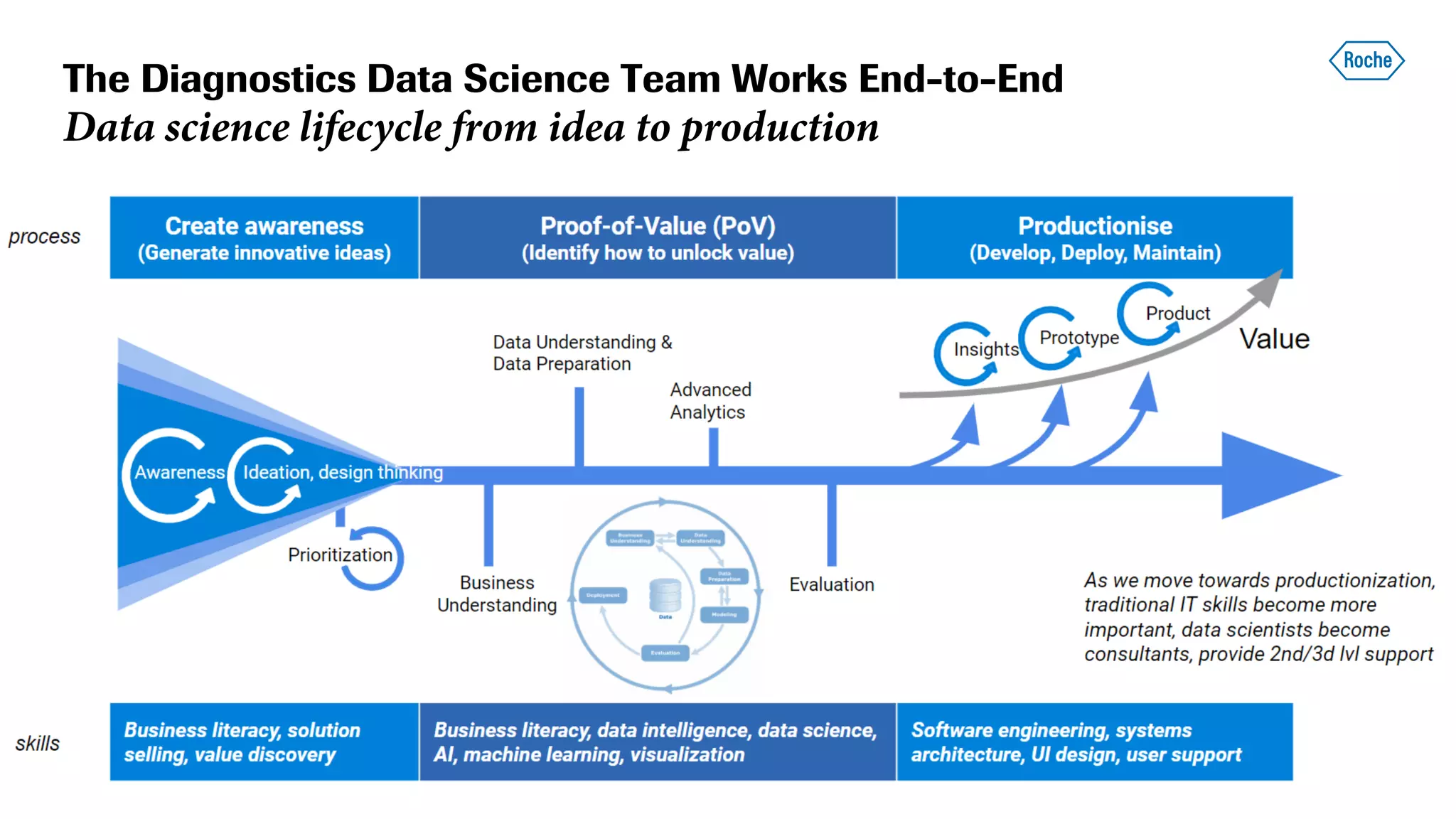
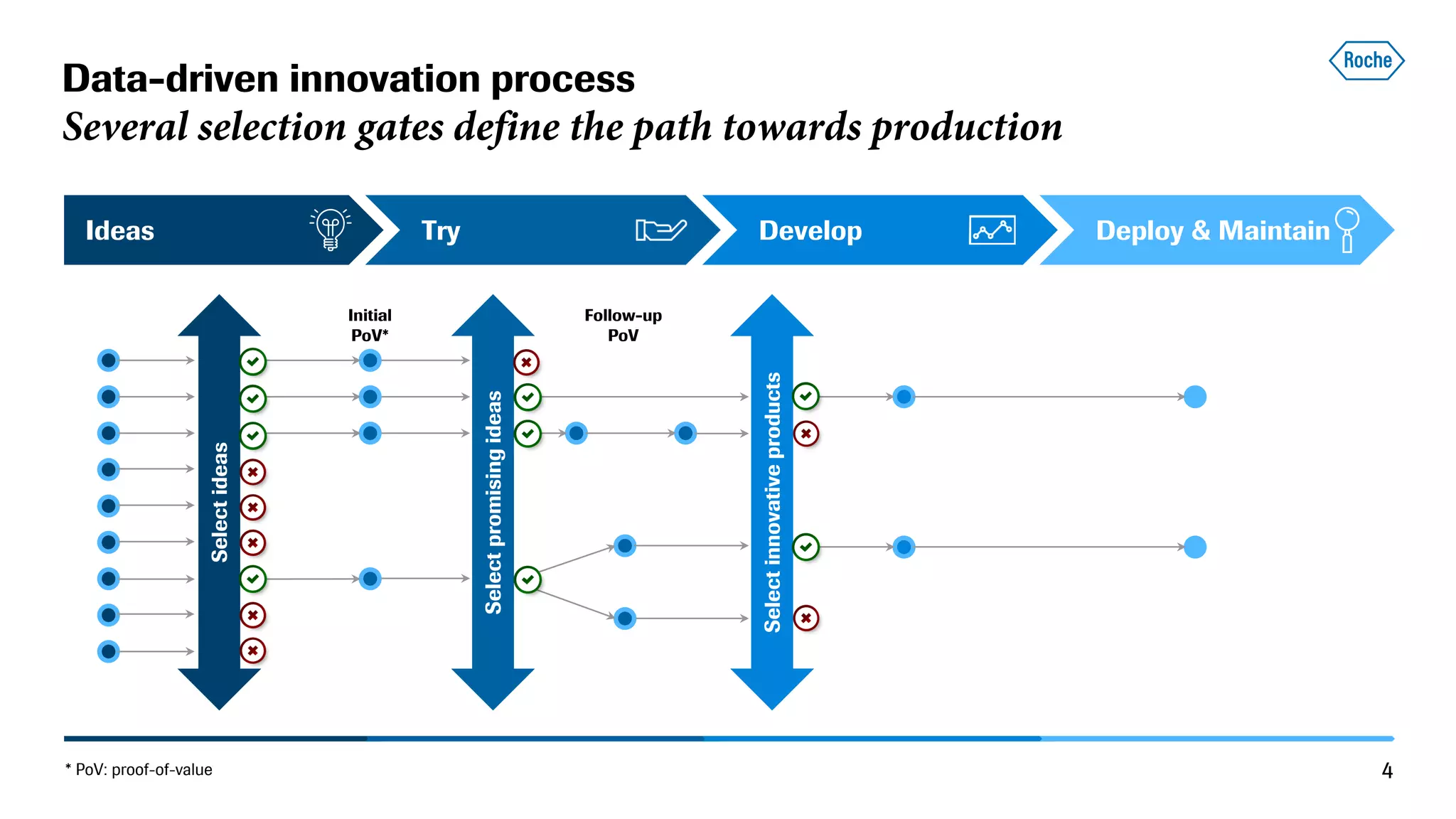
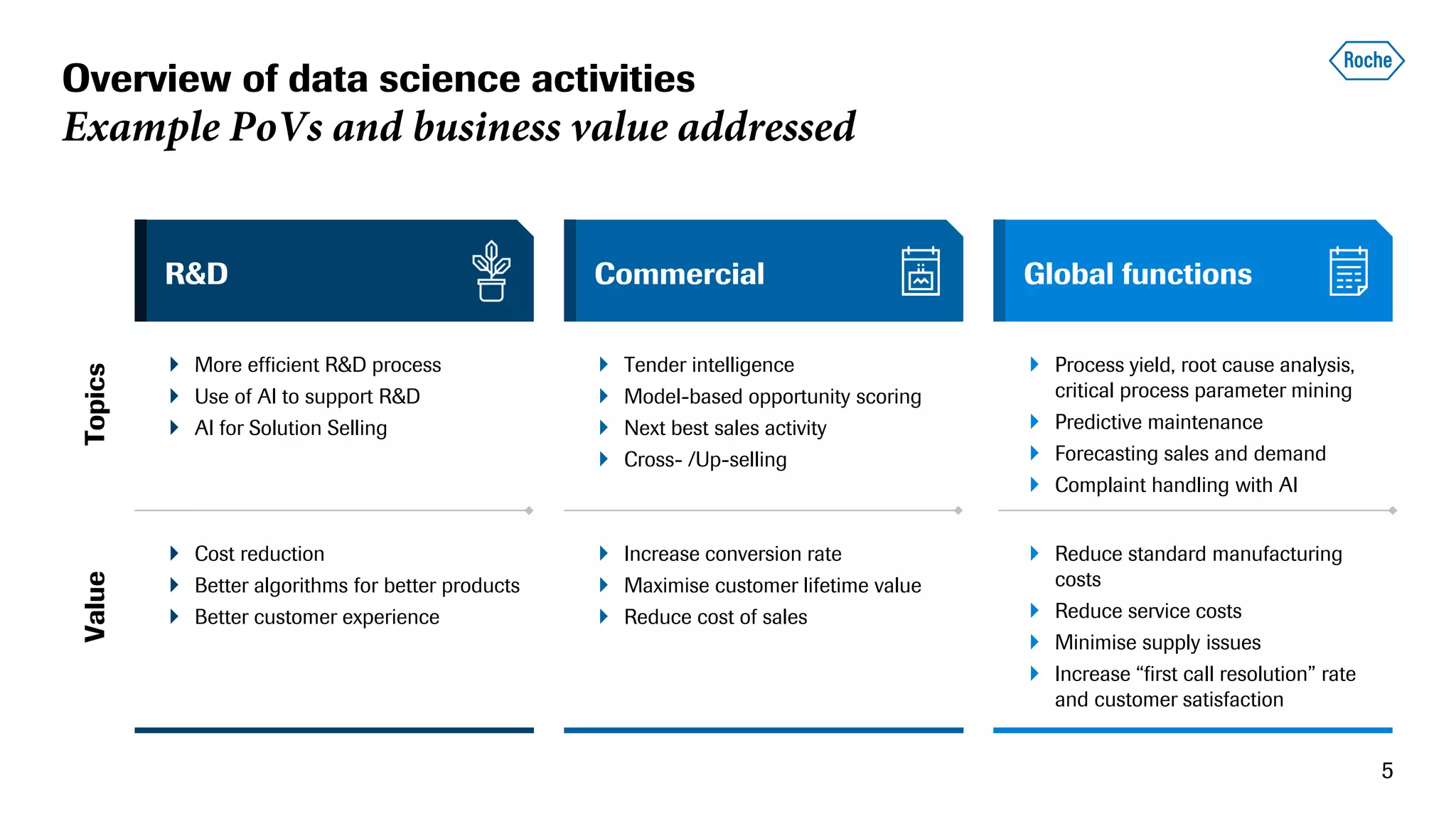
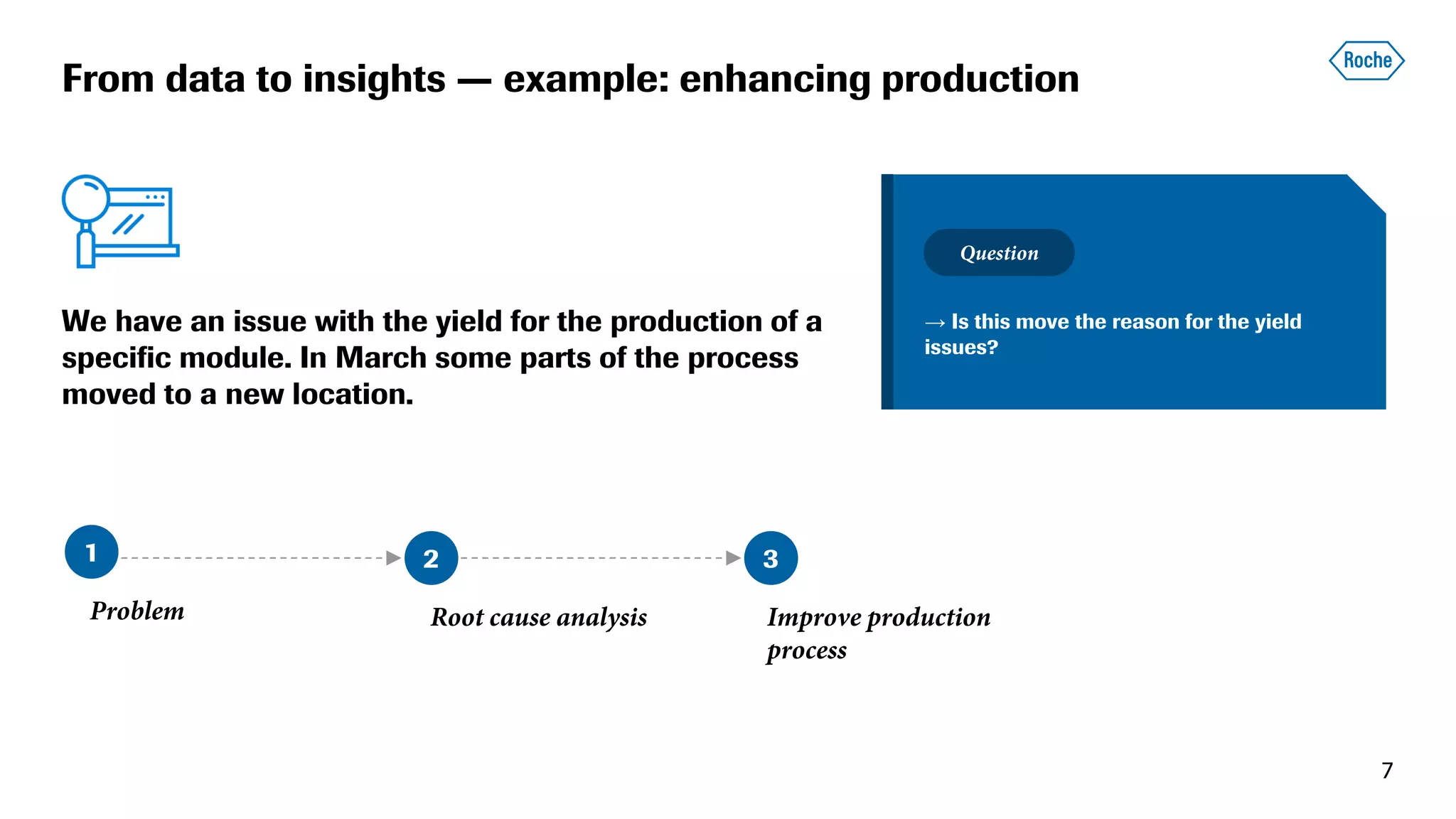
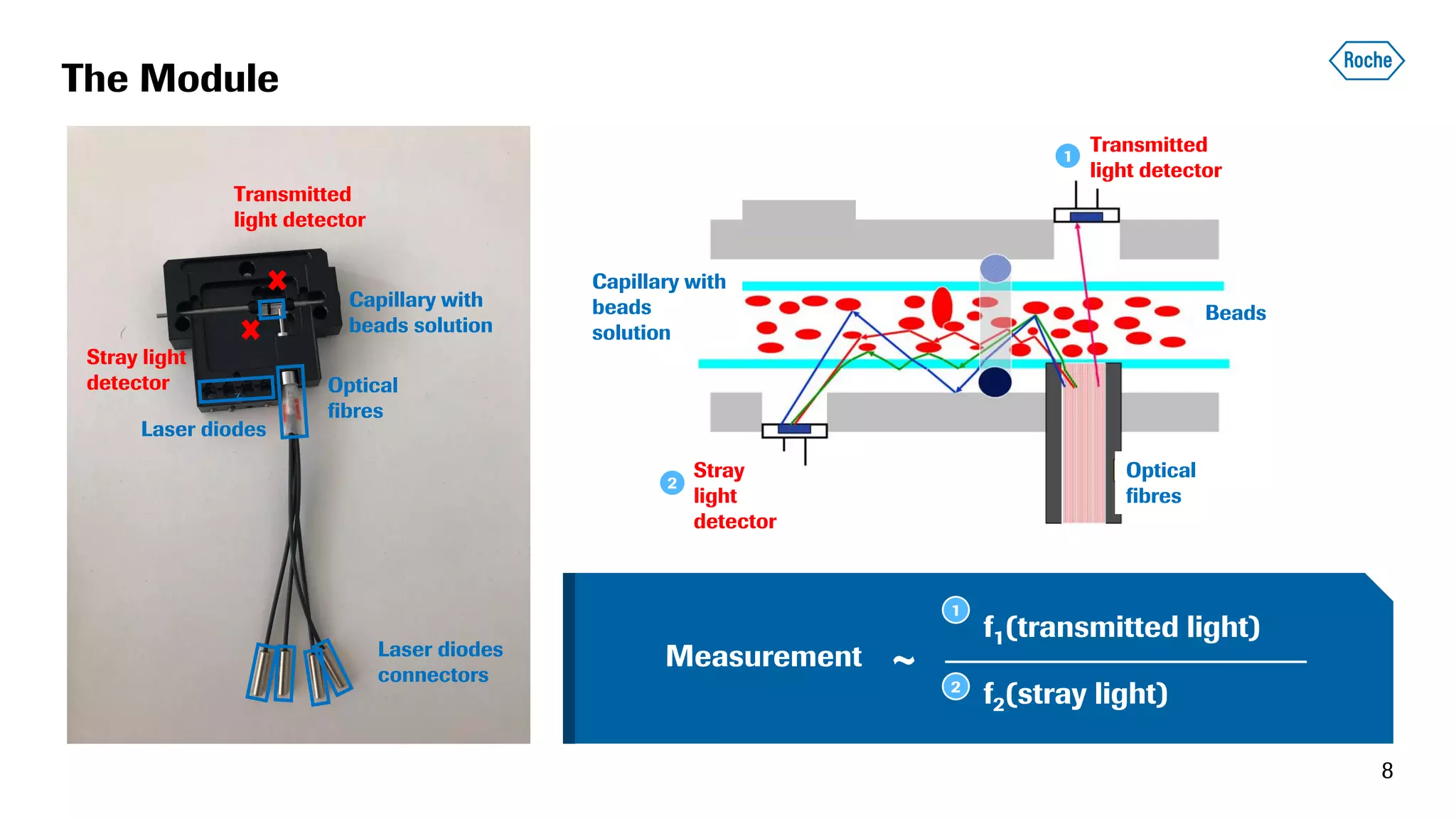
