1. Introduction to Algorithms
1.1 What is an Algorithm?
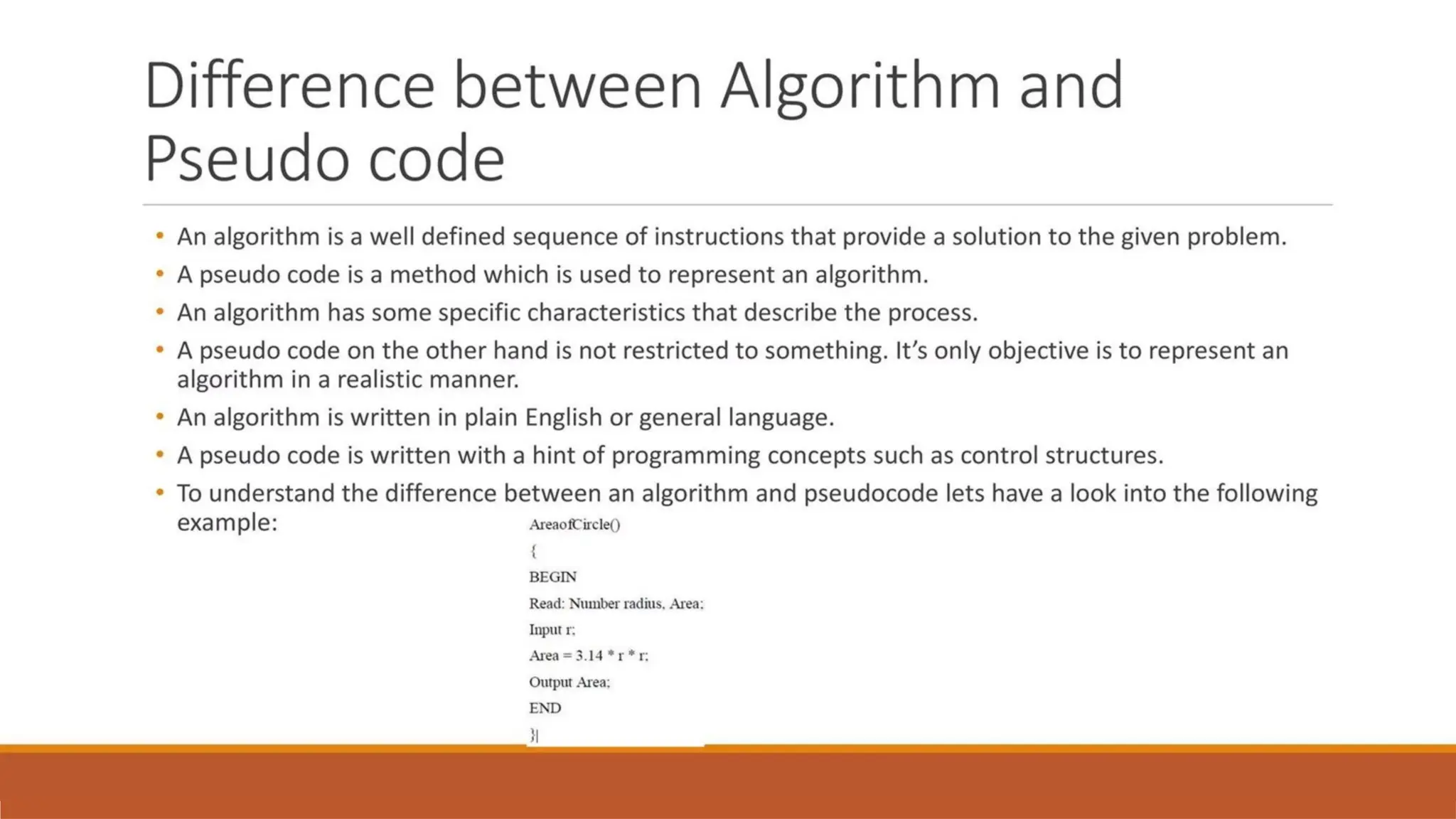
An algorithm is a finite set of instructions that, if followed, accomplishes a particular task. It is a well-defined procedure that takes some input, performs a sequence of computational steps, and produces an output.
Formally:
“An algorithm is a step-by-step procedure for solving a problem in a finite amount of time.”
