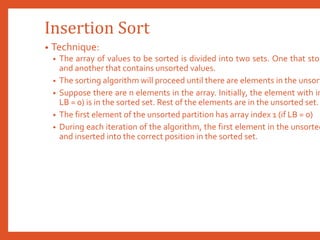
![Insertion Sort
• Procedure INSERTION_SORT (K, N) : Given an unordered vector K consisting of N
rearranges the vector in ascending order. The sorting process is based on the techniques ju
PASS denotes the pass index and the position of the element that needs to be compare
elements.TEMP is variable that holds the value which needs to be compared with previou
1. [Loop on pass index]
1. Repeat thru step 5 for PASS = 1 to N - 1
2. [Initialize a temporary variable to compare with]
1. TEMP K[PASS]
3. [Initialize variable for comparing with sorted array]
1. J PASS – 1
4. [Compare]
1. Repeat while TEMP ≤ K[J] AND J ≥ 0
1. K[J+1] K[J]
2. J J - 1
5. [Move the minimum value el
1. K[J+1] TEMP
6. [Finished]
1. Return](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructuresmoduleiiiiv-231118053936-965279fd/85/data-structures-module-III-IV-pptx-121-320.jpg)

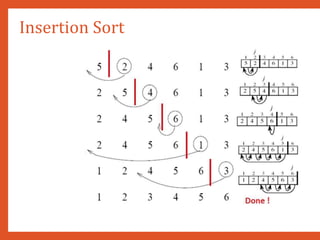
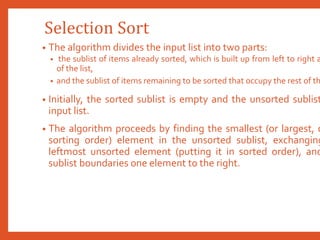
![Selection Sort
• Technique:
• Consider an array ARR with N elements. The selection sort takes N-1 p
entire array and works as follows. First find the smallest value in the arr
the first position. Then find the second smallest value in the array an
second position. Repeat this procedure until the entire array is sorted.Th
• In Pass 1, find the position POS of the smallest value in the array
ARR[POS] andARR[0].Thus, ARR[0] is sorted.
• In Pass 2, find the position POS of the smallest value in sub-array of N-1
ARR[POS] with ARR[1]. Now,A[0] andA[1] is sorted
• In Pass 3, find the position POS of the smallest value in sub-array of N-2
ARR[POS] with ARR[2]. Now,ARR[0],ARR[1] andARR[2] is sorted.
• In Pass N-1, find the position POS of the smaller of the elements ARR[N
1]. SwapARR[POS] and ARR[N-2] so that ARR[0],ARR[1], … , ARR[N-1] i](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructuresmoduleiiiiv-231118053936-965279fd/85/data-structures-module-III-IV-pptx-125-320.jpg)
![Selection Sort
• Procedure SELECTION_SORT (K, N) : Given an unordered vector K consisting of N elements
the vector in ascending order. The sorting process is based on the techniques just described.
the pass index and the position of the first element in the vector which is to be examined d
variable MIN_INDEX denotes the position of the smallest element encountered thus far in a pa
is used to index elements K[PASS] to K[N] in a given pass.
1. [Loop on pass index]
1. Repeat thru step 4 for PASS = 1 to N - 1
2. [Initialize minimum index]
1. MIN_INDEX PASS
3. [Make a pass and obtain element with smallest value]
1. Repeat for J = PASS + 1, … , N
1. If K[J] < K[MIN_INDEX]
2. Then MIN_INDEX J
4. [Exchange elements]
1. If MIN_INDEX ≠ PASS
2. Then K[PASS] K[MIN_INDEX]
5. [Finished]
1. Return](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructuresmoduleiiiiv-231118053936-965279fd/85/data-structures-module-III-IV-pptx-126-320.jpg)