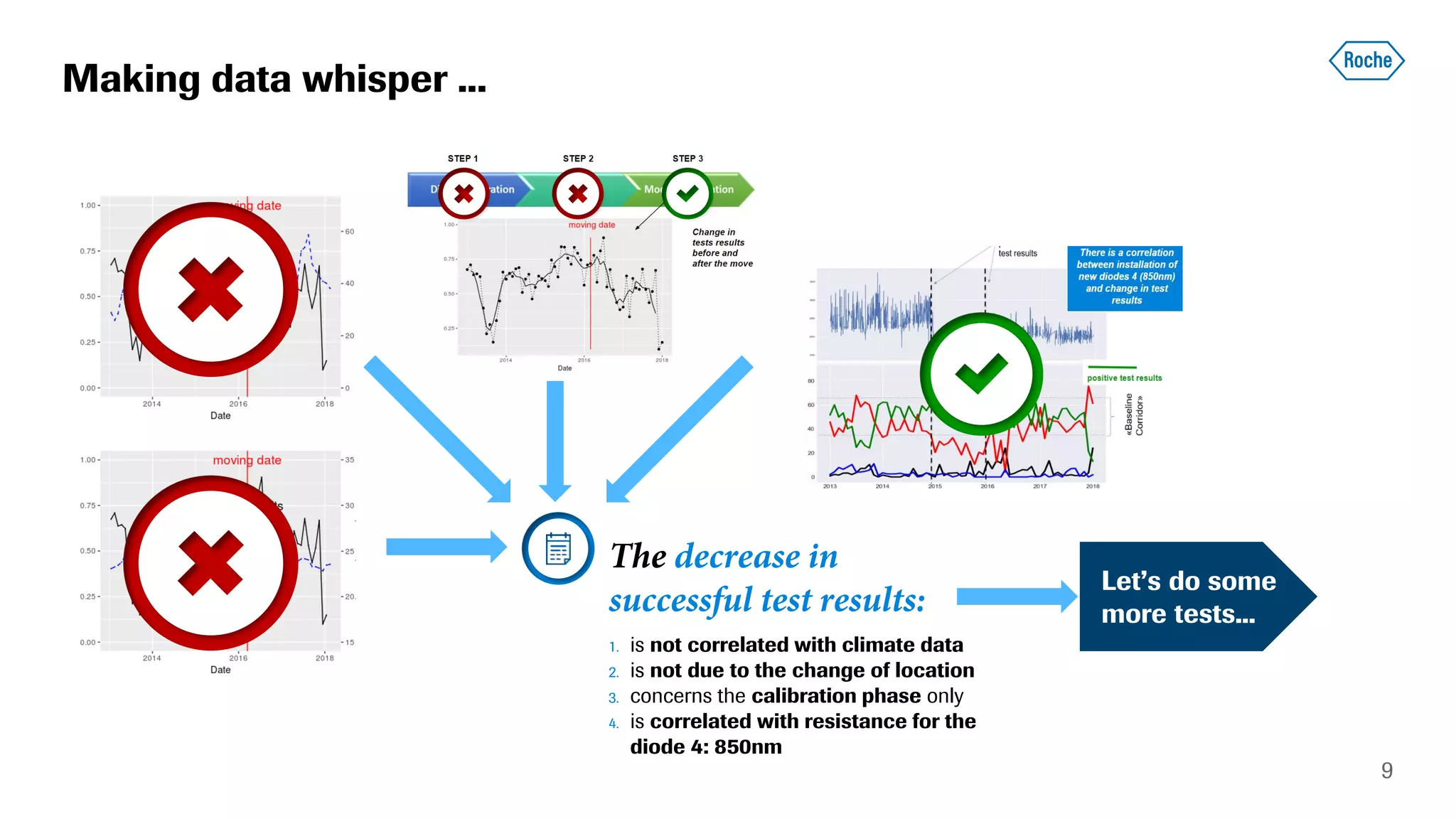
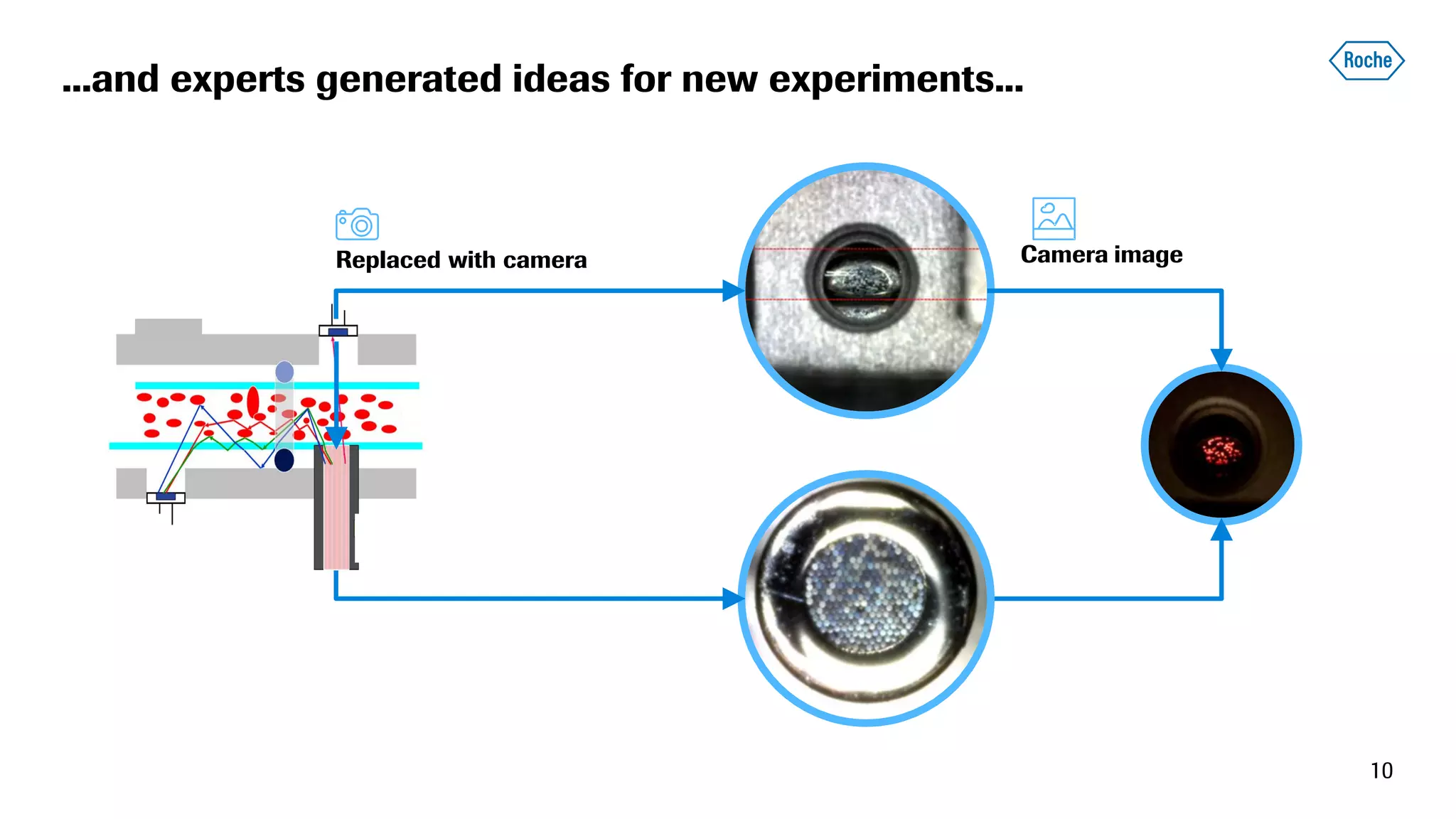
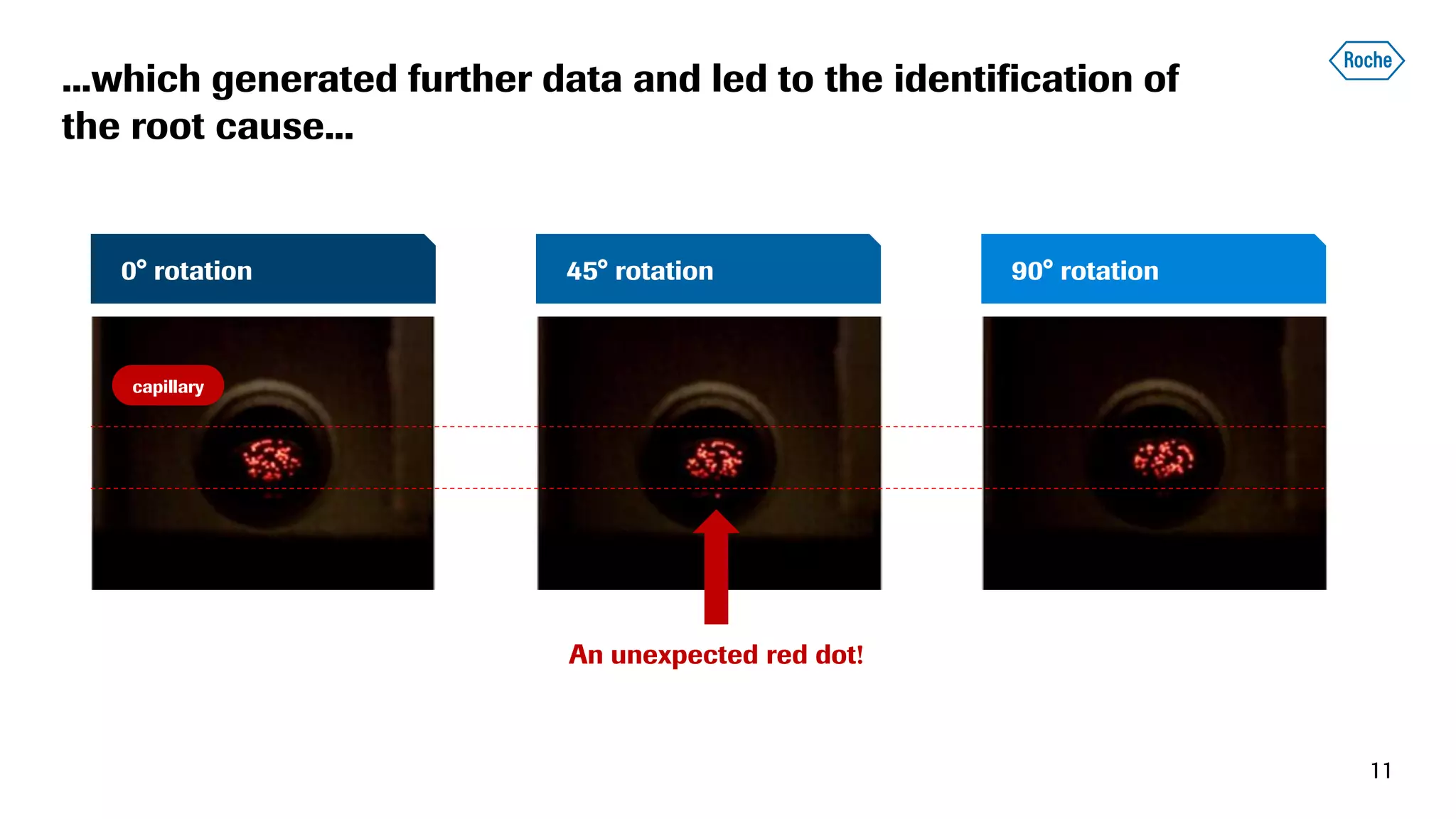
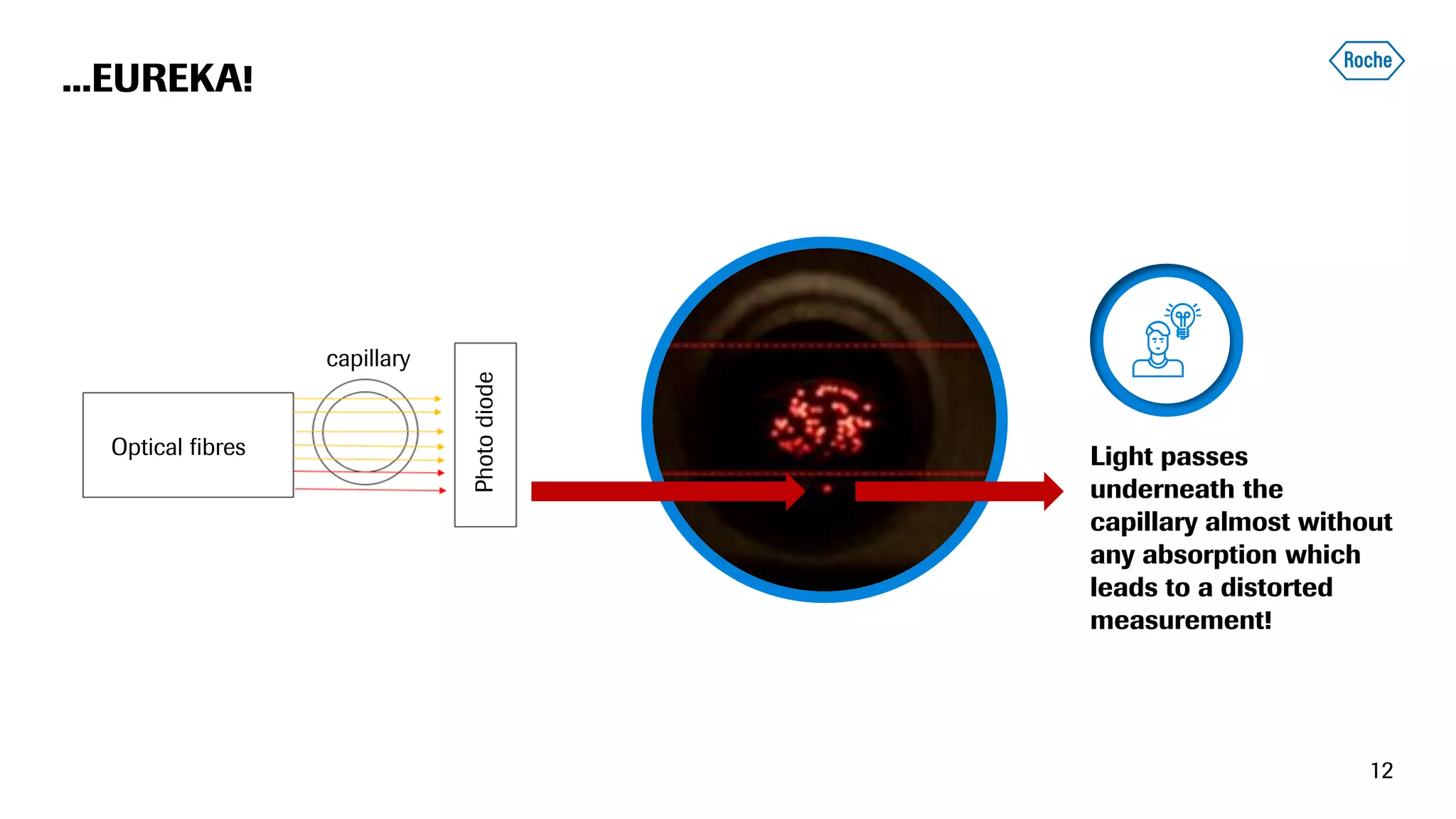
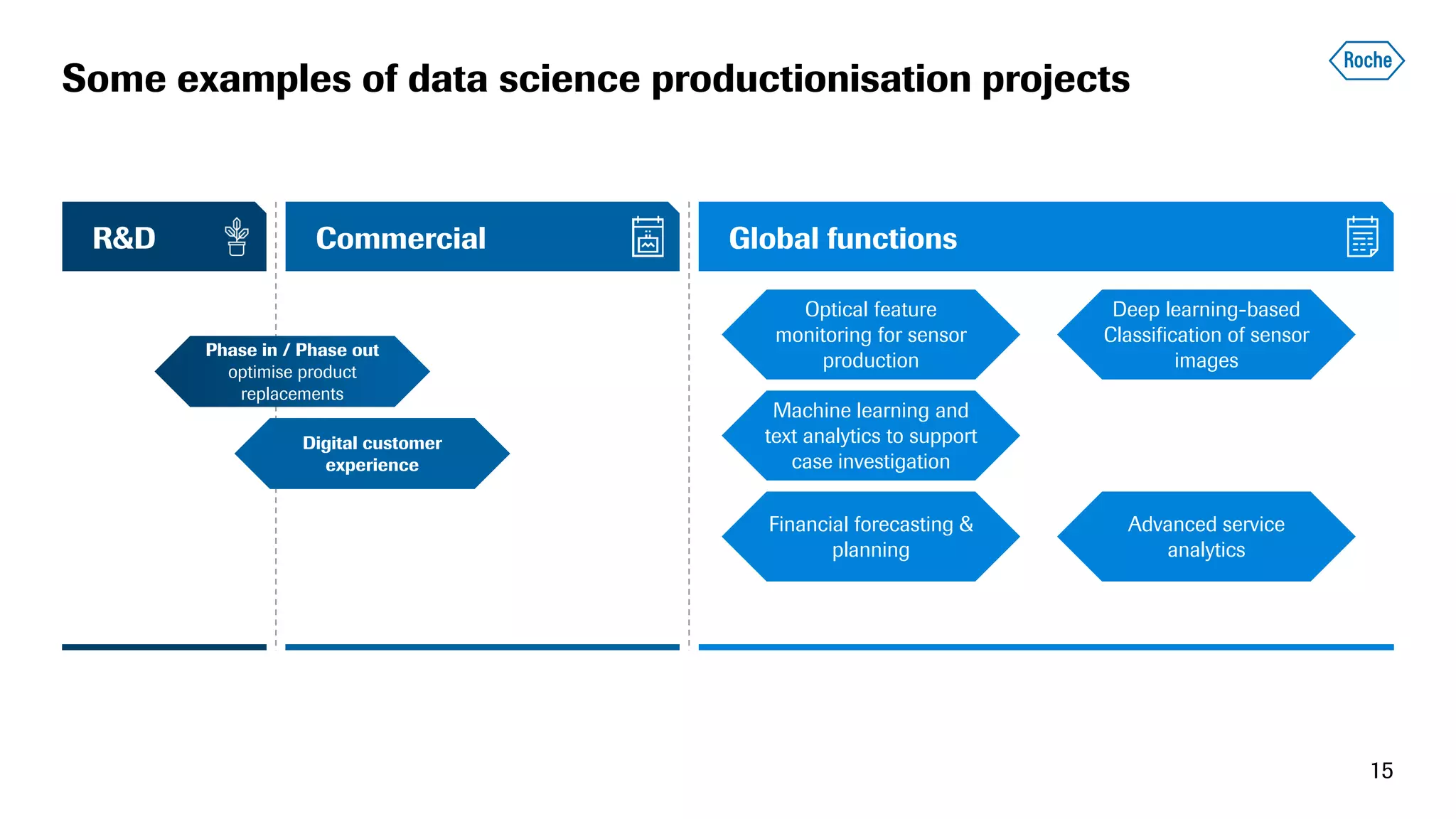