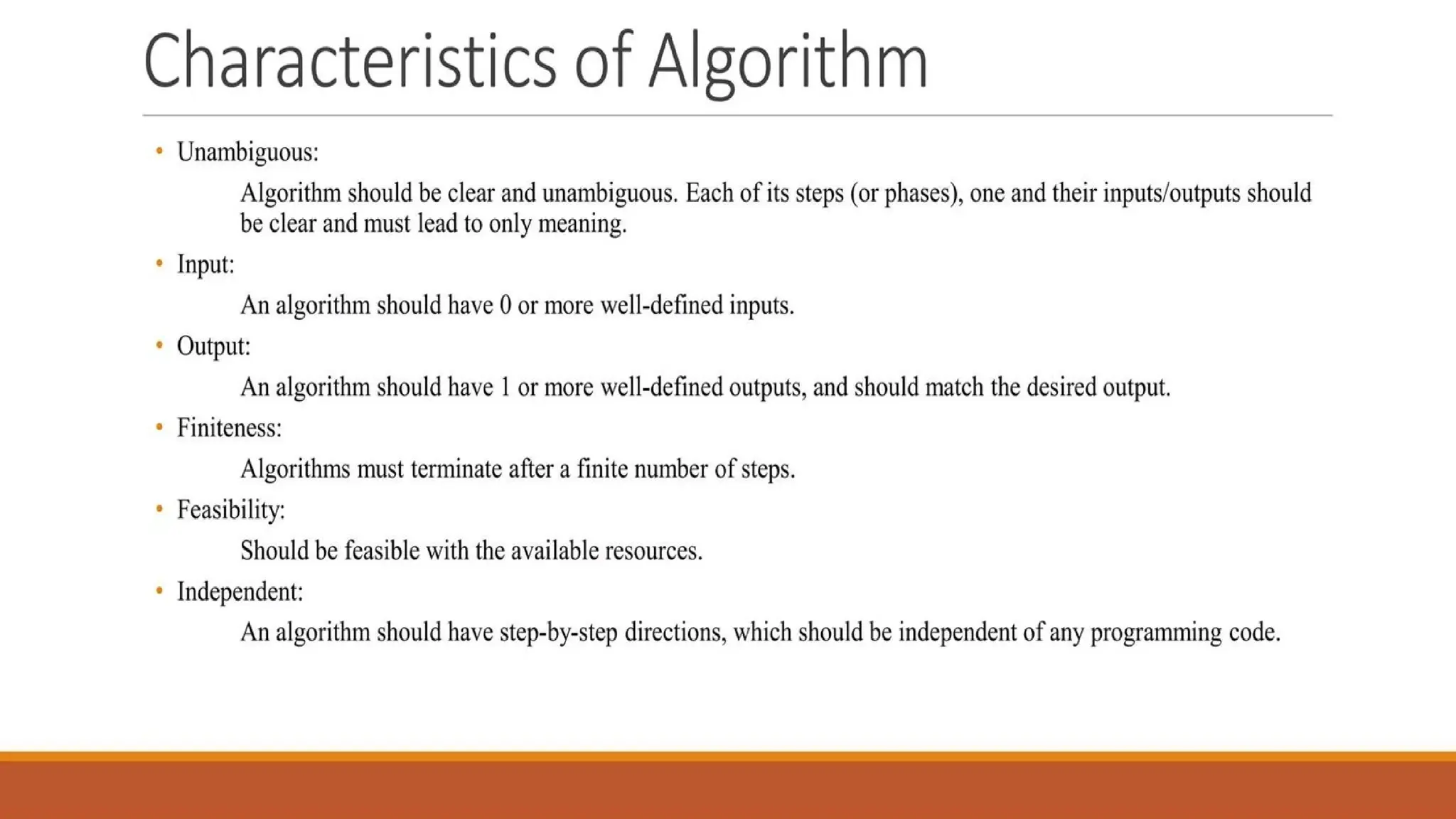
1.2 Characteristics of an Algorithm
For a procedure to qualify as an algorithm, it must satisfy the following properties:
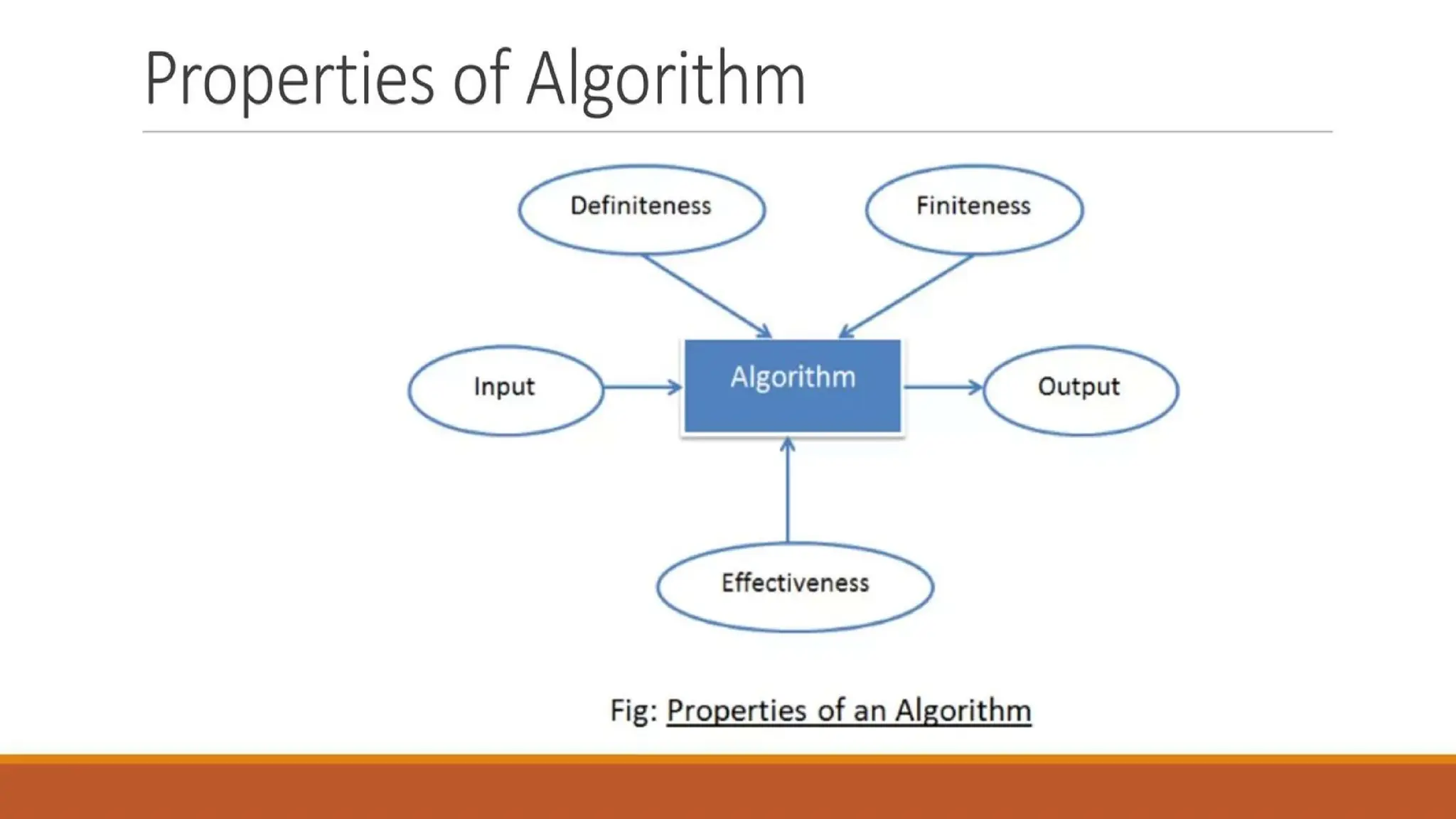
Finiteness – The algorithm must terminate after a finite number of steps.