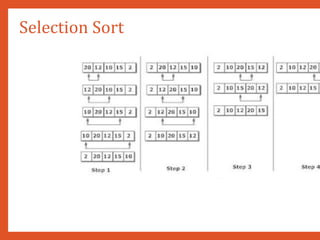

![Bubble Sort
• Technique:
• In Pass 1, A[0] and A[1] are compared, then A[1] is compared with A[2], A
with A[3] and so on. Finally, A[N-2] is compared with A[N-1]. Pass
comparisons and places the biggest element at the highest index of the
• In Pass 2, A[0] and A[1] are compared. then A[1] is compared with A[2],
with A[3] and so on. Finally, A[N-3] is compared with A[N-2]. Pass
comparisons and places the second biggest element at the second high
array.
• In Pass 3, A[0] and A[1] are compared. then A[1] is compared with A[2], A
with A[3] and so on. Finally, A[N-4] is compared with A[N-3]. Pass
comparisons and places the third biggest element at the third highest in
• In Pass n-1, A[0] and A[1] are compared so that A[0] < A[1]. After t
elements of the array are arranged in ascending order.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructuresmoduleiiiiv-231118053936-965279fd/85/data-structures-module-III-IV-pptx-130-320.jpg)
![Bubble Sort
• Procedure BUBBLE_SORT (A, N) : Given an unordered vector A consisting of N elements, this procedure rearrang
The sorting process is based on the techniques just described. The variable PASS denotes the pass index. The vari
first element that is compared with every consecutive element.
1. [Loop on pass index]
LAST = N
1. Repeat thru step 3 for PASS = 1 to N-1
2 [Initialize exchanges counter for this pass]
1. EXCHS 0
3 [Loop for iterating from start to end]
1. Repeat thru step 4 for J = 1 to LAST– 1
4 [Make pairwise comparisions on unsorted elements]
1. If A[J] > A[J+1]
1. Then A[J] A[J+1]
2. EXCHS EXCHS + 1
5 [Were any exchanges made on this pass?]
1. If EXCHS = 0
1. Then Return
else
LAST = LAST -1
5. [Finished]
1. Return](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructuresmoduleiiiiv-231118053936-965279fd/85/data-structures-module-III-IV-pptx-131-320.jpg)