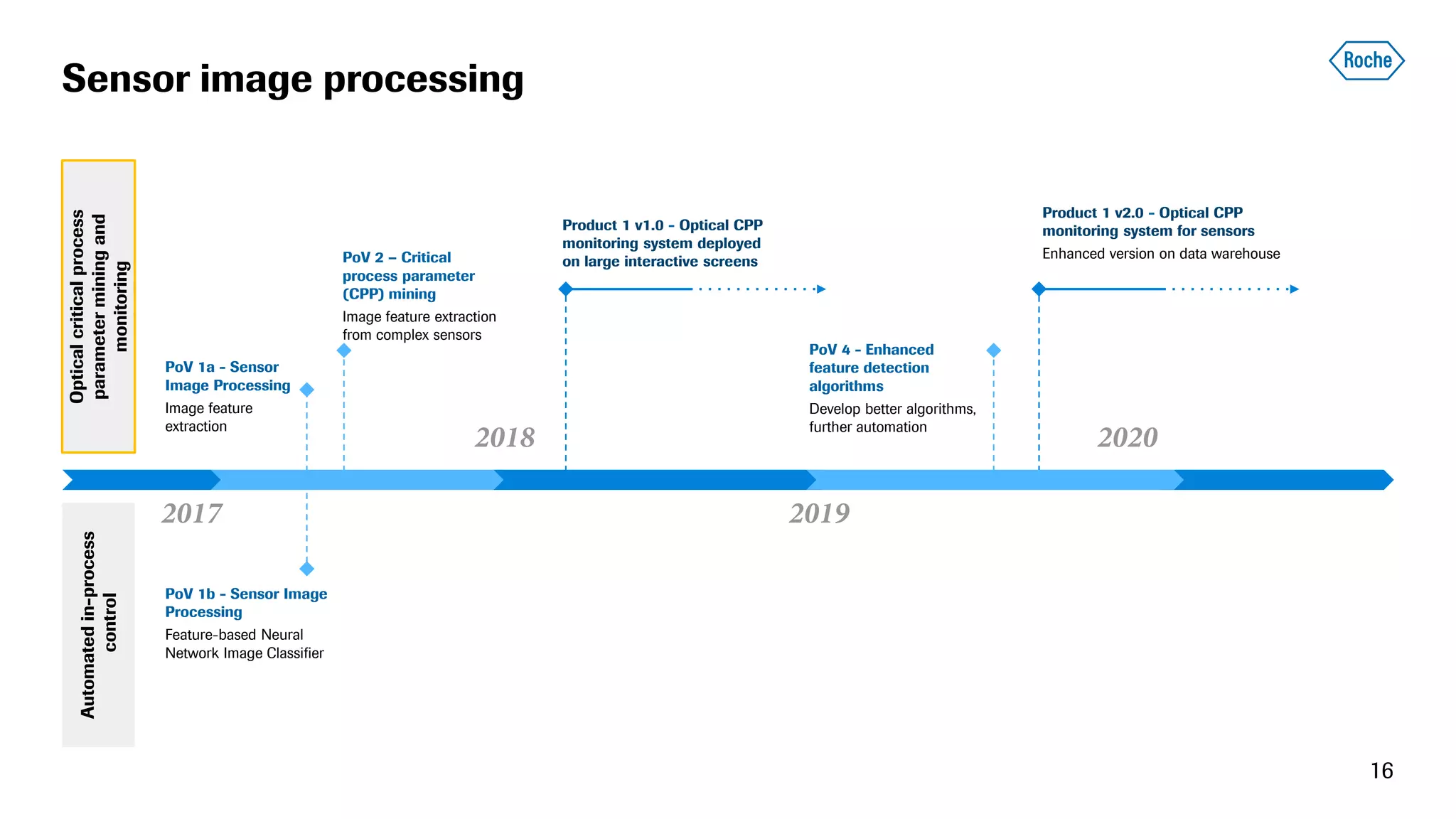
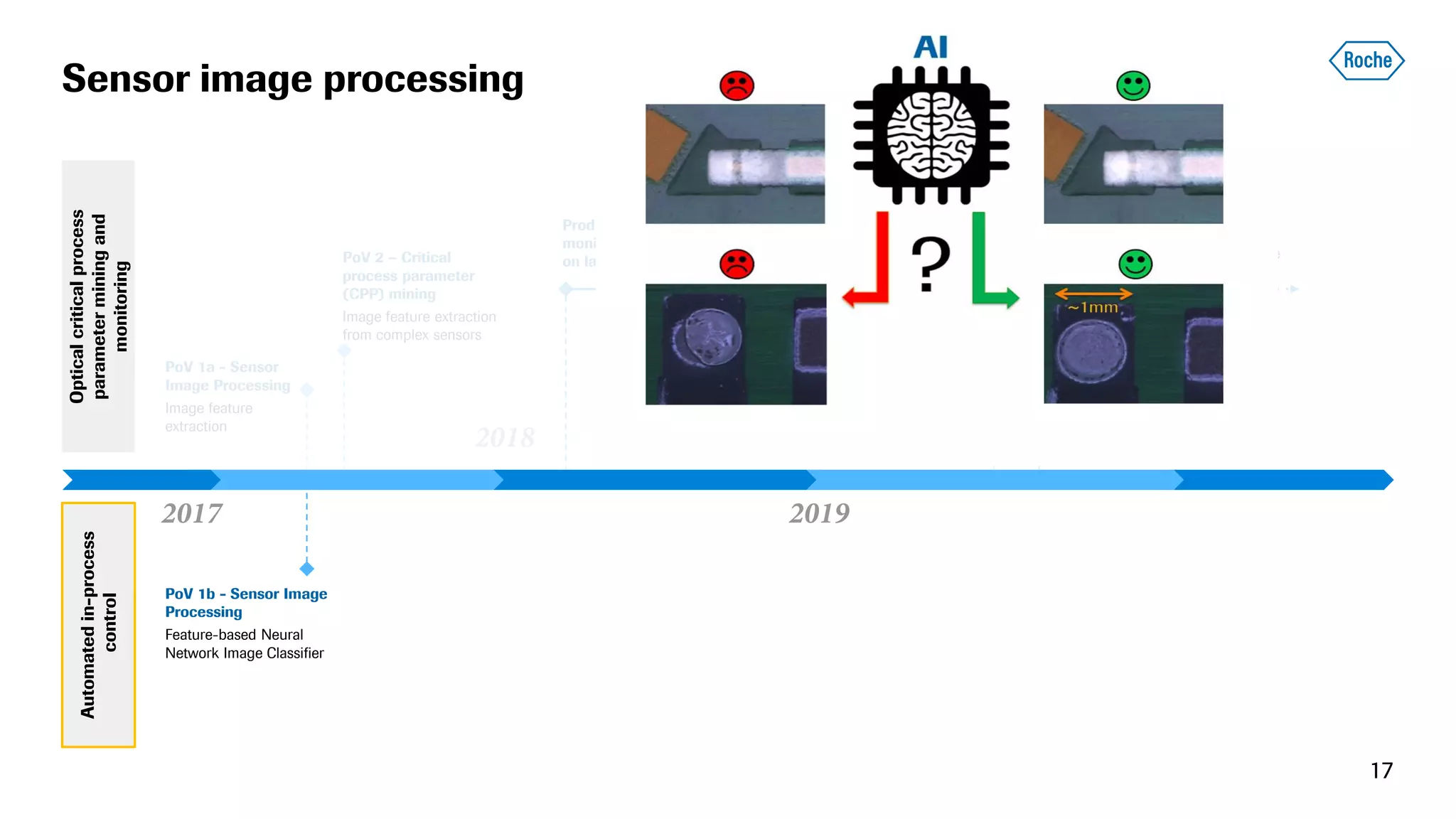
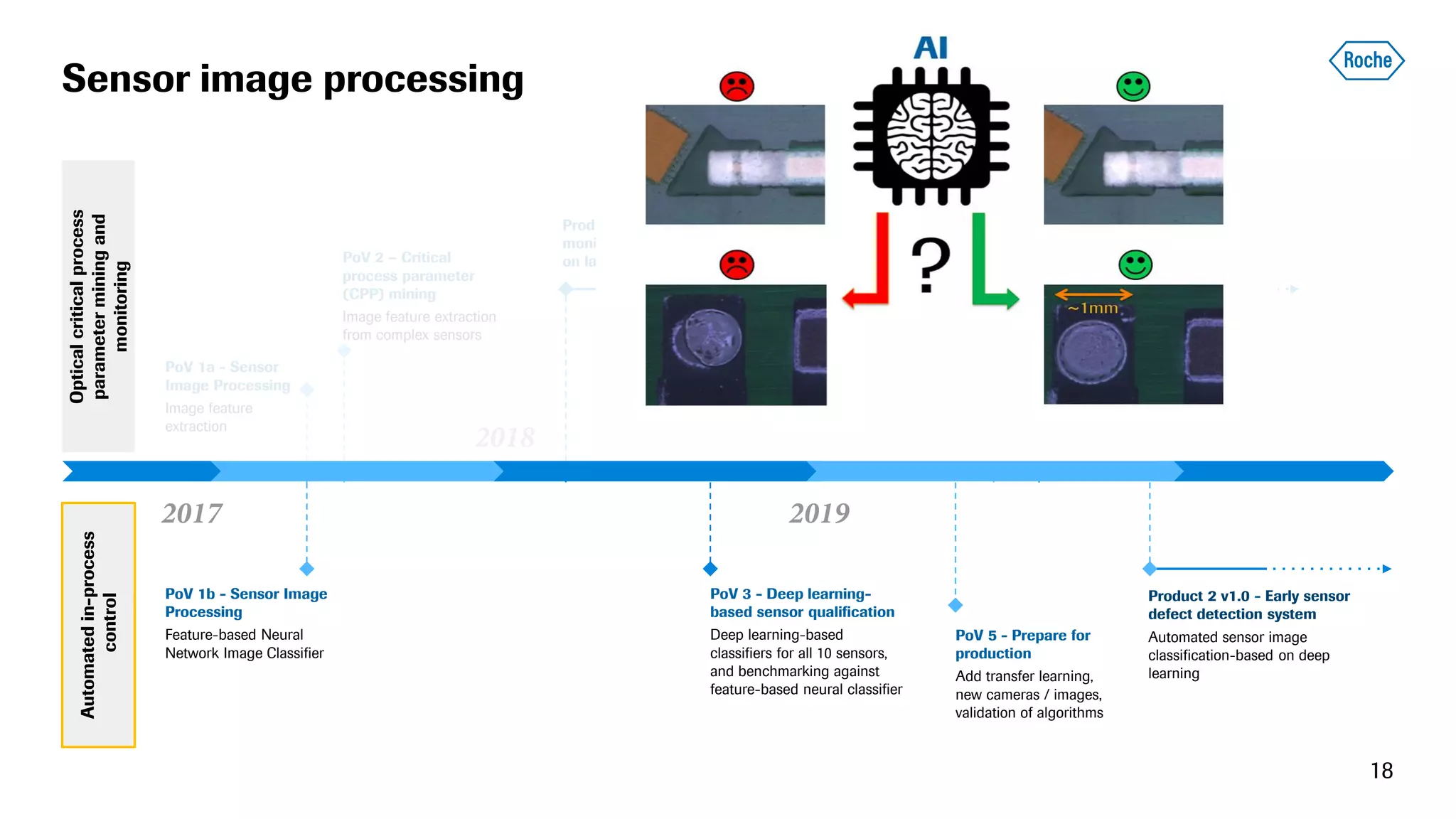
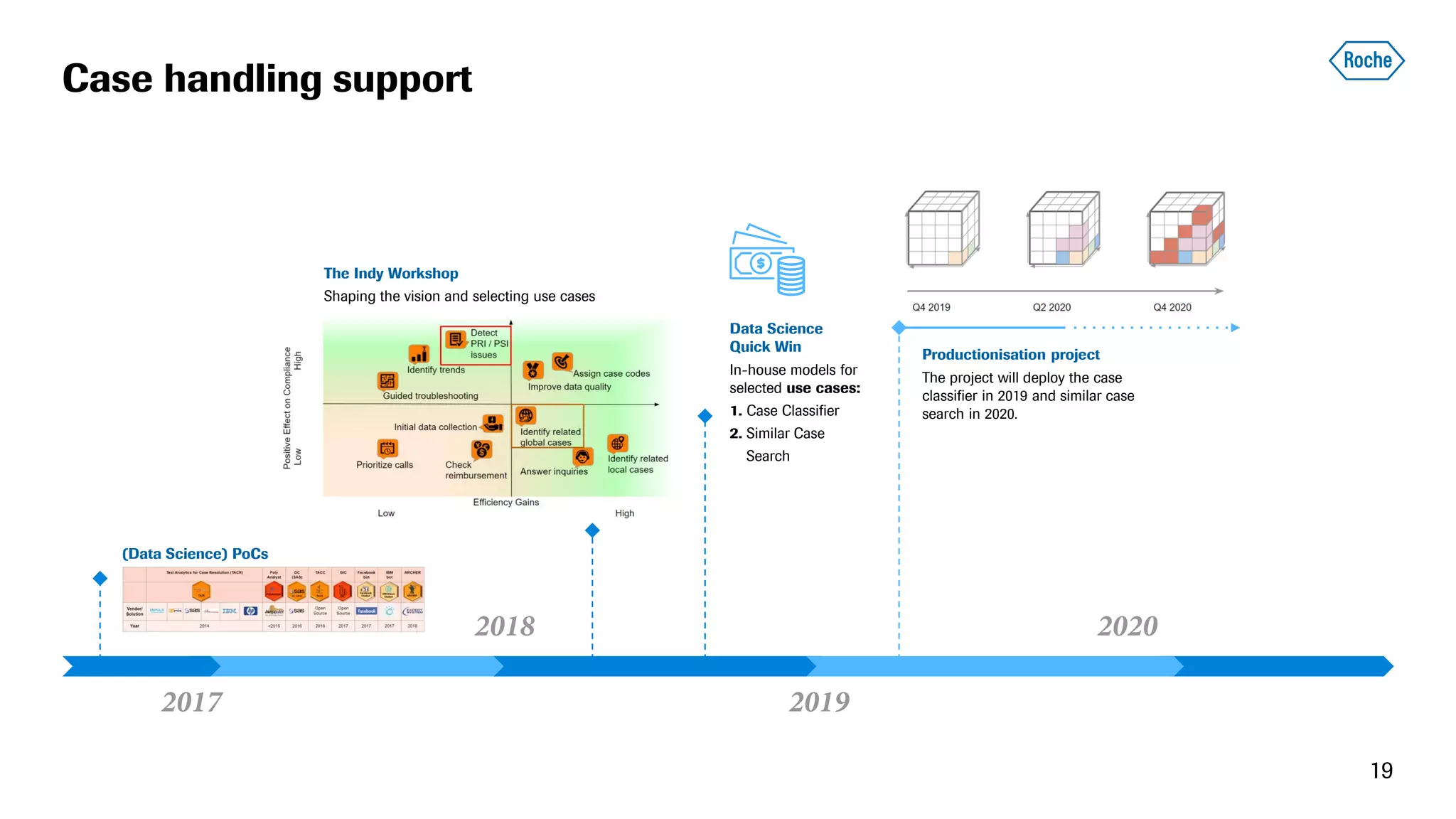
