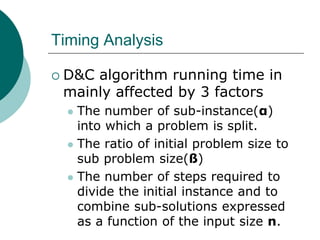
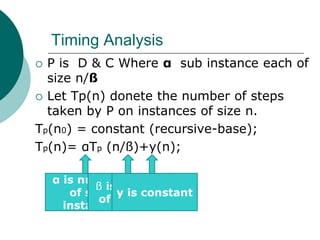
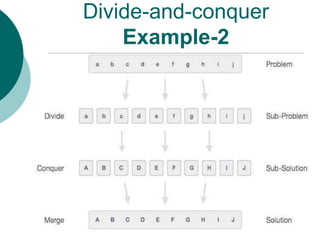
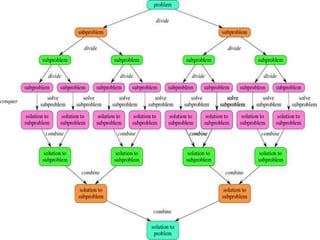
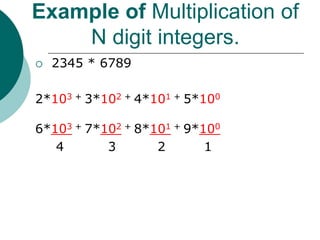
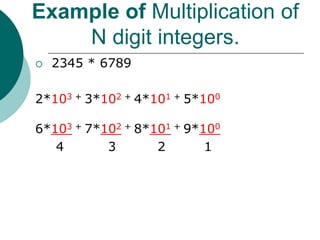
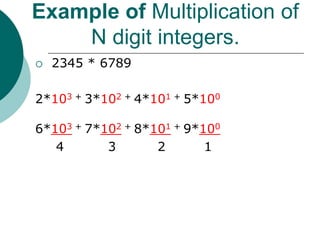
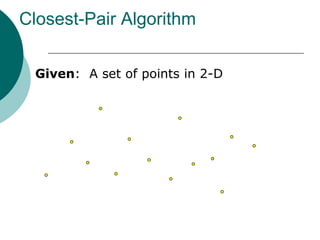
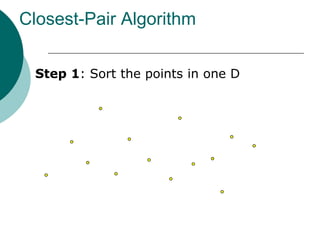
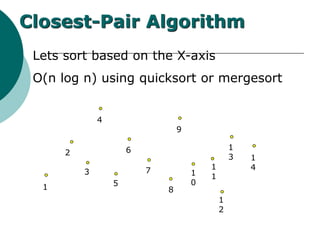
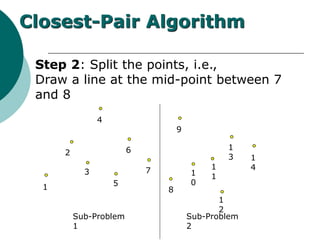
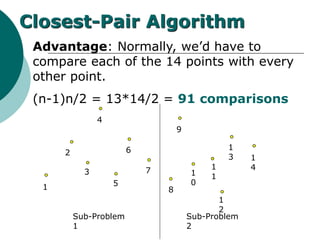
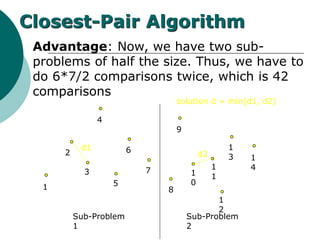
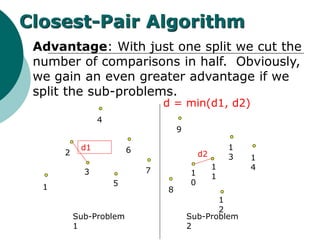
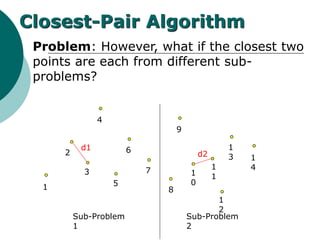
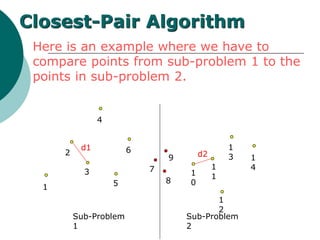
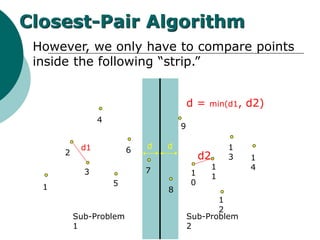
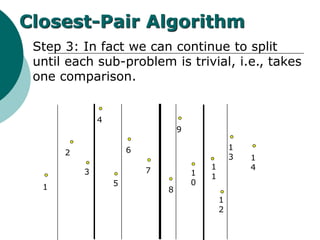
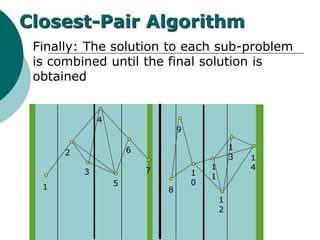
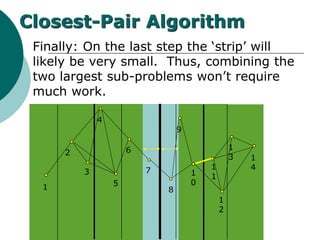
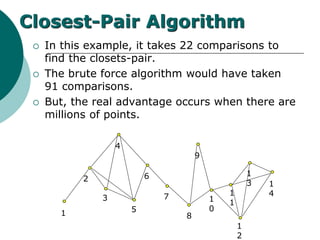
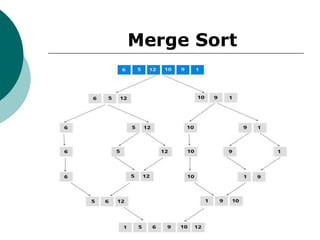
The document discusses the divide-and-conquer algorithm design paradigm. It defines divide-and-conquer as breaking a problem down into smaller subproblems, solving those subproblems recursively, and combining the solutions to solve the original problem. Examples of algorithms that use this approach include merge sort, quicksort, and matrix multiplication. Divide-and-conquer