Definiteness – Each step of the algorithm must be clear and unambiguous.
Input – An algorithm should have zero or more inputs.
Output – An algorithm should produce at least one output.
Effectiveness – Every step of the algorithm must be basic enough to be carried out by a computer in a finite amount of time.
2. Importance of Algorithm Analysis
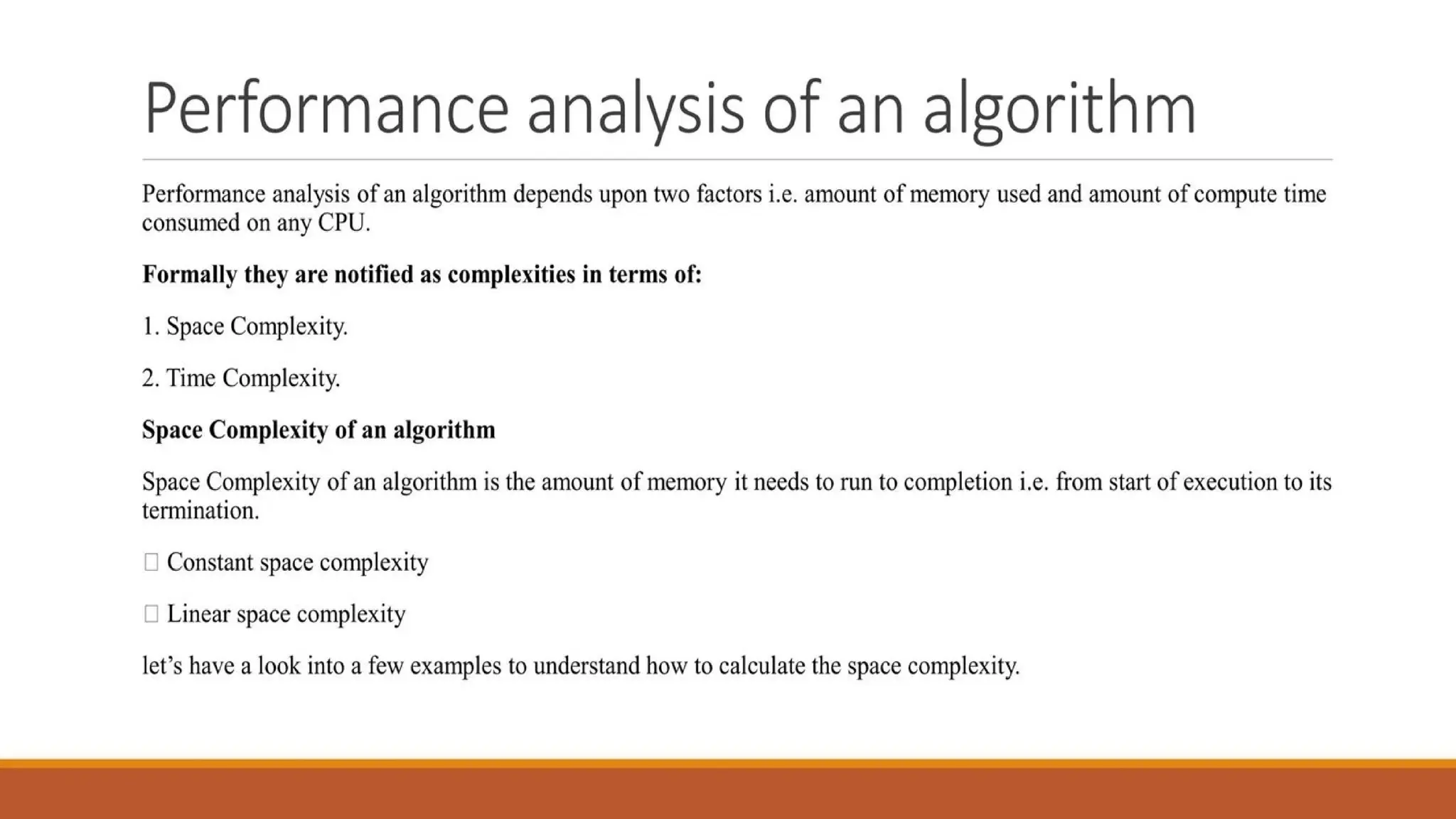
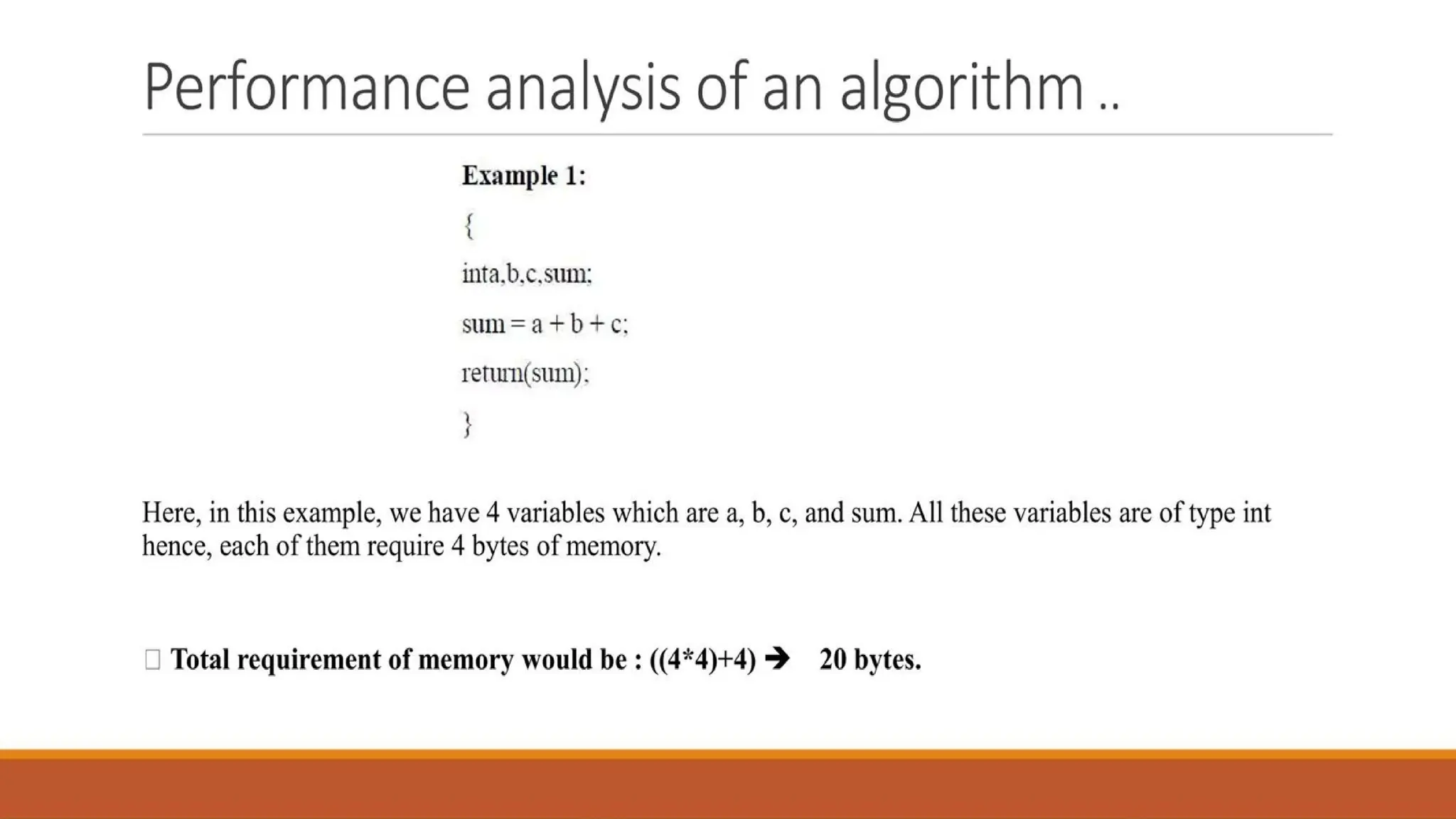
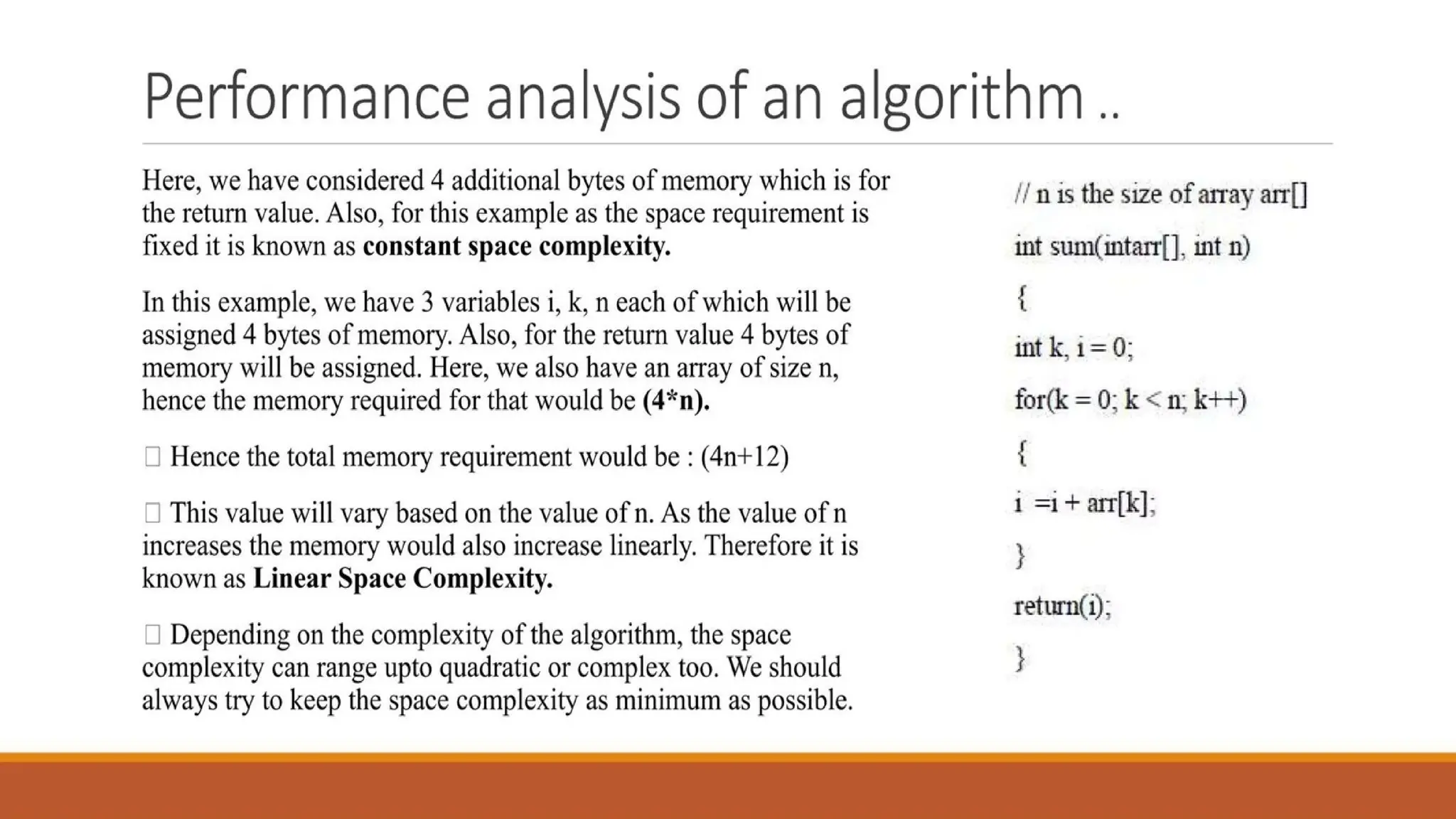
Writing an algorithm is not enough; we also need to evaluate its efficiency. With large datasets, the efficiency of an algorithm plays a crucial role in execution speed and resource usage.