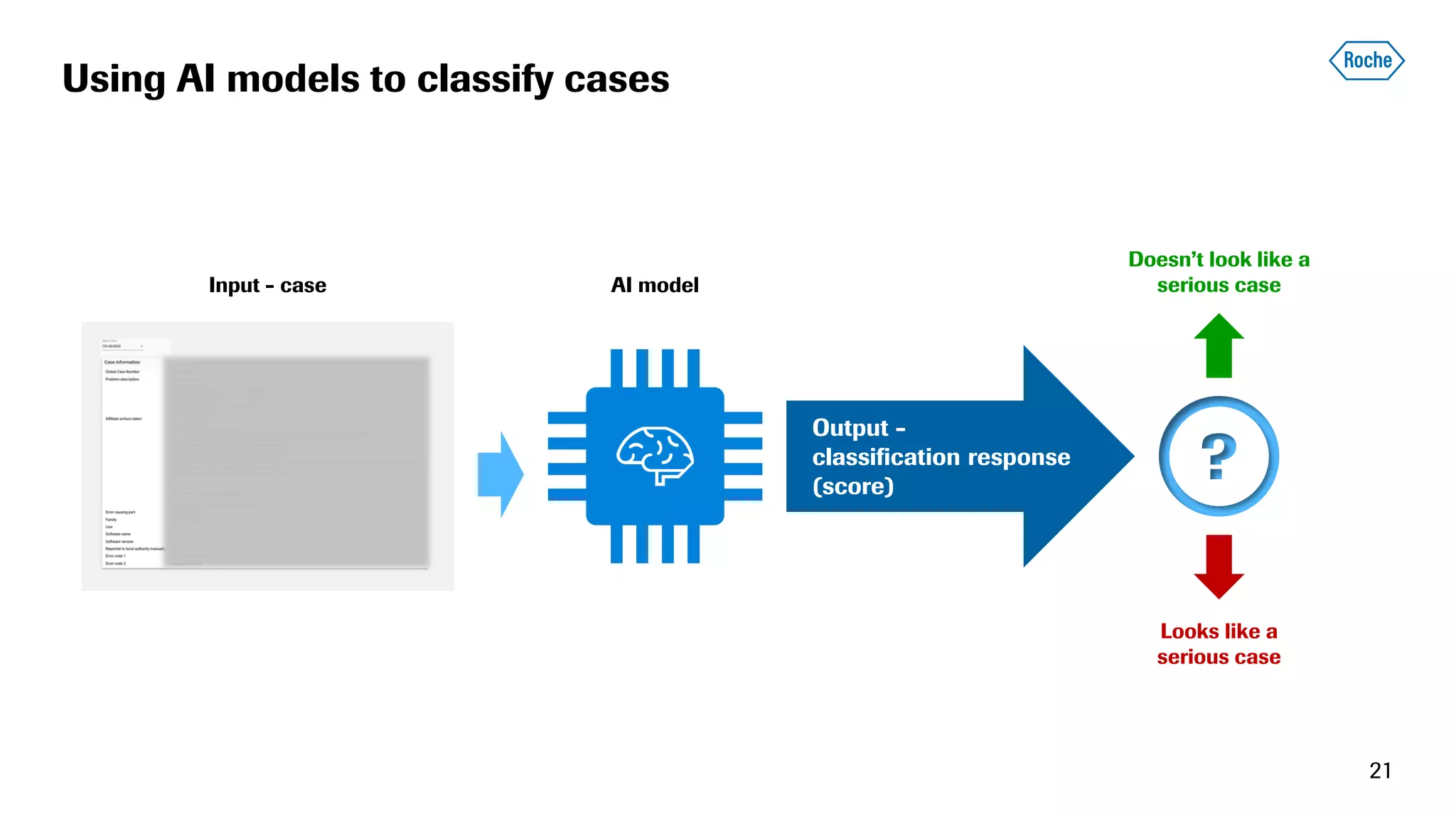
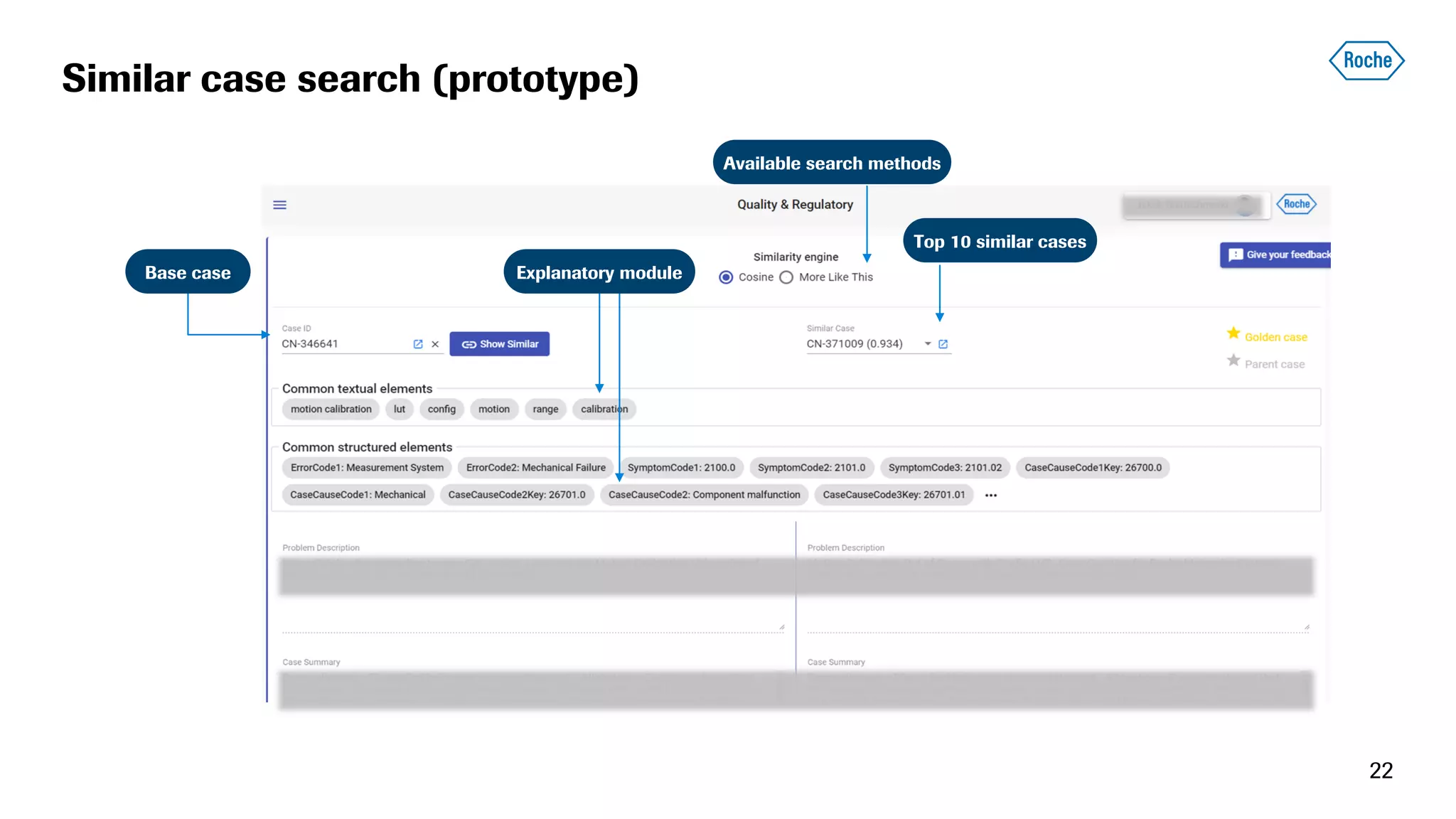
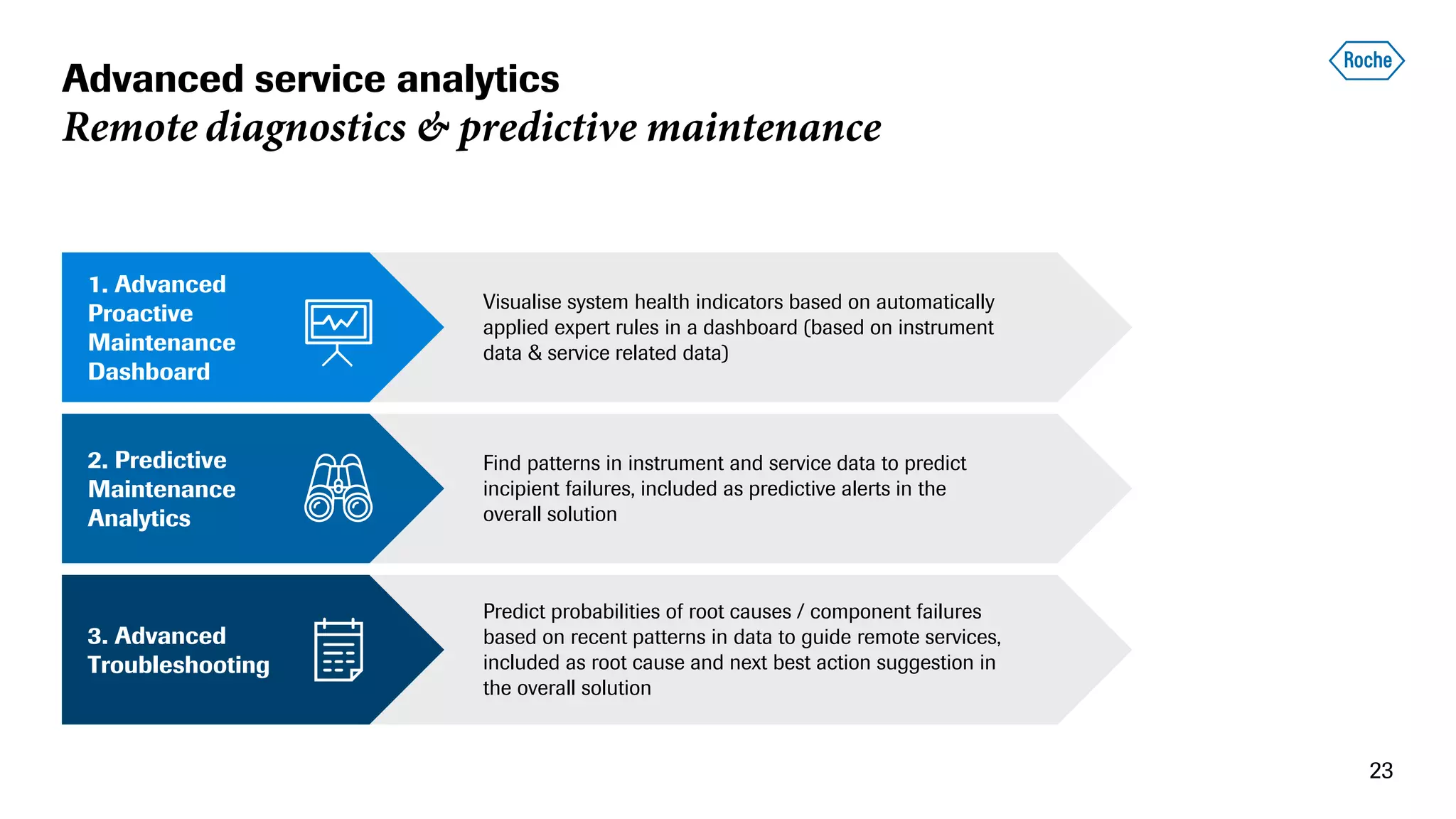
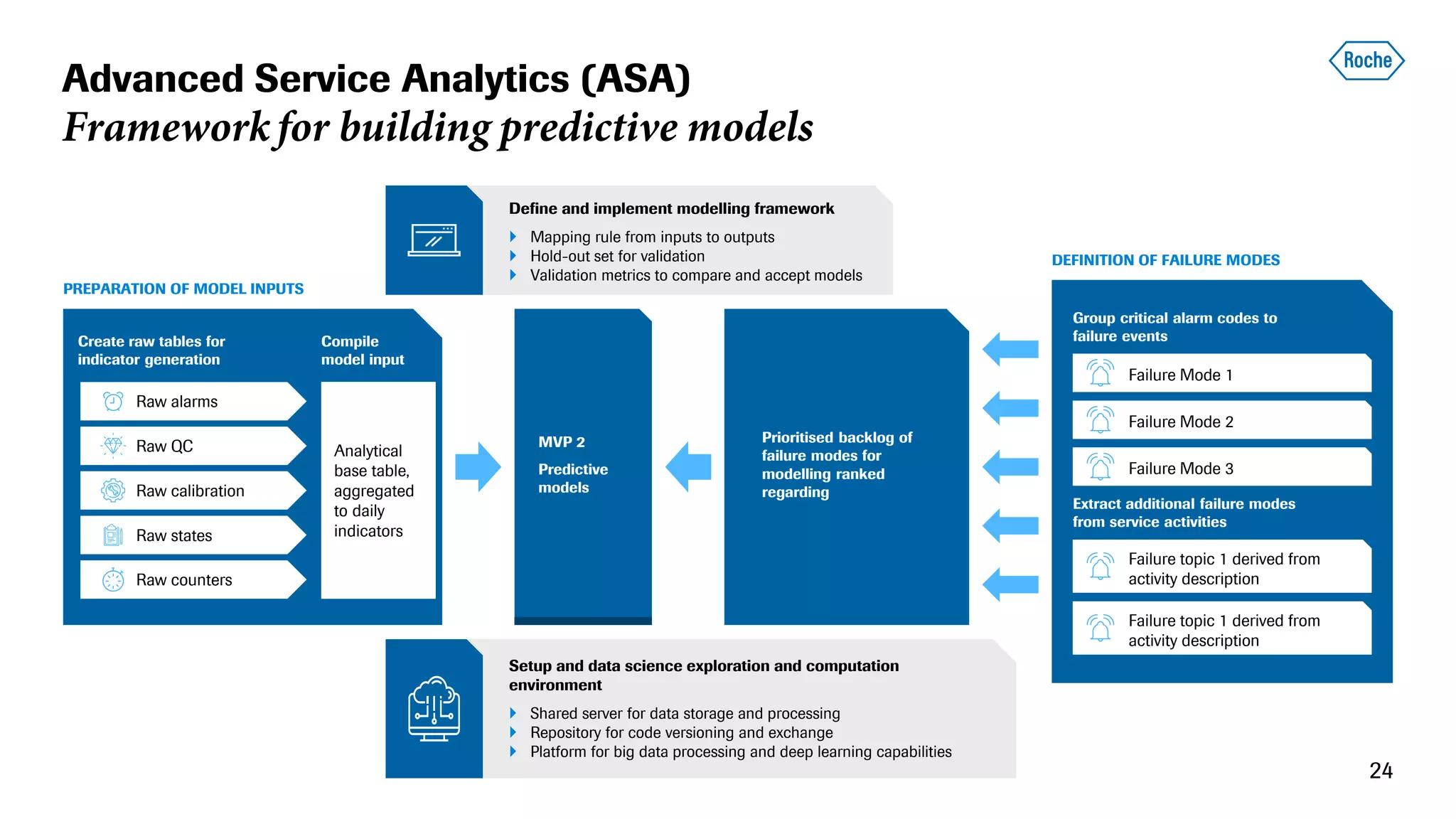
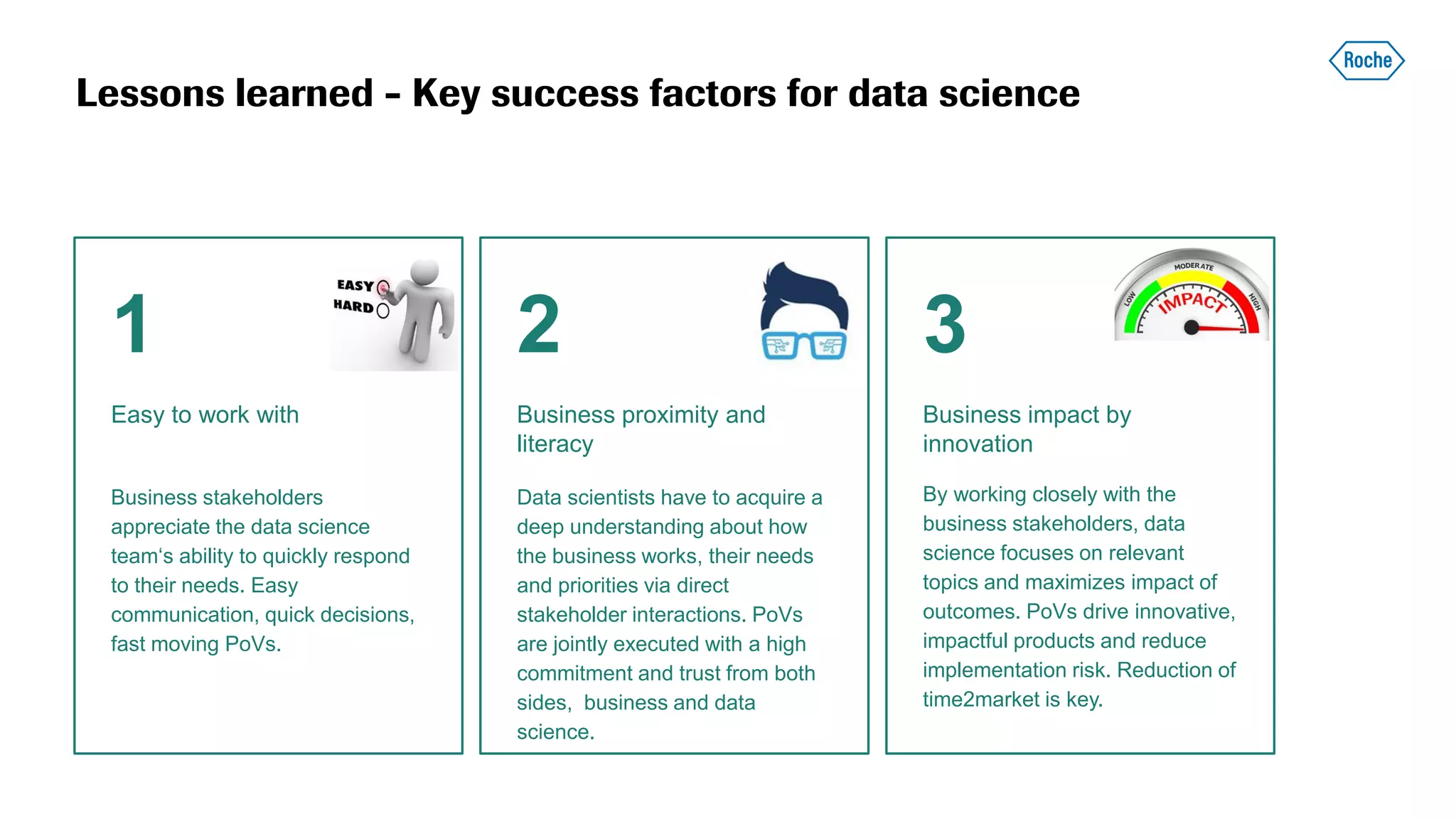