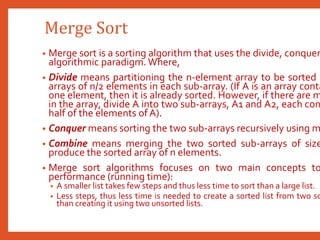

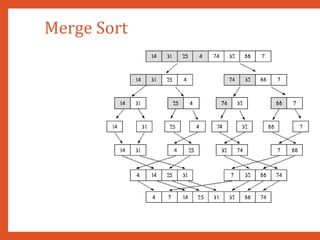
![Merge Sort
• Procedure MERGE_SORT (ARR, BEG, END) : Given an vector ARR, it is required to sort recur
positions BEG and END (inclusive). MID denotes the position of the middle element of that sub
1. [Test base condition]
1. If BEG < END
2. [Calculate the midpoint position of current subtable]
1. MID (BEG + END) / 2
3. [Recursively sort the first subtable]
1. Call MERGE_SORT (ARR, BEG, MID)
4. [Recursively sort the second subtable]
1. Call MERGE_SORT (ARR, MID + 1, END)
5. [Merge two ordered subtables]
1. MERGE (ARR, BEG, MID, END)
6. [Finished]
1. Return](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructuresmoduleiiiiv-231118053936-965279fd/85/data-structures-module-III-IV-pptx-138-320.jpg)
![Merge Sort
• Procedure MERGE (ARR, BEG, MID, END) : Given two ordered subtables stored in a vecto
END as just described, this procedure performs a simple merge. TEMP is a temporary v
process. The variables I and J denote the cursor associated with the first and second subt
is an index variable associated with the vectorTEMP.
1. [Initialize]
1. I BEG
2. J MID + 1
3. INDEX 0
2. [Compare corresponding elements and compute the smallest]
1. Repeat while ( I ≤ MID ) AND ( J ≤ END )
1. If ARR[I] < ARR[J]
1. Then TEMP[INDEX] ARR[I]
2. I I + 1
2. Else
1. TEMP [INDEX] ARR[J]
2. J J + 1
3. INDEX INDEX + 1
3. [Copy the remaining elements of
1. If I > MID
1. Repeat while J ≤ END
1. TEMP[INDEX]
2. INDEX INDEX
3. J J + 1
[Copy the remaining elements o
2. Else
1. Repeat while I ≤ MID
1. TEMP[INDEX]
2. INDEX INDEX
3. I I + 1
4. [Copy elements in temporary vec
1. K 0
2. Repeat while K < INDEX
1. ARR[K] = TEMP[K]
2. K K + 1
5. [Finished]
1. Return](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructuresmoduleiiiiv-231118053936-965279fd/85/data-structures-module-III-IV-pptx-139-320.jpg)
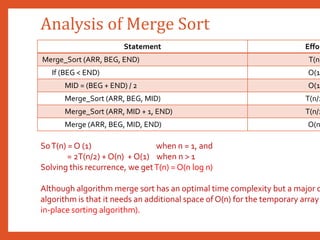
![Analysis of Merge Sort
• Assume n=2k for k>=1 k separate passes are required to merge 2k separa
single table.
• T(n) = 2T(n/2) + bn + c
• T(n/2) = 2T((n/2) /2) + b(n/2) + c = 2[2T(n/4) + b(n/2) + c] + bn +c
• = 4T(n/4)+ bn +2c +bn +c = 4T(n/4) + 2bn+ (1 + 2) c
• = 22T(n/22)+2bn+(20+21) = 4 [2T((n/4)/2) + b(n/4) + c] +2bn + (1
• =8T(n/8) + 3bn+ (1+2+4)c = 23T(n/23) + 3bn+ (20+21+22)c
• Generalizing, we can write
• 2kT(n/2k)+kbn+(20+21+...+2k-1)c
• T(1) = a, since n=2k log n = log2k = k
• T(n) = 2k. a + k bn + (20+21+...+2k-1) c
• = b. n log n+ (a + c) n – c
• = O (n log n) [Best, Average andWorst]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructuresmoduleiiiiv-231118053936-965279fd/85/data-structures-module-III-IV-pptx-141-320.jpg)

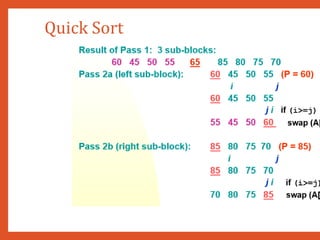
![Quick Sort
• Procedure QUICK_SORT (K, LB, UB) : Given a table K of N records, this recursive procedure
order. A dummy record with K[N + 1] assumed where K[I] ≤ K[N + 1] for all 1 ≤ I ≤ N. The inte
denote the lower and upper bounds of the certain subtable being processed. The indices I and
keys during the processing of each subtable. KEY contains the key value which is being places
sorted subtable. FLAG is a logical variable which indicates the end of the process that places a
When FLAG becomes false, the input subtable has been partitioned into two disjointed parts.
1. [Initialize]
1. FLAG TRUE
2. [Perform sort]
1. If LB < UB
2. Then I LB
1. J UB + 1
2. KEY K[LB]
3. Repeat while FLAG
1. I I + 1
2. Repeat while K[I] < KEY && I <= UB
1. I I + 1
3. J J - 1
4. Repeat while K[J] > K
1. J J – 1
5. If I < J
1. Then K[I] K
2. Else FLAG Fals
6. K[LB] K[J]
7. Call Quick_Sort(K, LB
8. Call Quick_Sort(K, J +
3. [Finished]
1. Return](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructuresmoduleiiiiv-231118053936-965279fd/85/data-structures-module-III-IV-pptx-143-320.jpg)











