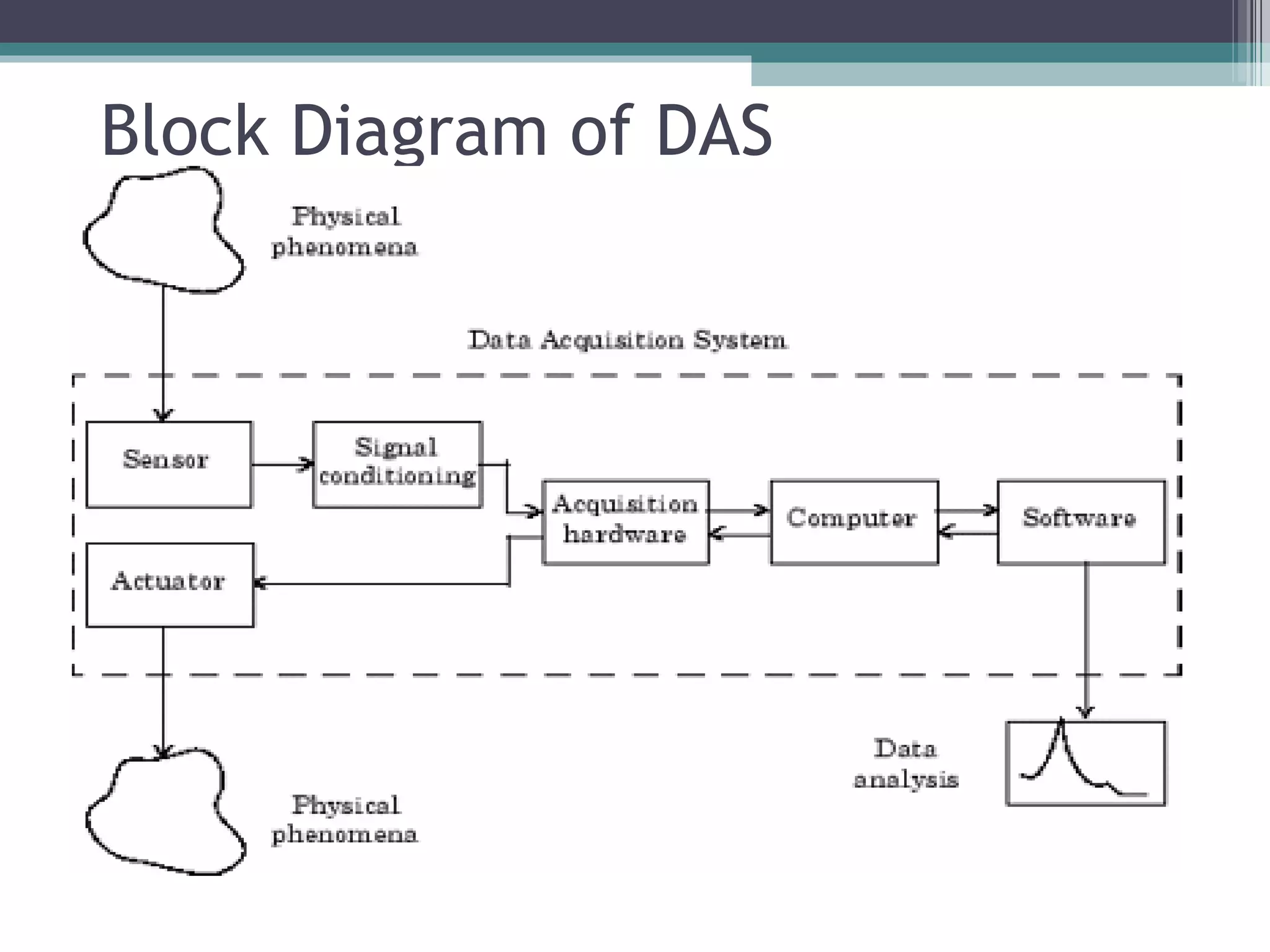
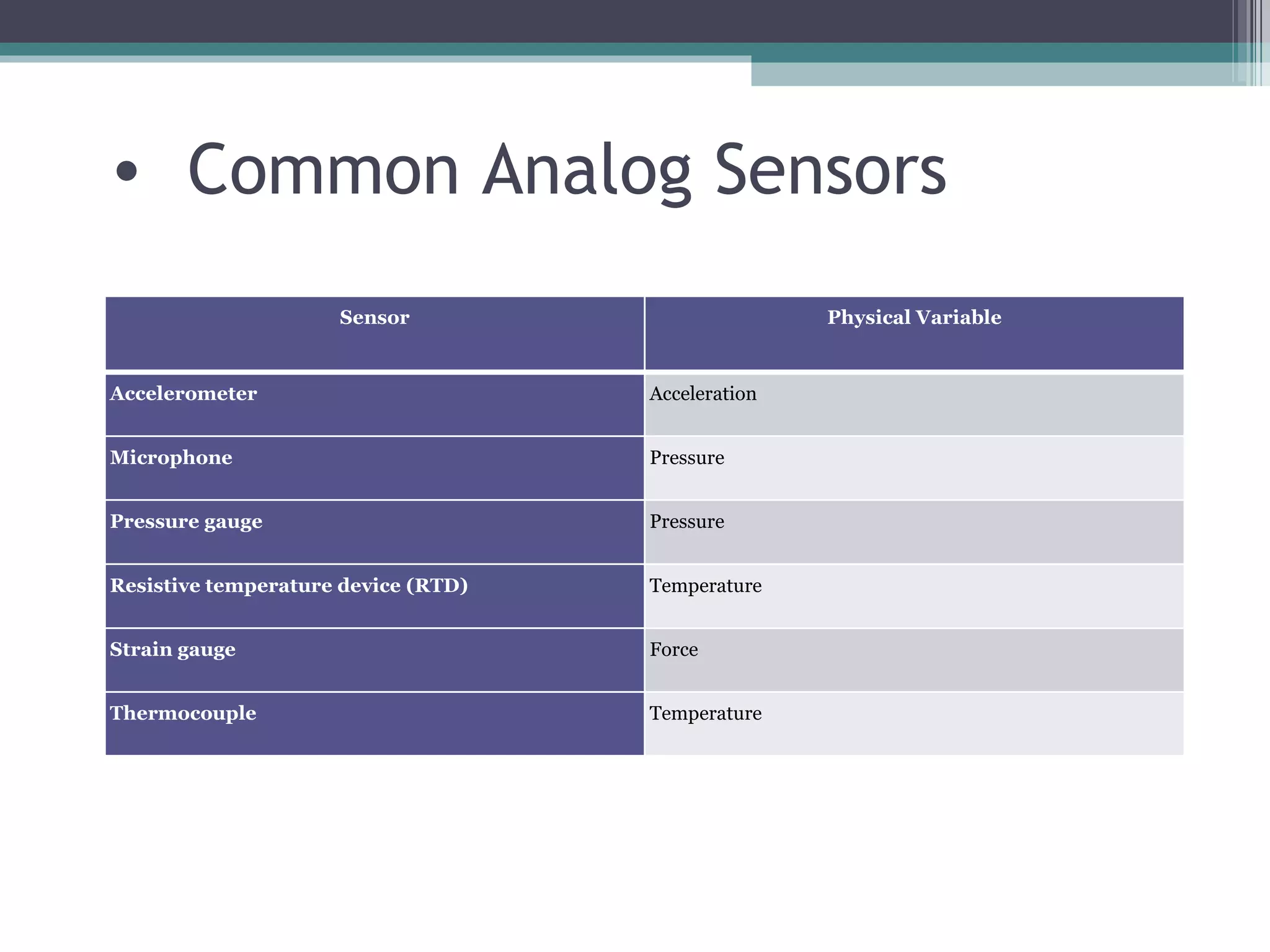
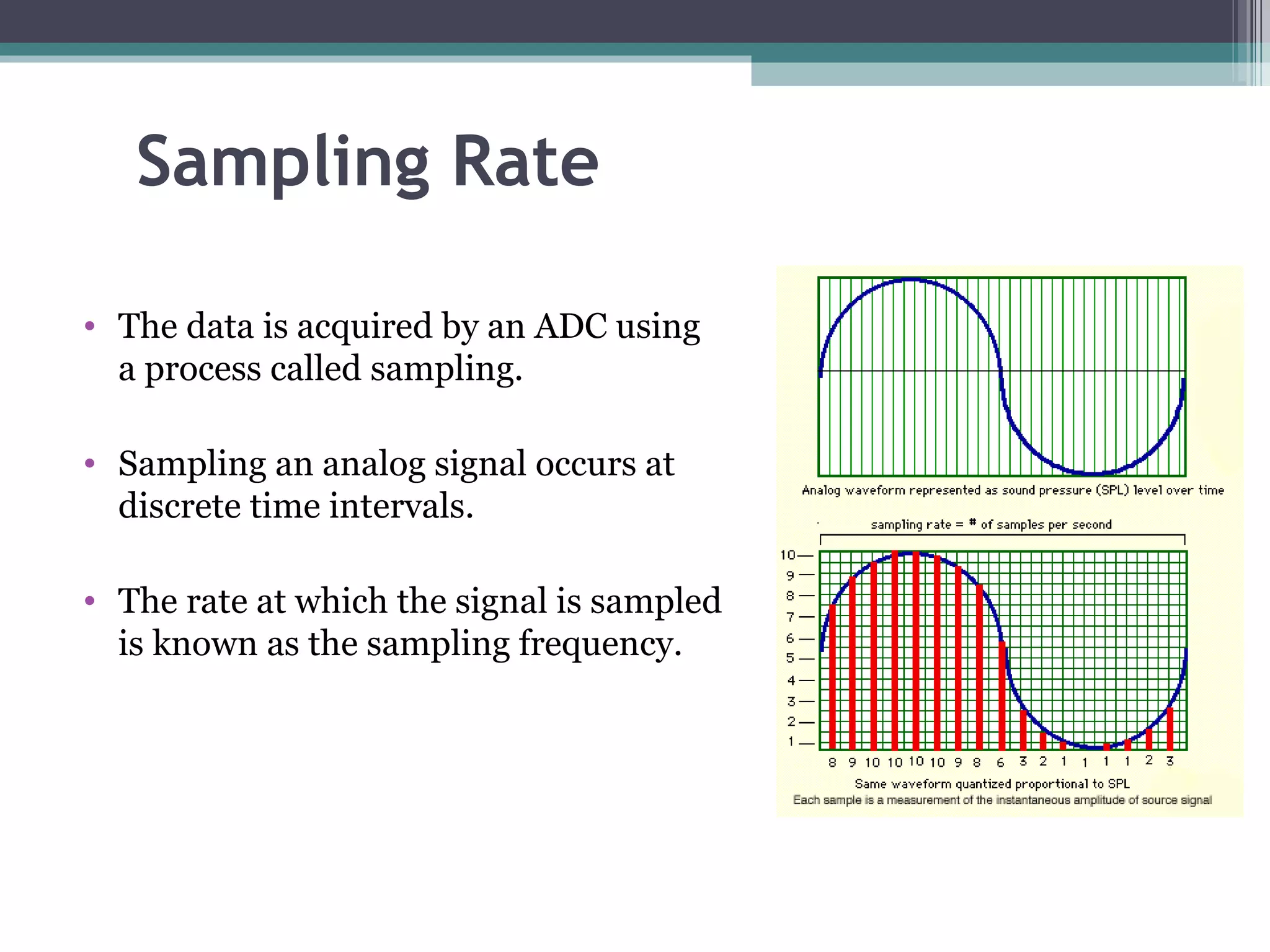
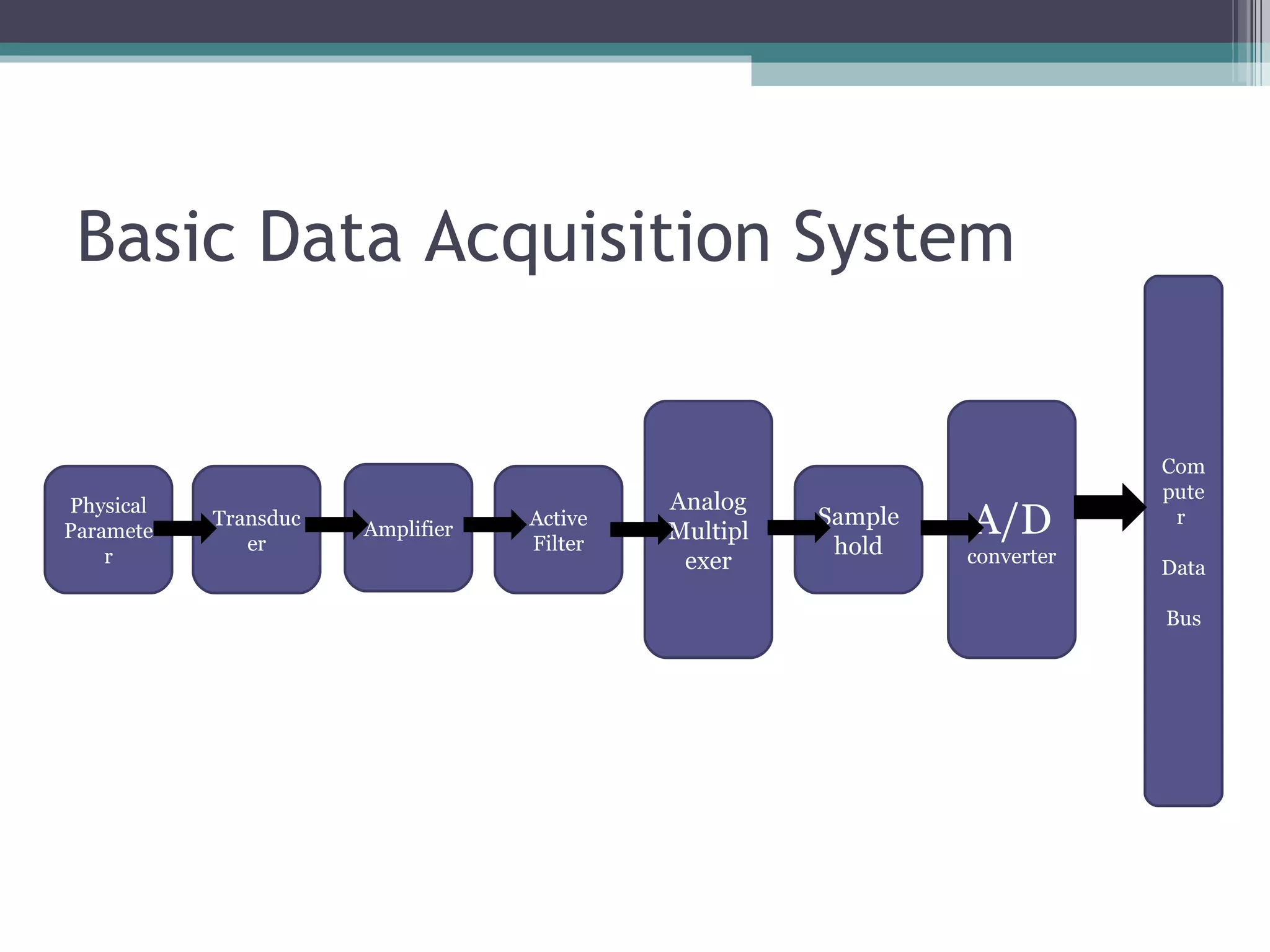
