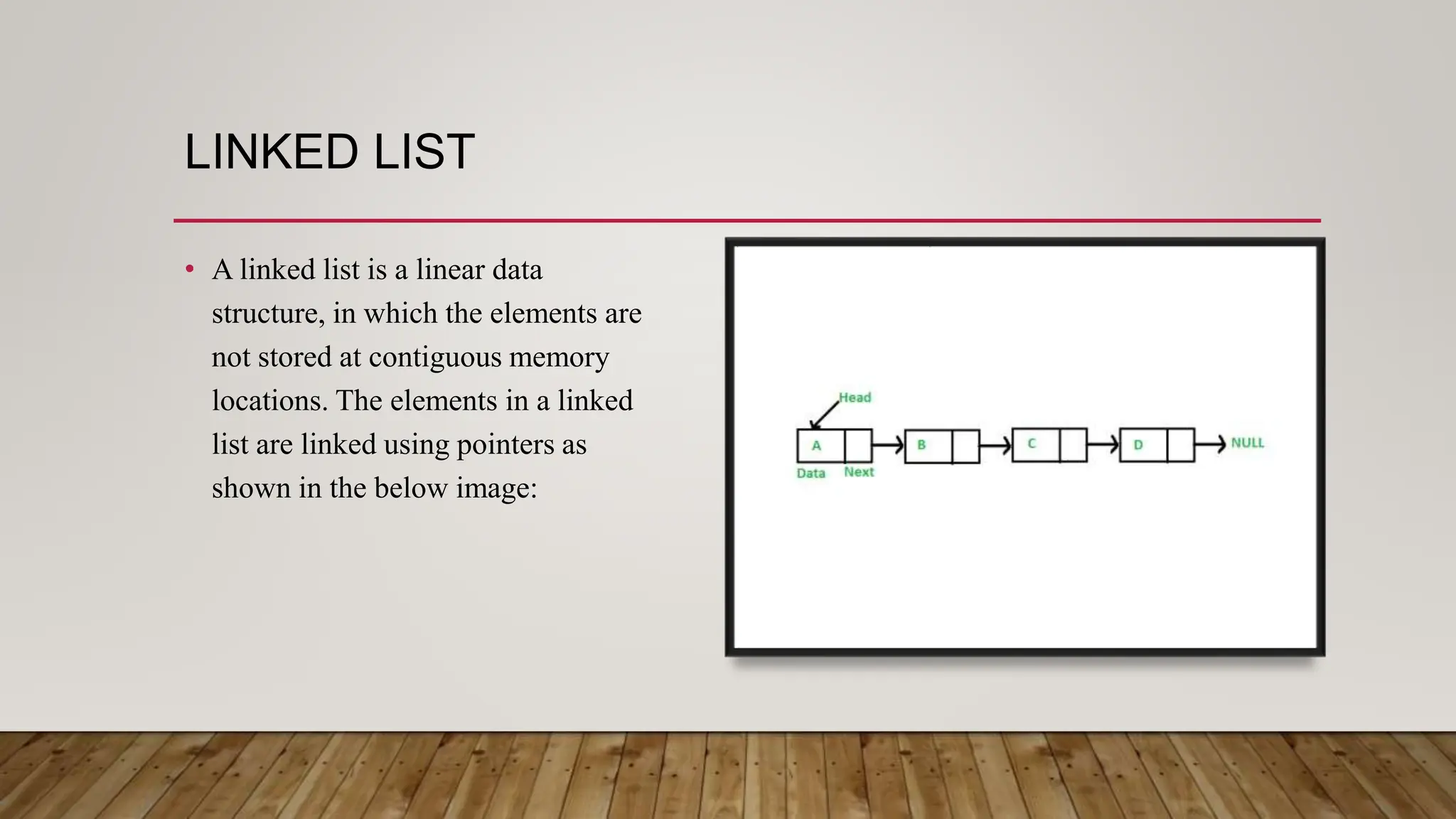
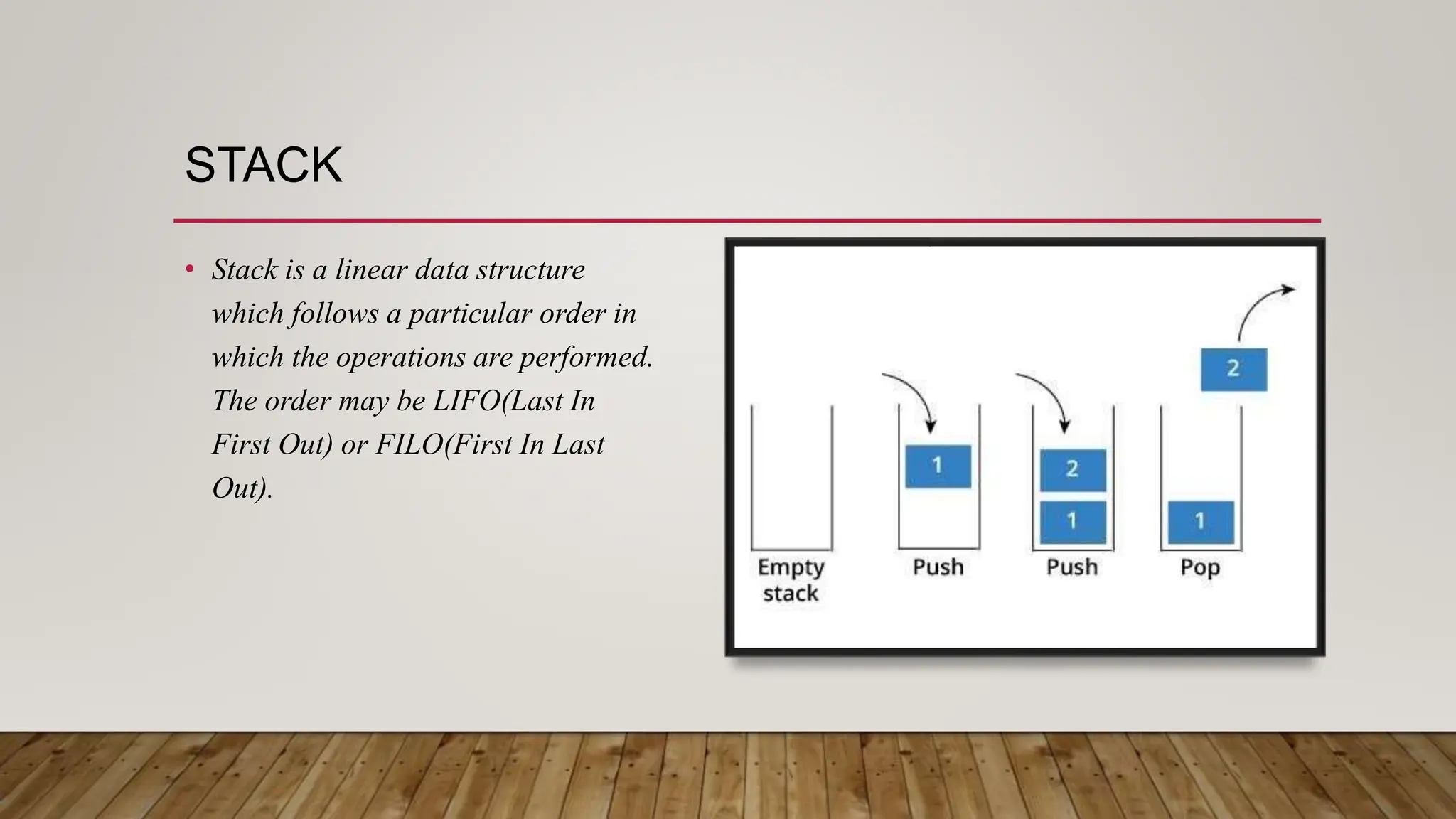
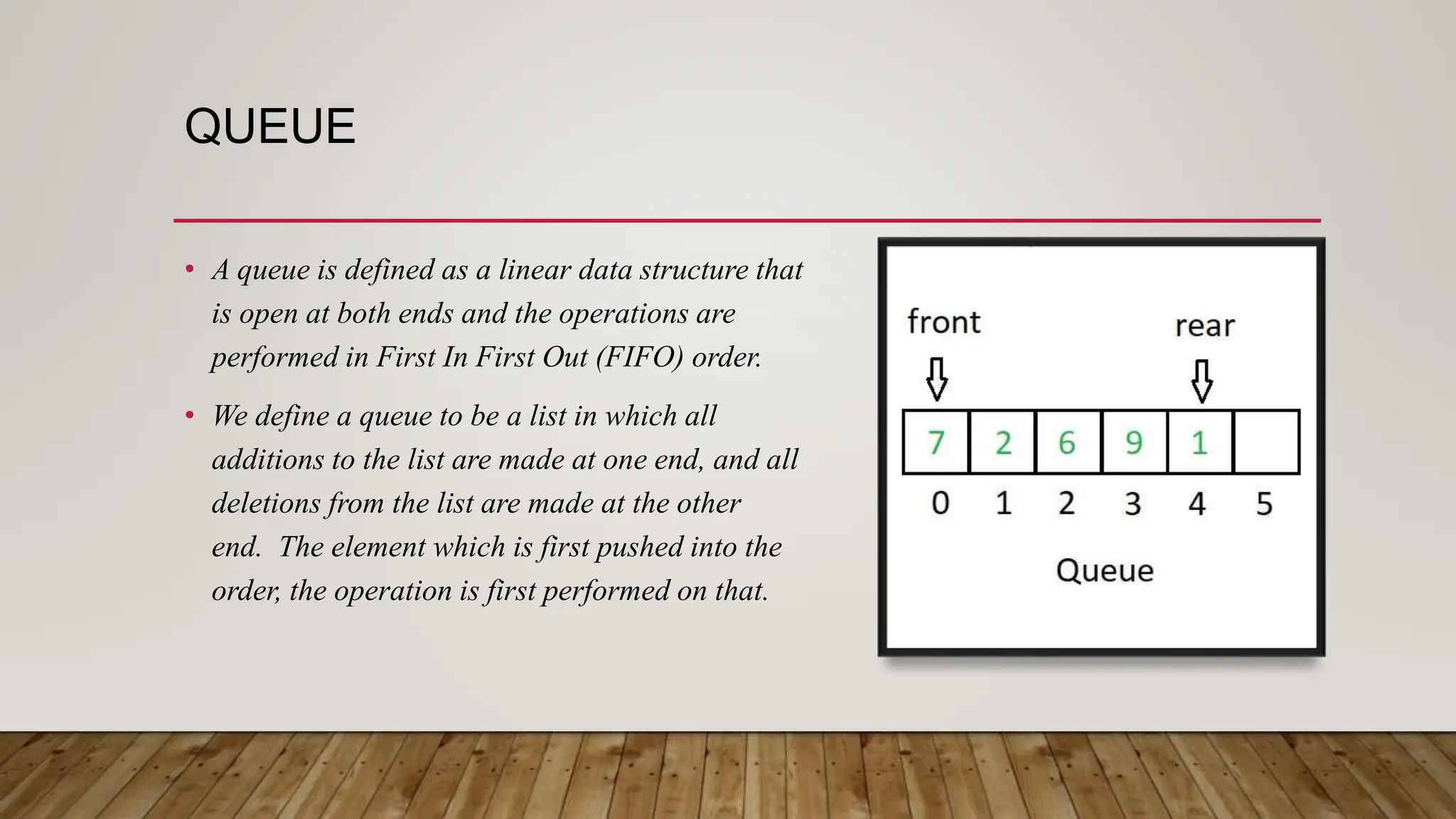
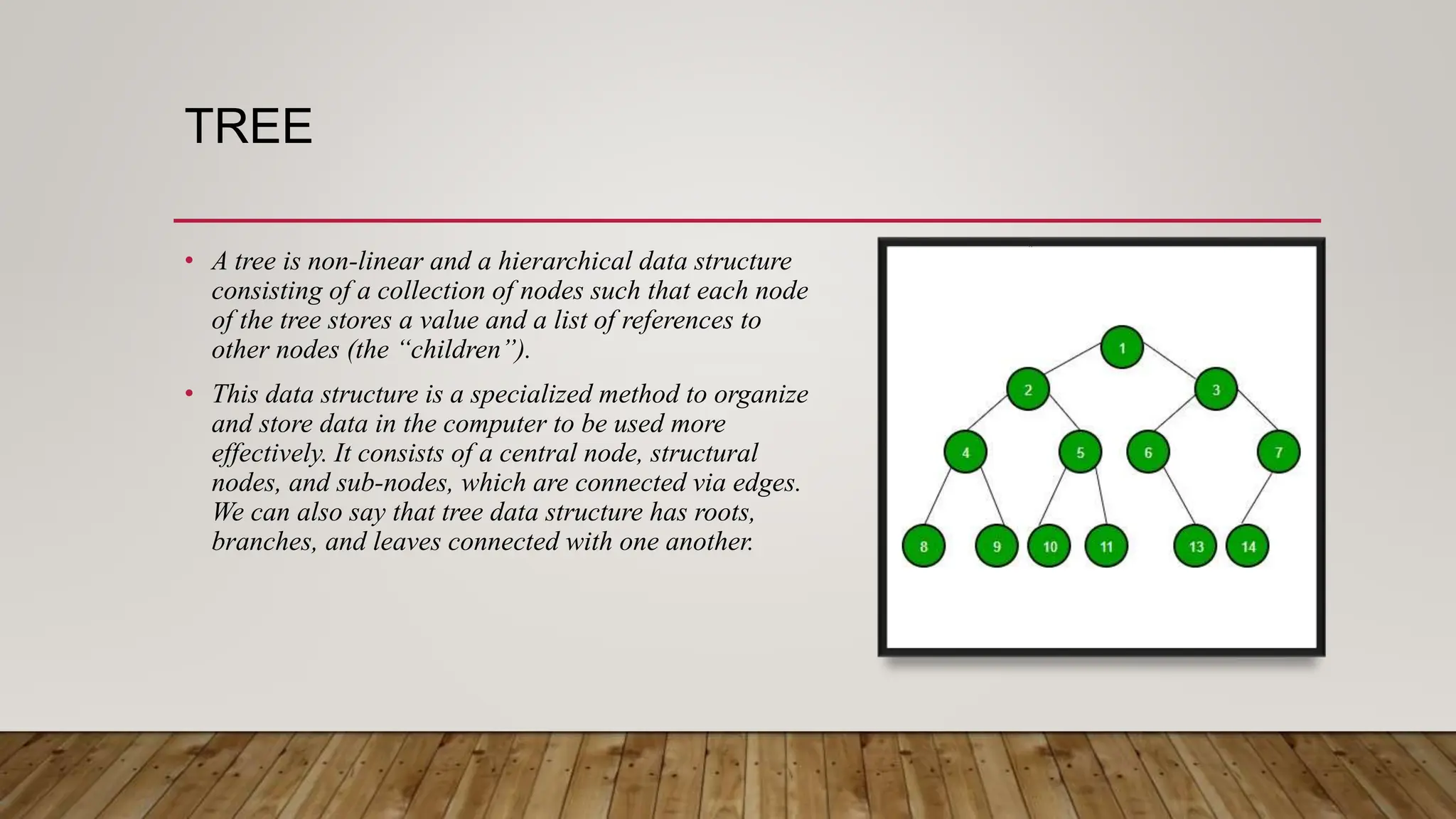
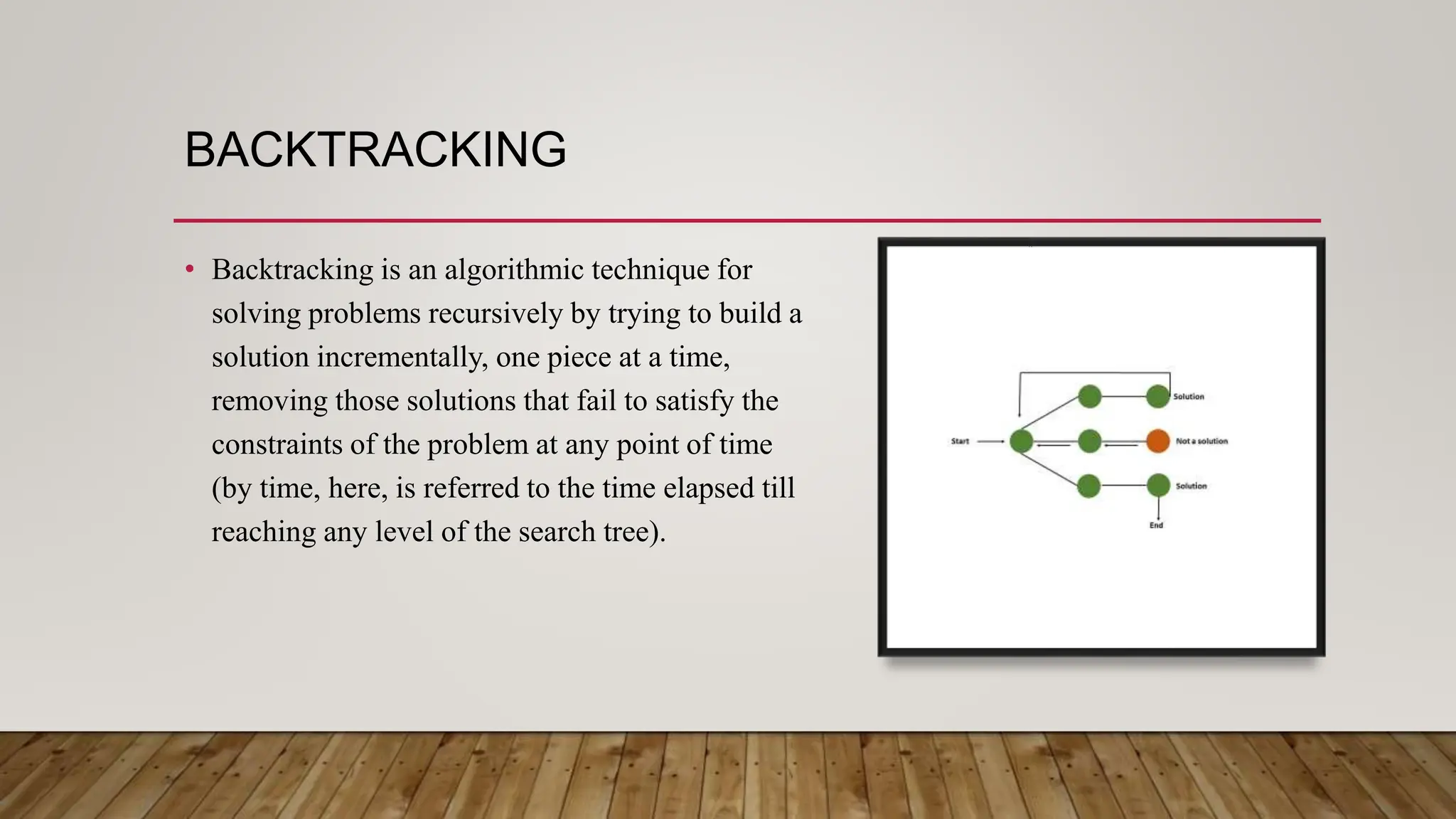
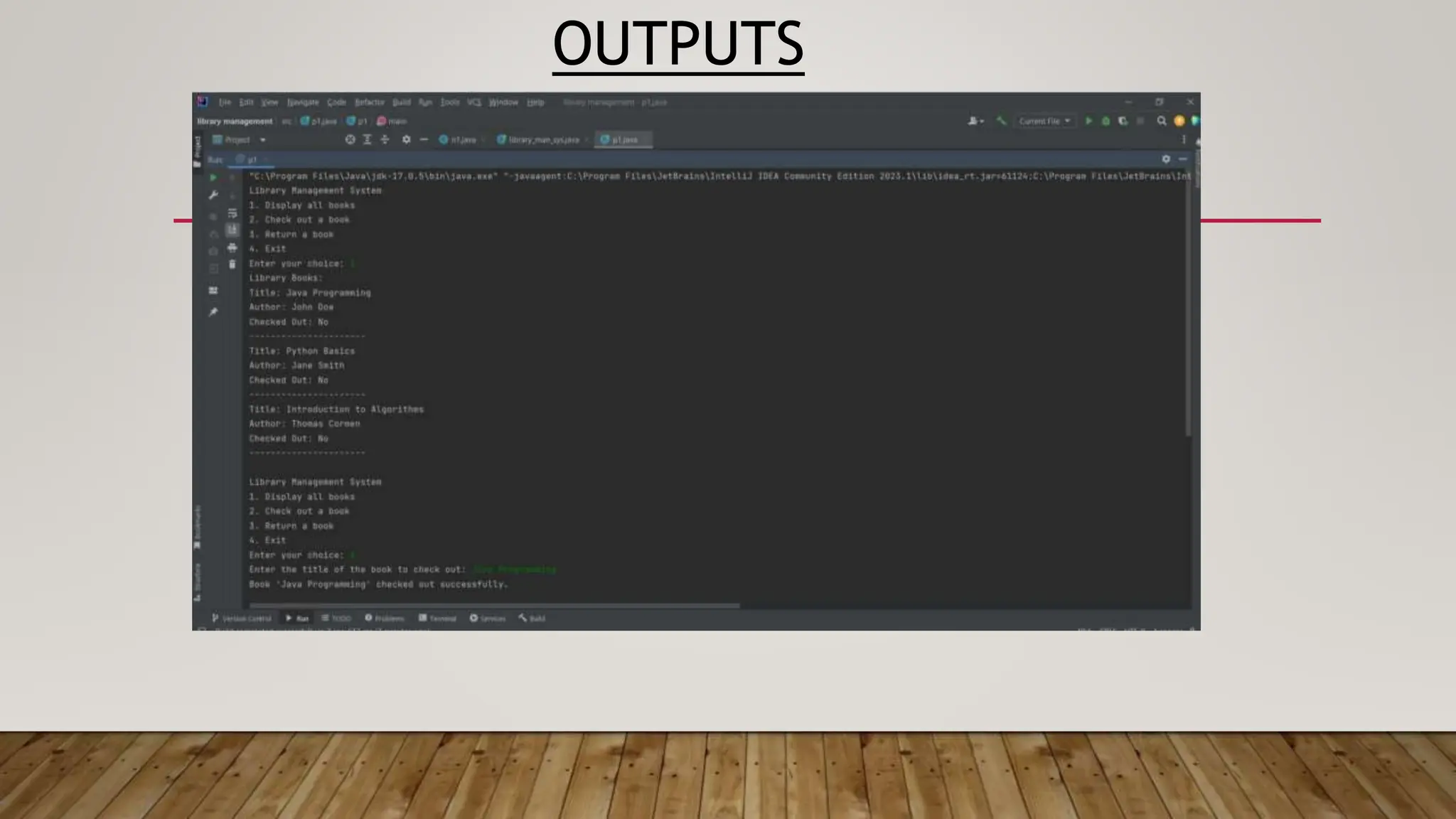