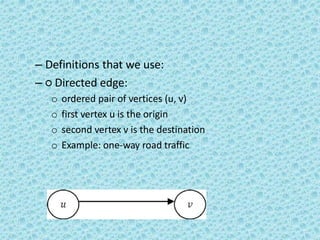
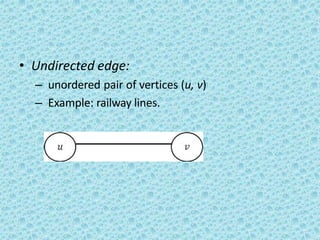
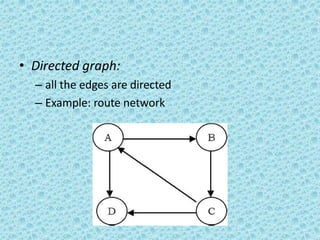
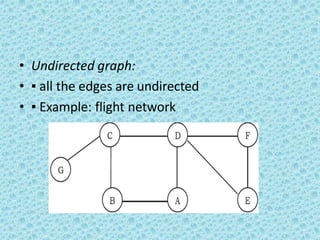




![• A directed acyclic graph [DAG] is a directed
graph with no cycles.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructuresmoduleiiiiv-231118053936-965279fd/85/data-structures-module-III-IV-pptx-167-320.jpg)


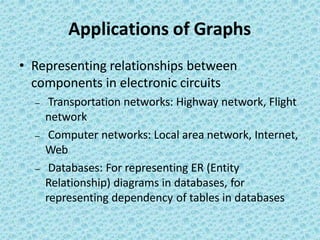



![• Description
• In this method, we use a matrix with size V × V. The
values of matrix are boolean. Let us assume the matrix
is Adj. The value Adj[u, v] is set to 1 if there is an edge
from vertex u to vertex v and 0 otherwise.
• In the matrix, each edge is represented by two bits for
undirected graphs. That means, an edge from u to v is
represented by 1 value in both Adj[u,v ] and Adj[u,v].
To save time, we can process only half of this
symmetric matrix. Also, we can assume that there is an
“edge” from each vertex to itself. So, Adj[u, u] is set to
1 for all vertices.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructuresmoduleiiiiv-231118053936-965279fd/85/data-structures-module-III-IV-pptx-176-320.jpg)
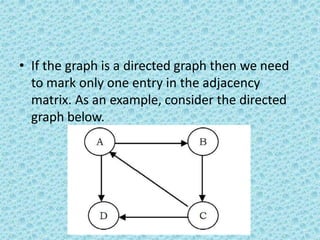






