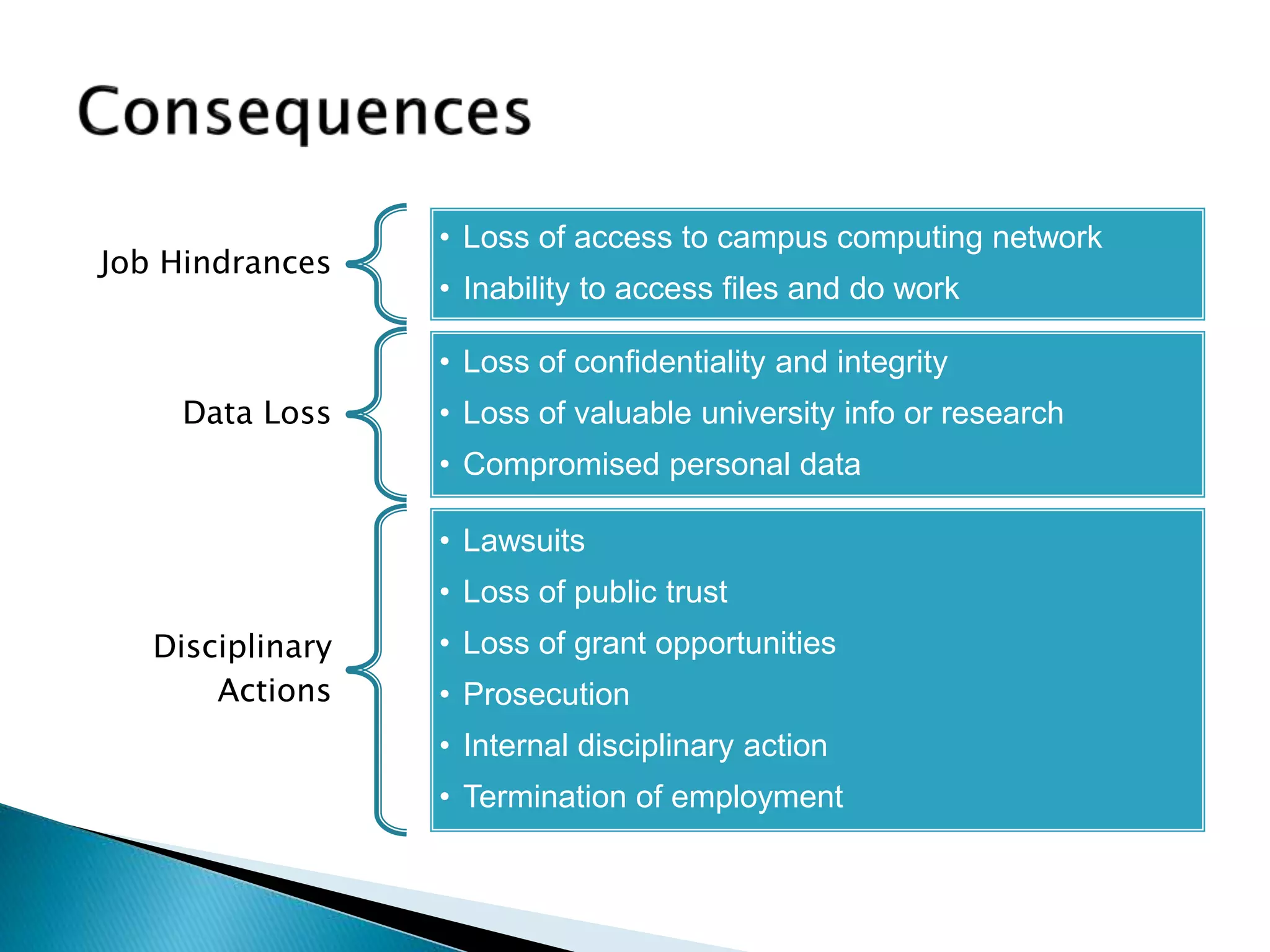
This document discusses the scope and definitions of cyber security. It outlines typical cyber attacks like phishing, malware, and denial of service attacks. Recent significant cyber incidents are mentioned from 2019 targeting governments, companies, and individuals. The consequences of cyber attacks are job hindrances, data loss, and disciplinary actions. Finally, the document lists the top eight cyber safety actions to protect passwords, prevent identity theft, beware of phishing, avoid malware, run antivirus software, install updates, back up files, and turn on firewalls.