2.1 Why Analyze Algorithms?
To choose the best algorithm for solving a problem.
To compare algorithms based on time and space requirements.
To understand the scalability of the algorithm as input size grows.
3. Algorithm Design Goals
When designing an algorithm, the following goals are kept in mind:
Correctness – Algorithm should solve the problem accurately.
Efficiency – It should use minimum resources (time and memory).
Readability & Simplicity – Easy to understand, maintain, and implement.
Scalability – Should handle larger inputs without breaking down.
Generality – Should be applicable to different types of inputs.
4. Algorithm Analysis
4.1 Types of Analysis
Worst Case Analysis
Maximum time taken on any input of size n.
Guarantees performance in the worst scenario.
Example: In Linear Search, worst case is when the element is not present.
Best Case Analysis
Minimum time taken on any input of size n.
Example: In Linear Search, best case is when the first element matches.
Average Case Analysis
Expected time over all possible inputs.
Often provides a realistic measure.
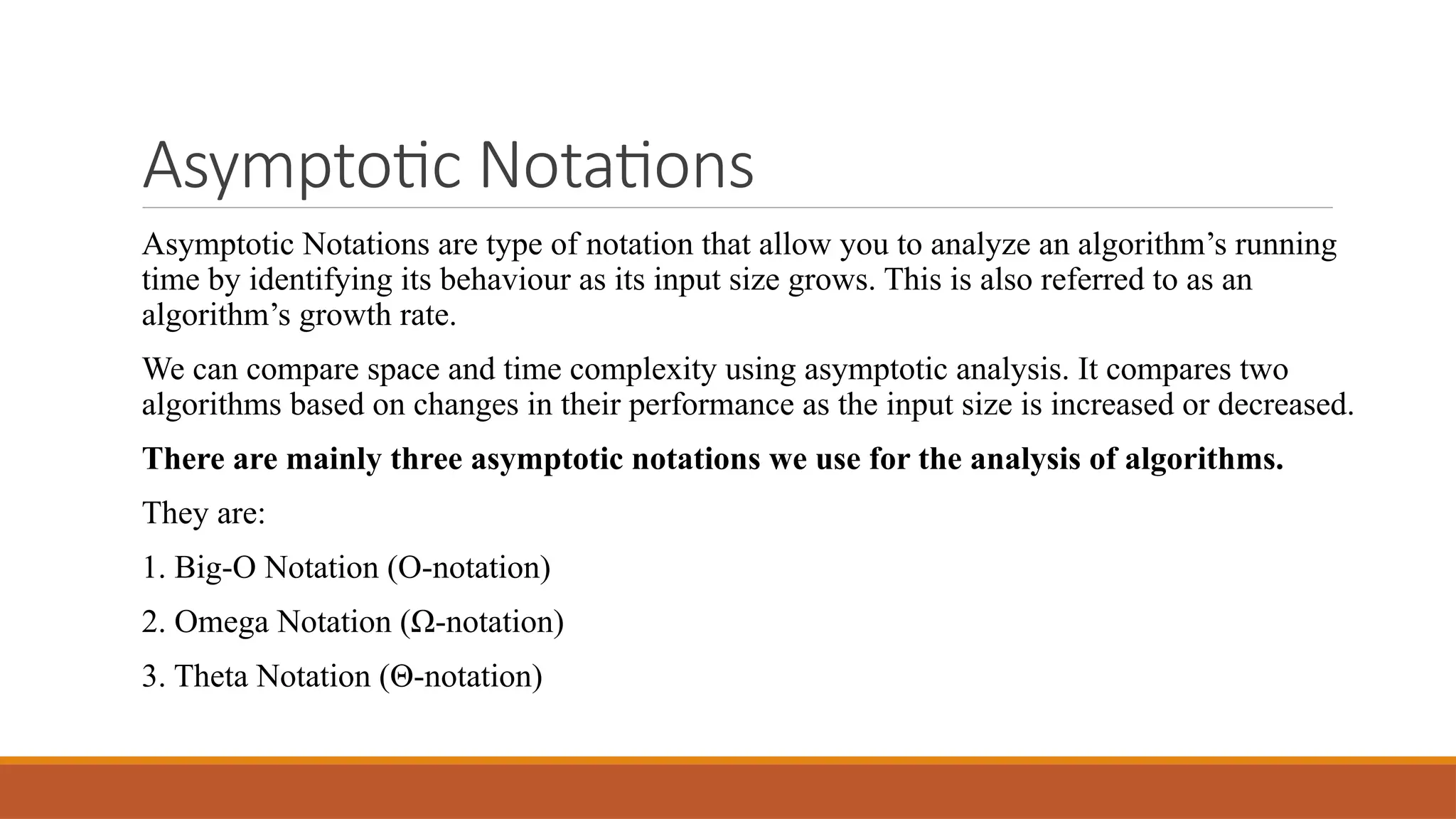
4.2 Asymptotic Notations
Asymptotic analysis describes the running time of an algorithm in terms of input size n for large inputs.