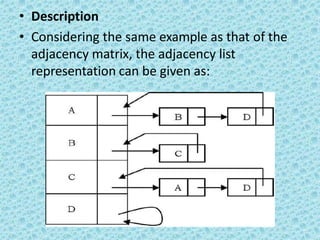






![• Adjacency Set
• It is very much similar to adjacency list but
instead of using Linked lists, Disjoint Sets
[Union- Find] are used.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructuresmoduleiiiiv-231118053936-965279fd/85/data-structures-module-III-IV-pptx-191-320.jpg)
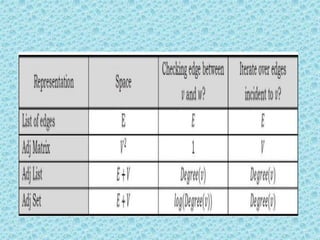
![• Comparison of Graph Representations:
• Directed and undirected graphs are represented
with the same structures.
• For directed graphs,everything is the same,
except that each edge is represented just once.
An edge from x to y is represented by a 1 value in
Agj[x][y] in the adjacency matrix, or by adding y
on x’s adjacency list.
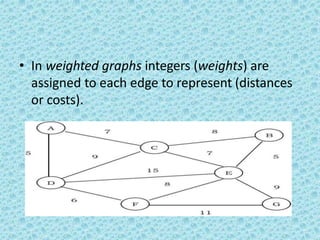
• For weighted graphs, everything is the same,
except fill the adjacency matrix with weights
instead of boolean values.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructuresmoduleiiiiv-231118053936-965279fd/85/data-structures-module-III-IV-pptx-192-320.jpg)
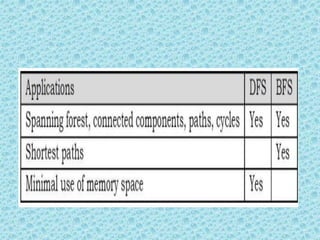
![Graph Traversals
• To solve problems on graphs, we need a mechanism for
traversing the graphs. Graph traversal algorithms are
also called graph search algorithms. Like trees traversal
algorithms (Inorder, Preorder, Postorder and Level-
Order traversals), graph search algorithms can be
thought of as starting at some source vertex in a graph
and “searching” the graph by going through the edges
and marking the vertices. Now, we will discuss two
such algorithms for traversing the graphs.
– Depth First Search [DFS]
– Breadth First Search [BFS]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructuresmoduleiiiiv-231118053936-965279fd/85/data-structures-module-III-IV-pptx-194-320.jpg)
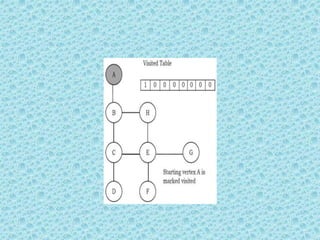
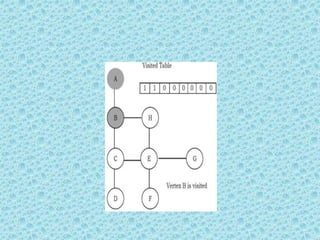
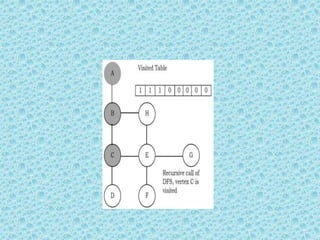
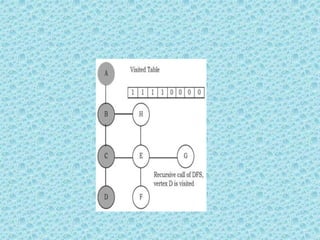
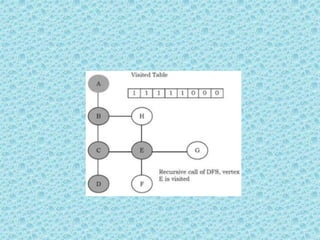
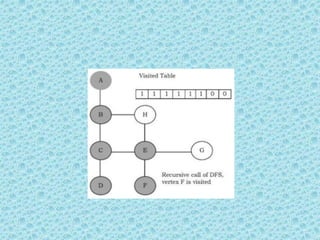
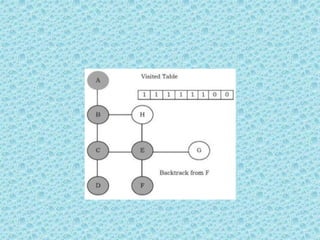
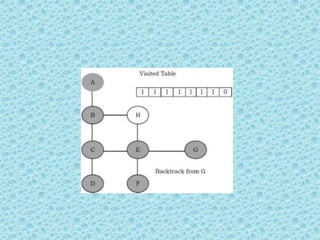
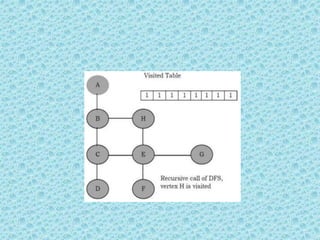
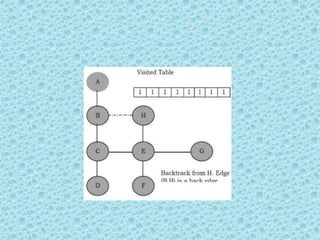
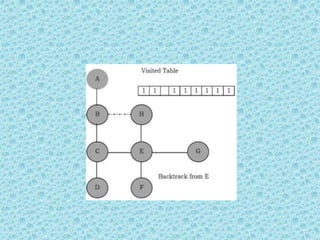
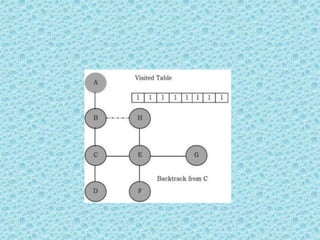
![• Depth First Search [DFS]:
• DFS algorithm works in a manner similar to
preorder traversal of the trees. Like preorder
traversal, internally this algorithm also uses
stack.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructuresmoduleiiiiv-231118053936-965279fd/85/data-structures-module-III-IV-pptx-195-320.jpg)