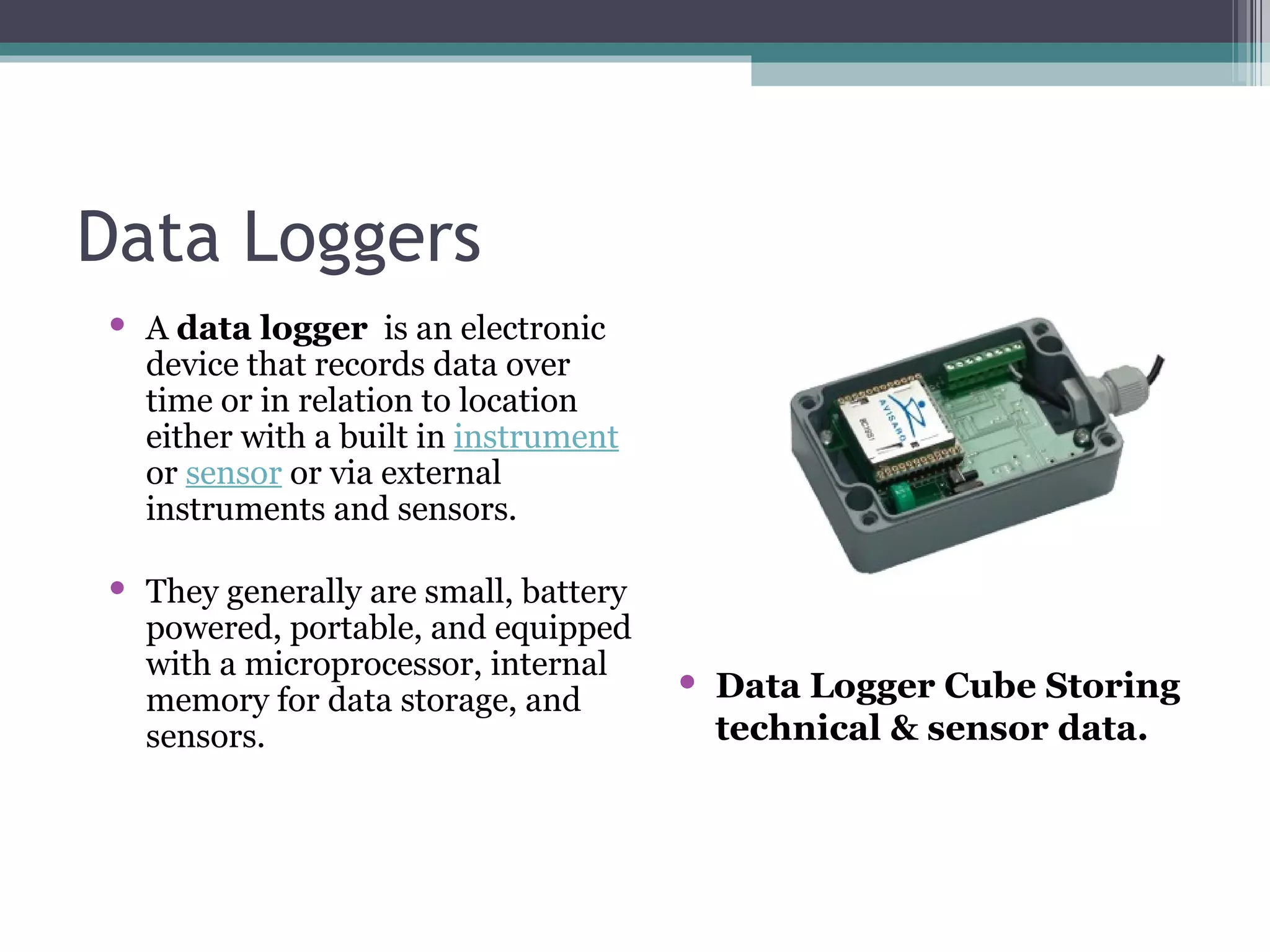
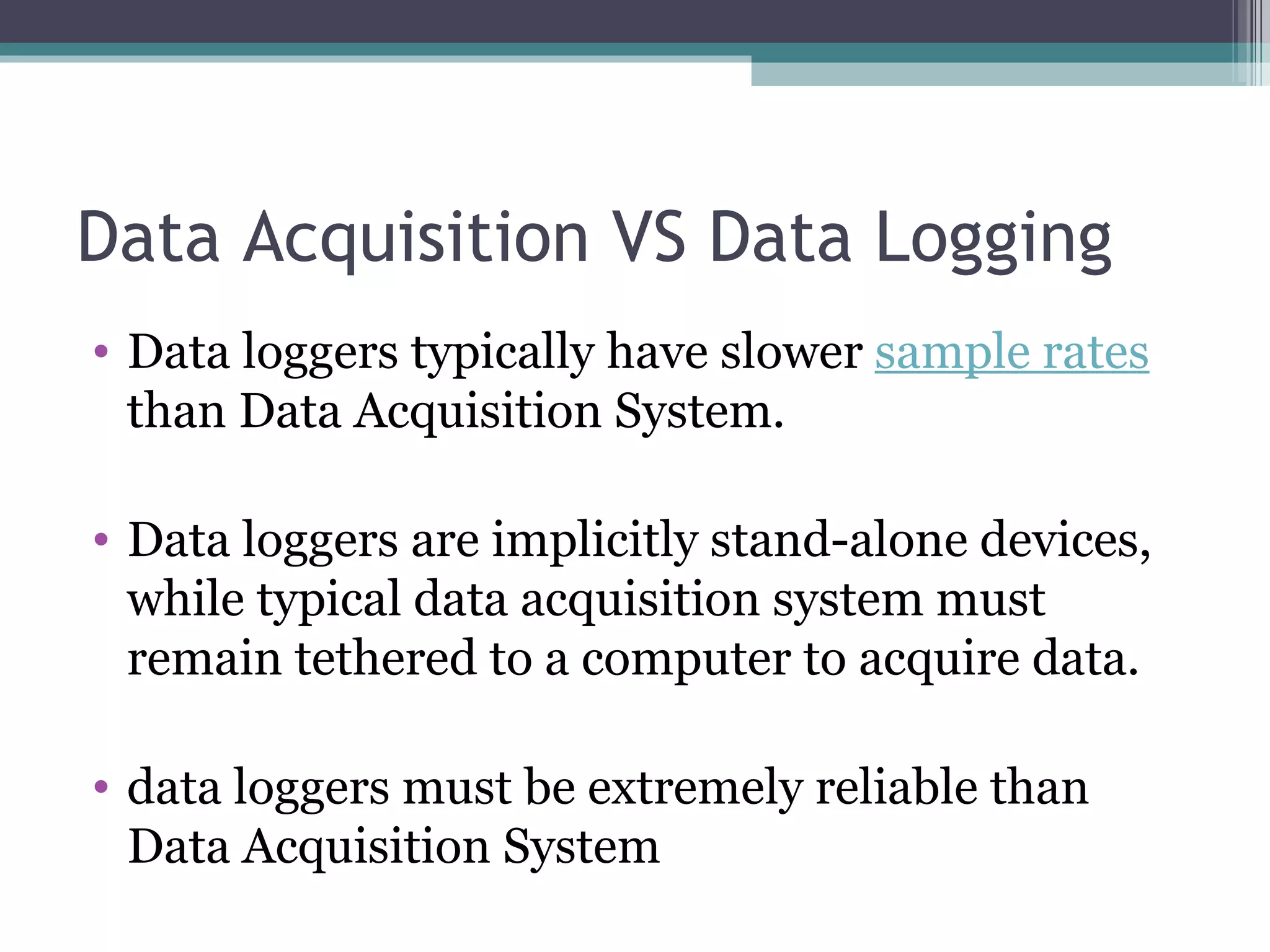
Data acquisition systems capture and measure physical phenomena like temperature, pressure, and light and convert them into electrical signals that can be processed by a computer. The key components are transducers that convert physical values into electrical signals, signal conditioning hardware to prepare signals for measurement, and data acquisition hardware and software for measuring and analyzing the data. Data loggers are portable electronic devices that record data over time from internal or external sensors and instruments to internal memory for later retrieval. They are used in various applications like environmental monitoring and machinery performance testing.