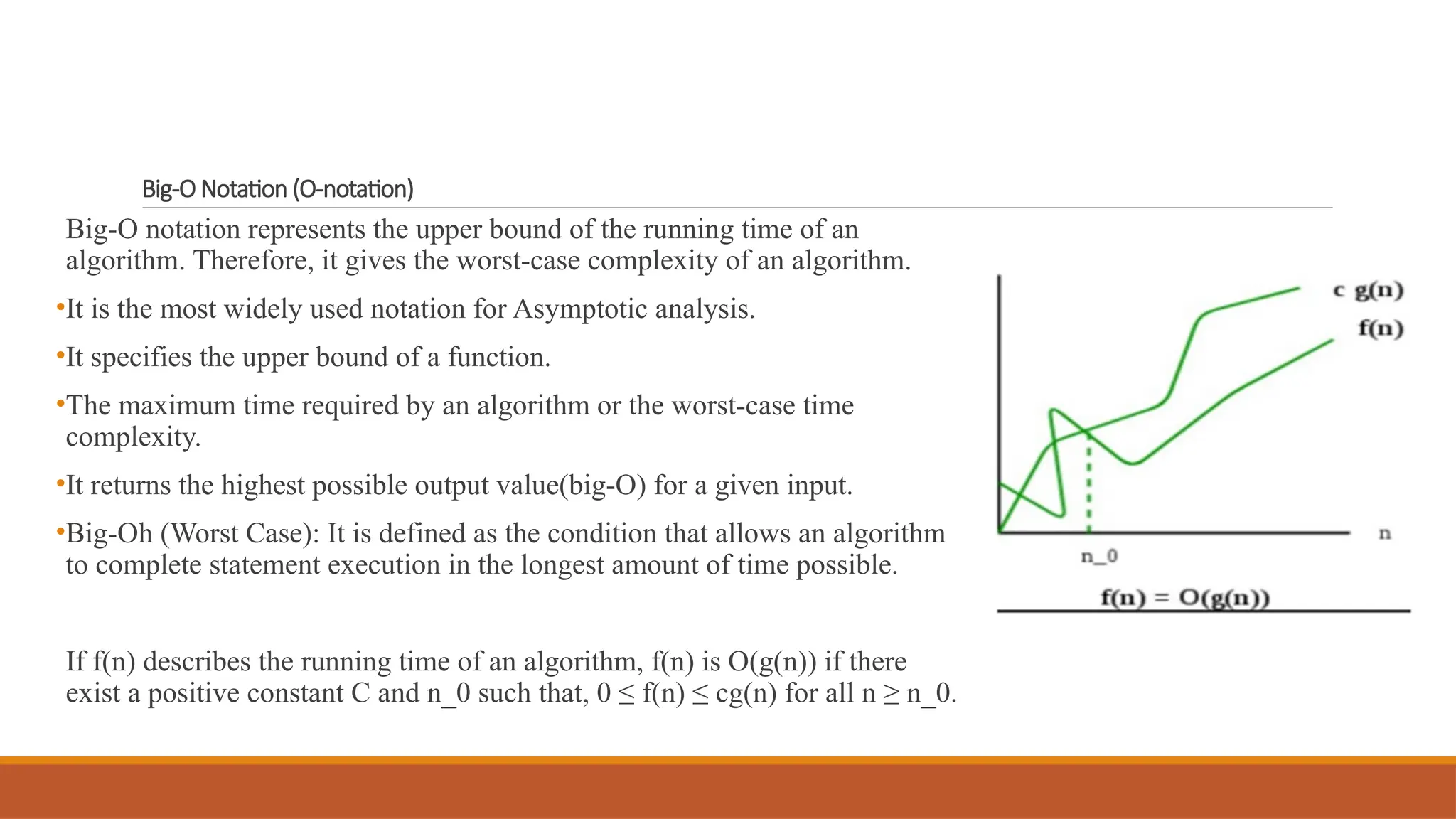
Big-O Notation (O)
Represents the upper bound of the growth rate.
Example: Linear Search → O(n).