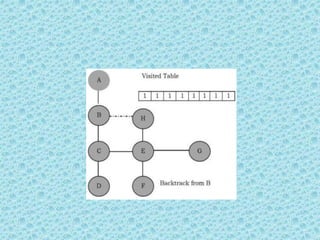
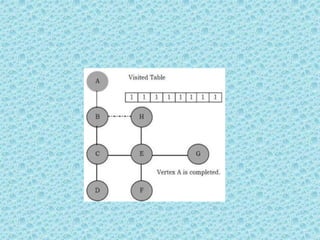
![• The process terminates when backtracking
leads back to the start vertex. The algorithm
based on this mechanism is given below:
assume Visited[] is a global array.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructuresmoduleiiiiv-231118053936-965279fd/85/data-structures-module-III-IV-pptx-202-320.jpg)





![• Breadth First Search [BFS]:
• The BFS algorithm works similar to level – order
traversal of the trees. Like level – order traversal, BFS
also uses queues. In fact, level – order traversal got
inspired from BFS. BFS works level by level. Initially, BFS
starts at a given vertex, which is at level 0. In the first
stage it visits all vertices at level 1 (that means, vertices
whose distance is 1 from the start vertex of the graph).
In the second stage, it visits all vertices at the second
level. These new vertices are the ones which are
adjacent to level 1 vertices.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructuresmoduleiiiiv-231118053936-965279fd/85/data-structures-module-III-IV-pptx-222-320.jpg)

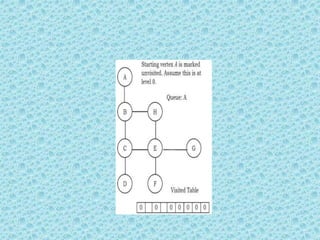
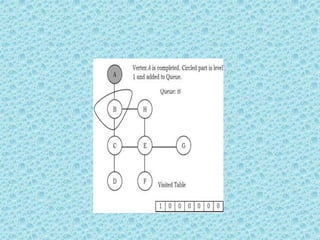
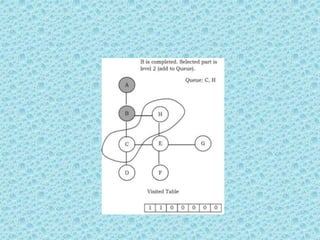
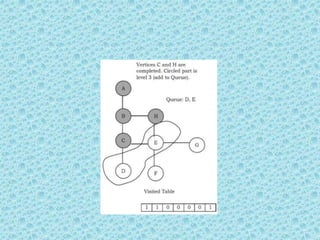
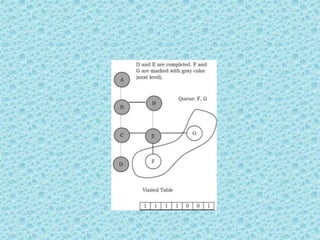
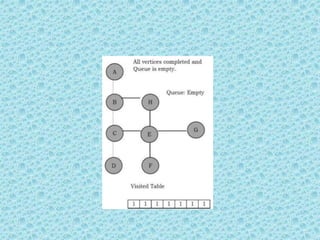
![• Breadth First Search [BFS]:
• As similar to DFS, assume that initially all
vertices are marked unvisited (false). Vertices
that have been processed and removed from
the queue are marked visited (true).
• We use a queue to represent the visited set as
it will keep the vertices in the order of when
they were first visited. The implementation for
the above discussion can be given as:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructuresmoduleiiiiv-231118053936-965279fd/85/data-structures-module-III-IV-pptx-224-320.jpg)