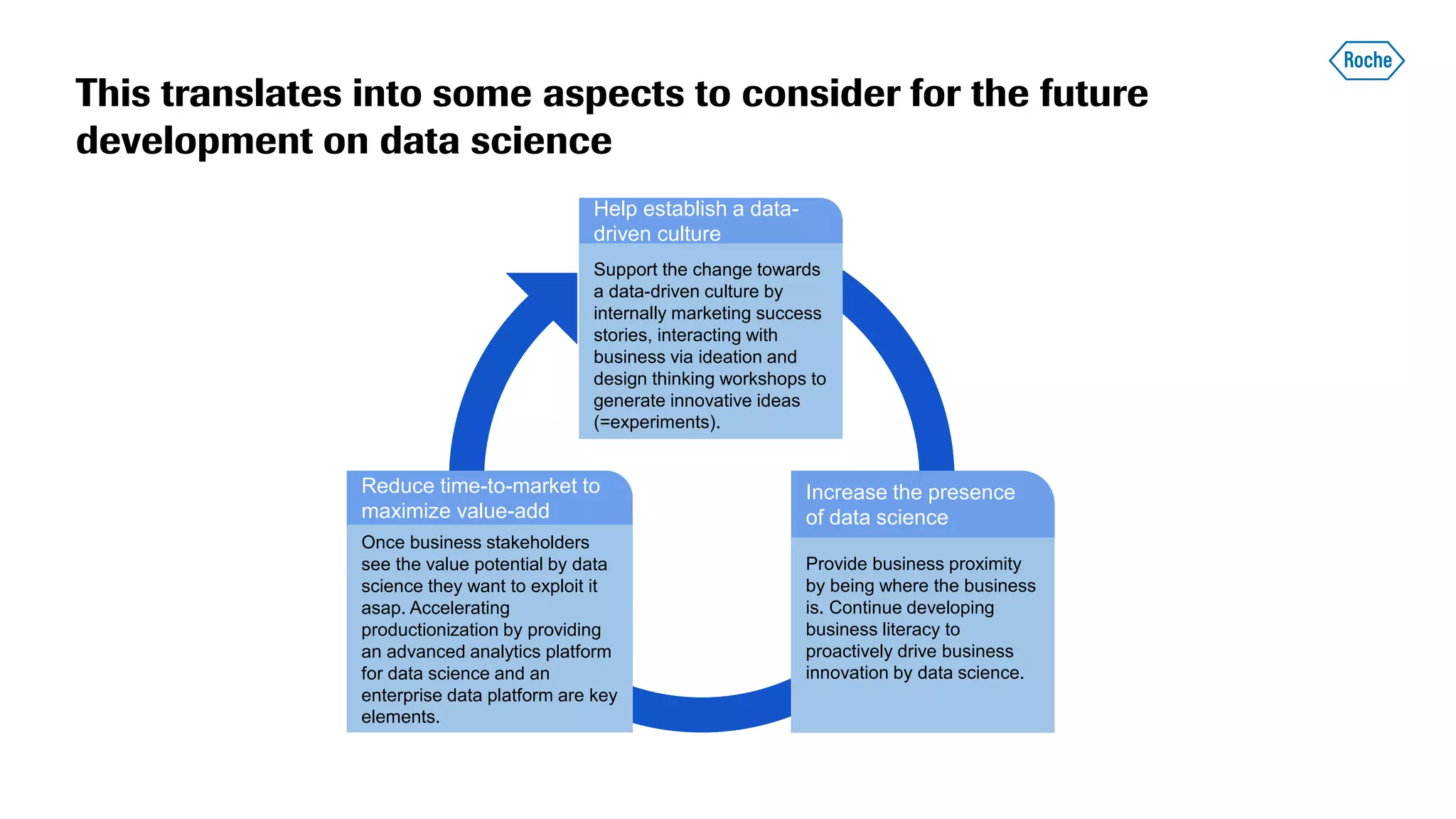
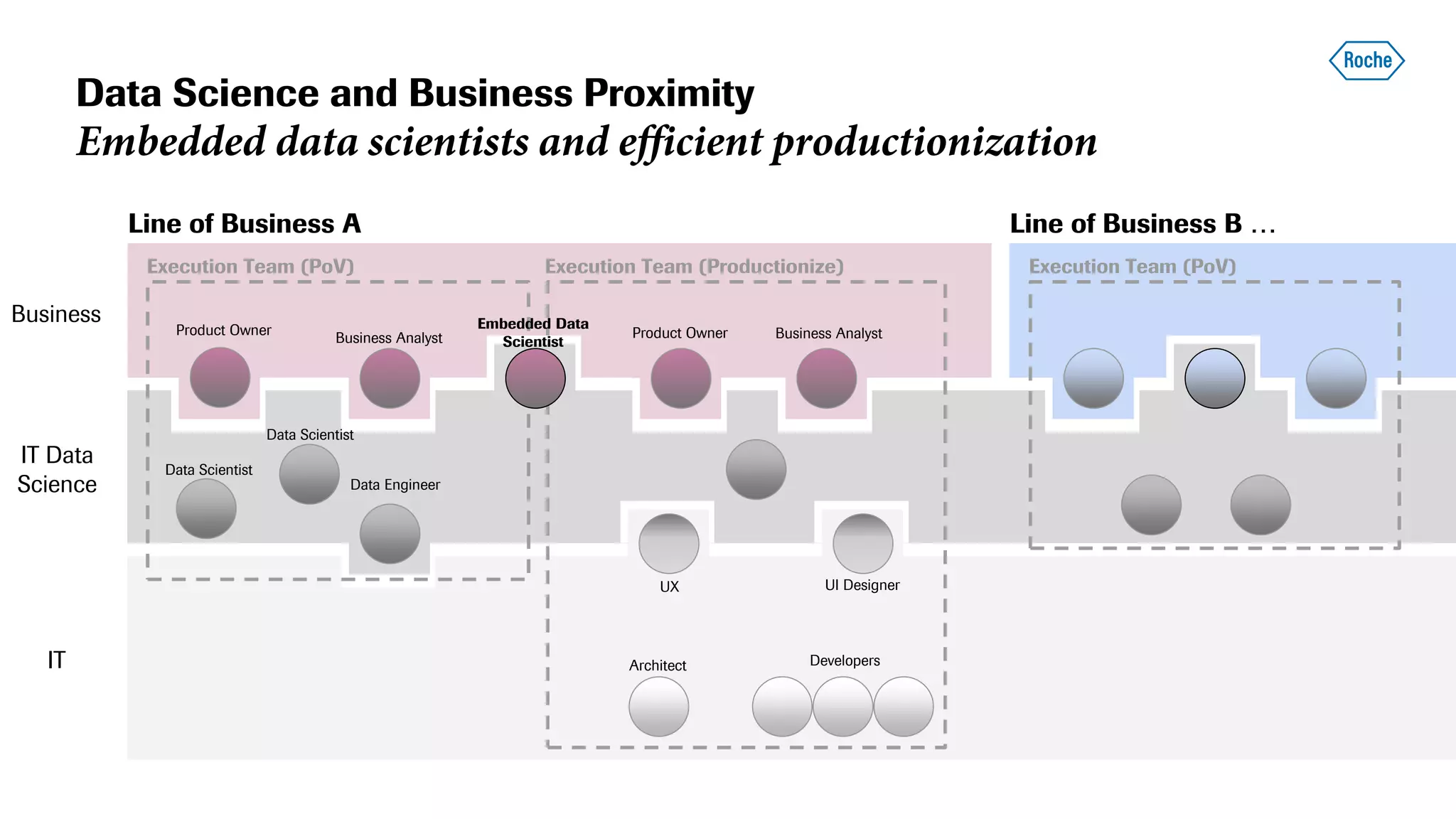
The document summarizes the data science process at Roche Diagnostics from initial ideas through productionization. It discusses how the data science team works end-to-end from initial proofs-of-value (POVs) through several selection gates to deploy models into production. Examples are provided of how data insights led to identifying issues in production processes and developing predictive models for applications like sensor image processing, case classification, and advanced service analytics. Key lessons highlighted include the importance of business proximity, developing business literacy, and focusing on innovative ideas that maximize impact to successfully transition data science projects to production.