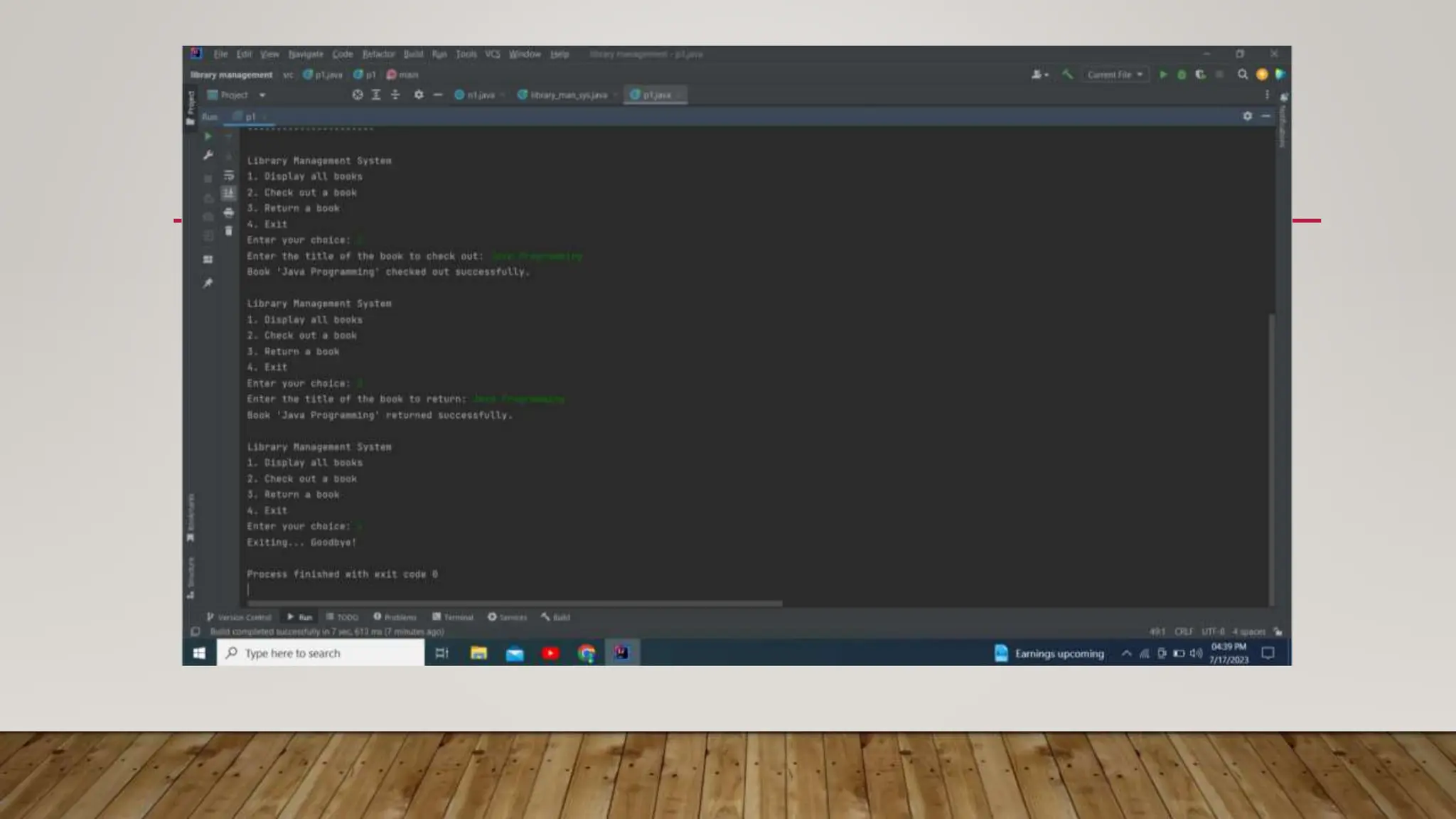
This document provides an overview of different data structures and algorithms topics covered in a 6-week CSE-443 training course, including searching, sorting, arrays, linked lists, stacks, queues, trees, binary search trees, backtracking, and why learning data structures and algorithms is important. It also describes a library management system project that uses a hashmap to implement functions like adding, removing, and searching books, issuing books, and finding which books students need.


![SORTING
A Sorting Algorithm is used to
rearrange a given array or list of
elements according to a
comparison operator on the
elements. The comparison operator
is used to decide the new order of
elements in the respective data
structure.
For Example: The Array
[45,25,65,10,90] can be written in
a sorted way as [10,25,45,65,90].
Its very helpful in searching any
element in any given array.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dsatejesh-231025163246-01993b4d/75/data-science-4-2048.jpg)

![2-D ARRAY
• A 2-D Array represents a collection of numbers
arranged in an order of rows and columns. It is
necessary to enclose the elements of the array in
parentheses or brackets.
• For example:
• This array has 3 rows and 3 columns. Each
element of array can be referred to by its row
and column number. For example, a[0][0]=1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dsatejesh-231025163246-01993b4d/75/data-science-6-2048.jpg)