allows for problems to be solved in parallel and more efficiently uses memory caches. The closest pair problem is then presented as a detailed example of how a divide-and-conquer algorithm works to solve this problem in O(n log n) time compared to the brute force O(n2) approach.













![Closest-Pair Algo
For I in 1---s do
for j in i+1..s do
if(|x[i] – x[j] | > DELTA and
|y[i] – y[j]|> DELTA ) then
exit;
end
if(distance(q[I],q[j] <DELTA)) then
DELTA <- distance (q[i],q[j]);
end
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/daaunit2-170919090151/85/Daa-unit-2-36-320.jpg)
![Closest-Pair Algo
Array a[]
Array b[]
Integer h,i,j,k;
h<- low;
i <- low;
j=<- mid + 1;
While( h<= mid and j<= high) do
if(a[h] <= a[j]) then
b[i]<- a[h]
h<-h+1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/daaunit2-170919090151/85/Daa-unit-2-38-320.jpg)
![Closest-Pair Algo
Else
b[i]<- a[j]
j<- j+1;
end
i<- i+1;
End
If(h>mid) then
for(k<-j to high) do
b[i] <- a[k];
i<-i+1;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/daaunit2-170919090151/85/Daa-unit-2-39-320.jpg)
![Closest-Pair Algo
Else
for(k<- to mid) do
b[i] <- a[k]
i=i+1;
End
For(k<-low to high)
a[k]<- b[k]
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/daaunit2-170919090151/85/Daa-unit-2-40-320.jpg)