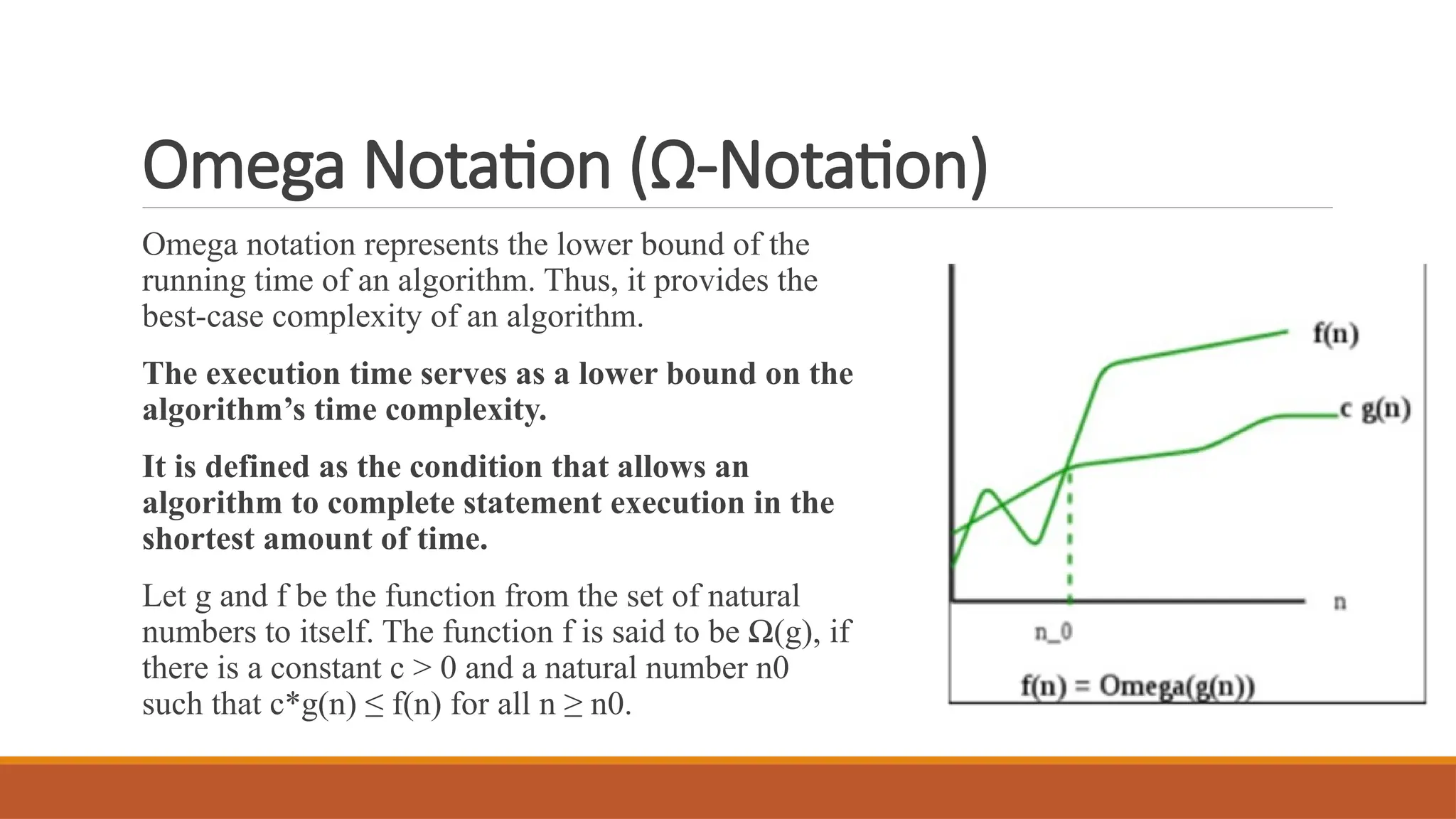
Omega Notation (Ω)
Represents the lower bound of the growth rate.
Example: Linear Search → Ω(1).
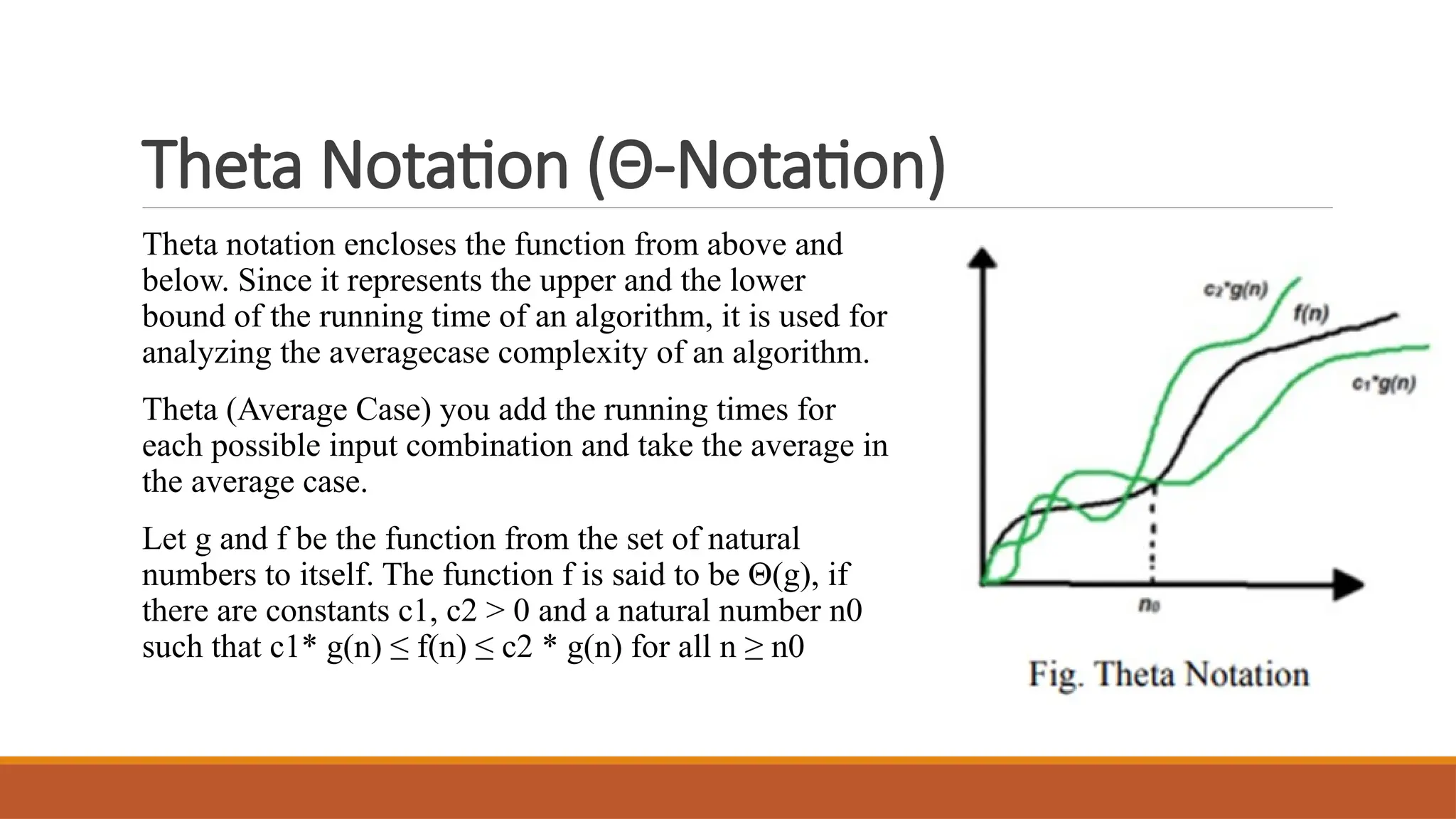
Theta Notation (Θ)
Represents the tight bound (both upper and lower).