![• The entire implementation of this algorithm is
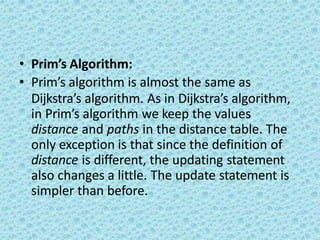
identical to that of Dijkstra’s algorithm. The
running time is O(|V|2) without heaps [good
for dense graphs], and O (ElogV) using binary
heaps [good for sparse graphs].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructuresmoduleiiiiv-231118053936-965279fd/85/data-structures-module-III-IV-pptx-243-320.jpg)

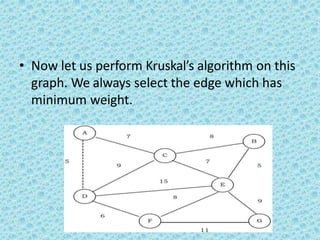
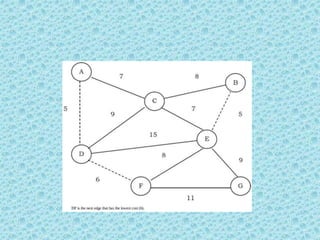
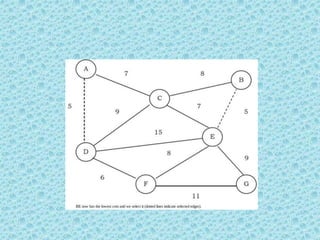
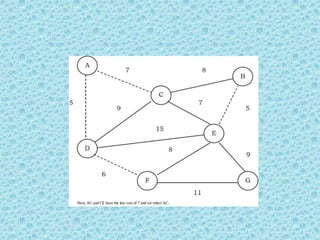
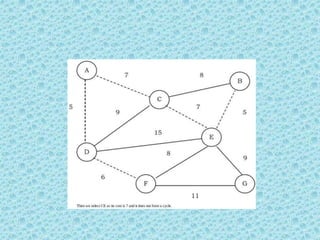
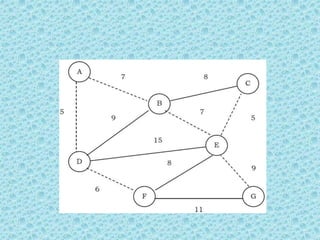
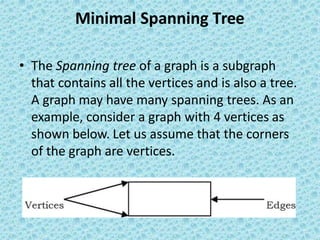
![• The appropriate data structure is the UNION/FIND
belong to the same set if and only
algorithm [for implementing forests]. Two vertices
if they are
connected in the current spanning forest.
• Each vertex is initially in its own set. If u and v are in
the same set, the edge is rejected because it forms a
cycle. Otherwise, the edge is accepted, and a UNION is
performed on the two sets containing u and v.
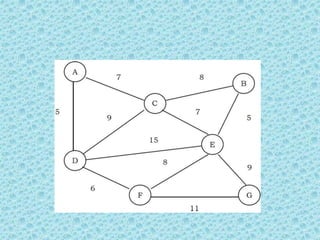
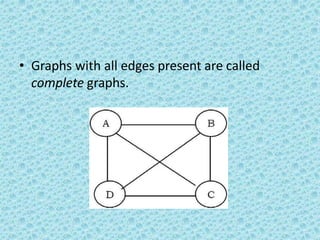
• As an example, consider the following graph (the edges
show the weights).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructuresmoduleiiiiv-231118053936-965279fd/85/data-structures-module-III-IV-pptx-245-320.jpg)