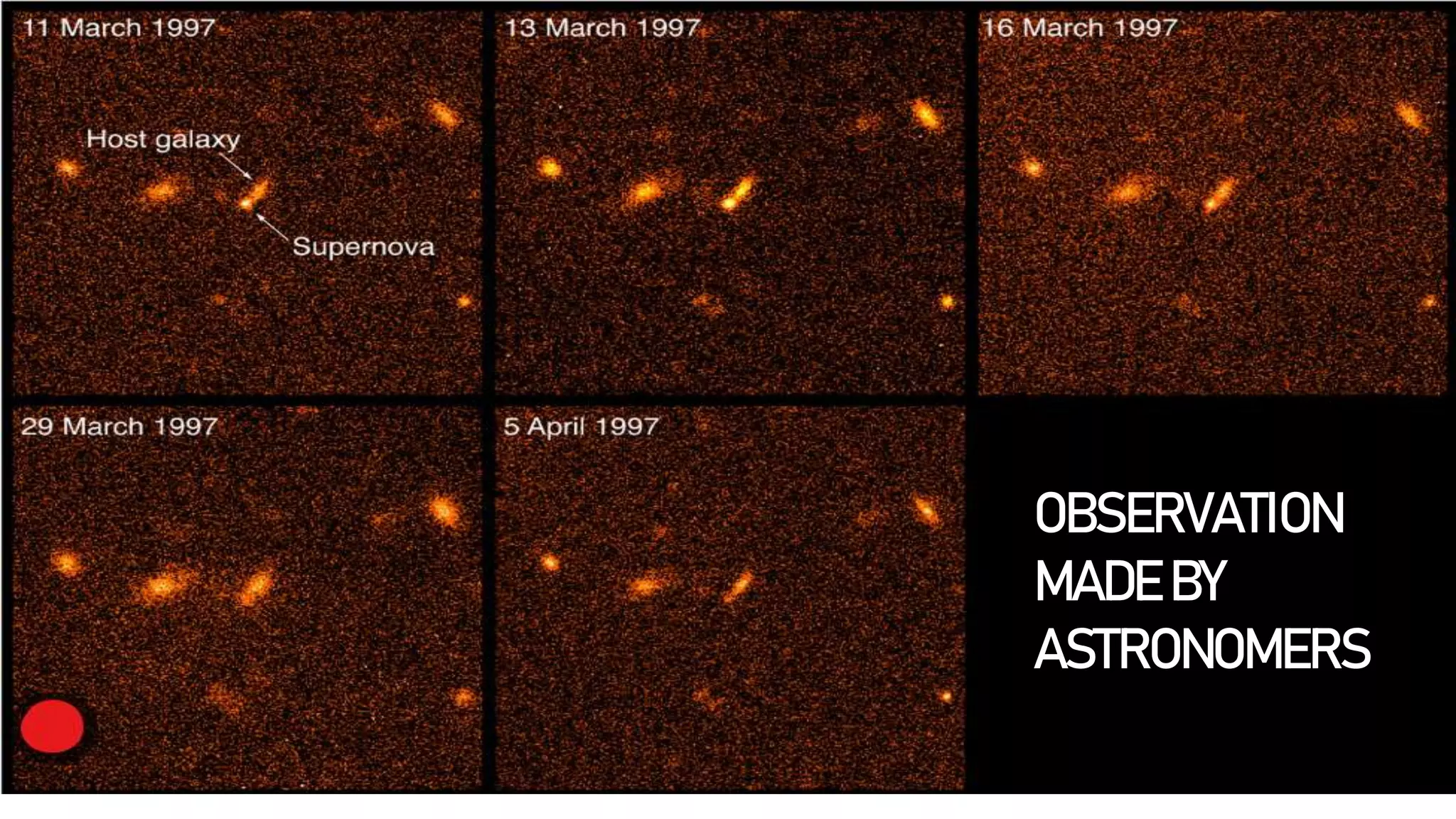
The document discusses dark matter and dark energy, explaining that dark energy constitutes approximately 68% of the universe, while dark matter makes up around 27%, with visible matter accounting for less than 5%. Dark matter interacts with gravity but does not emit or reflect light, while dark energy is considered a repulsive force driving the universe's accelerated expansion. Overall, dark matter slows down the expansion of the universe, whereas dark energy speeds it up, highlighting the significant unanswered questions in the field of astrophysics.