Example: Linear Search → Θ(n).
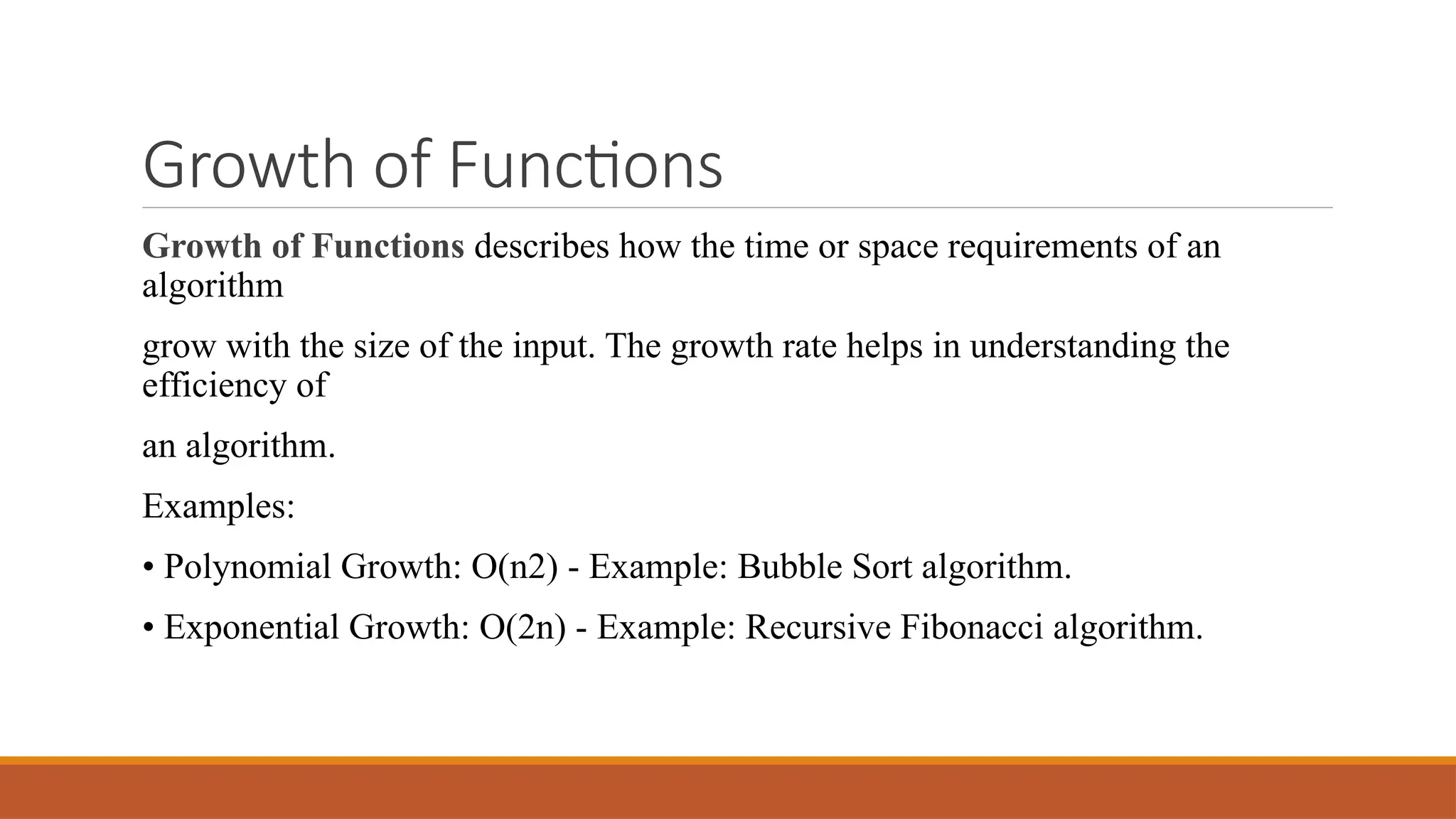
5. Growth of Functions
The efficiency of an algorithm is influenced by how its running time grows with input size. Some common growth rates:
Constant → O(1)
Logarithmic → O(log n)
Linear → O(n)
Linearithmic → O(n log n)
Quadratic → O(n²)
Cubic → O(n³)
Exponential → O(2^n)
Factorial → O(n!)
6. Recurrence Relations
Many rec