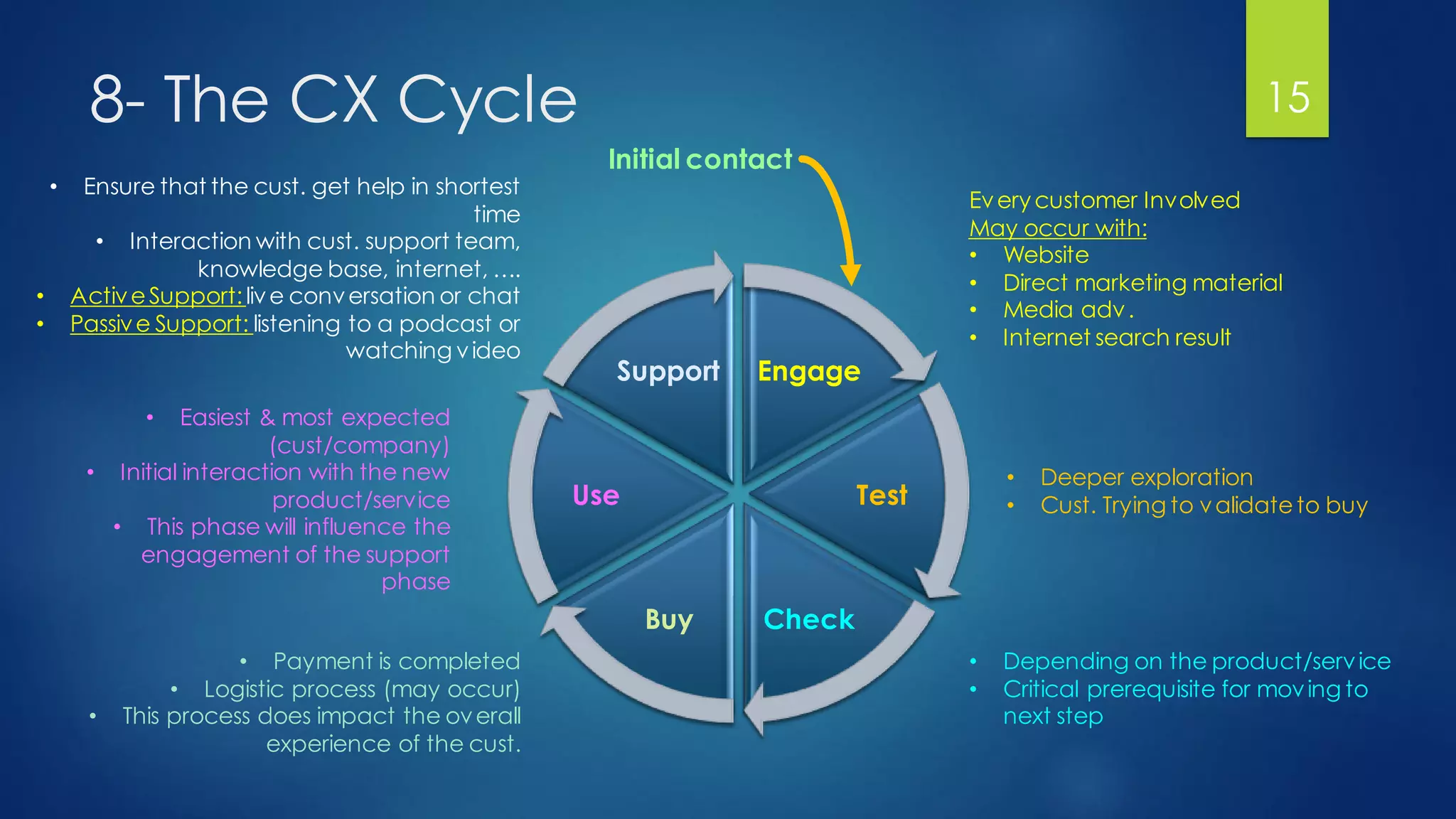
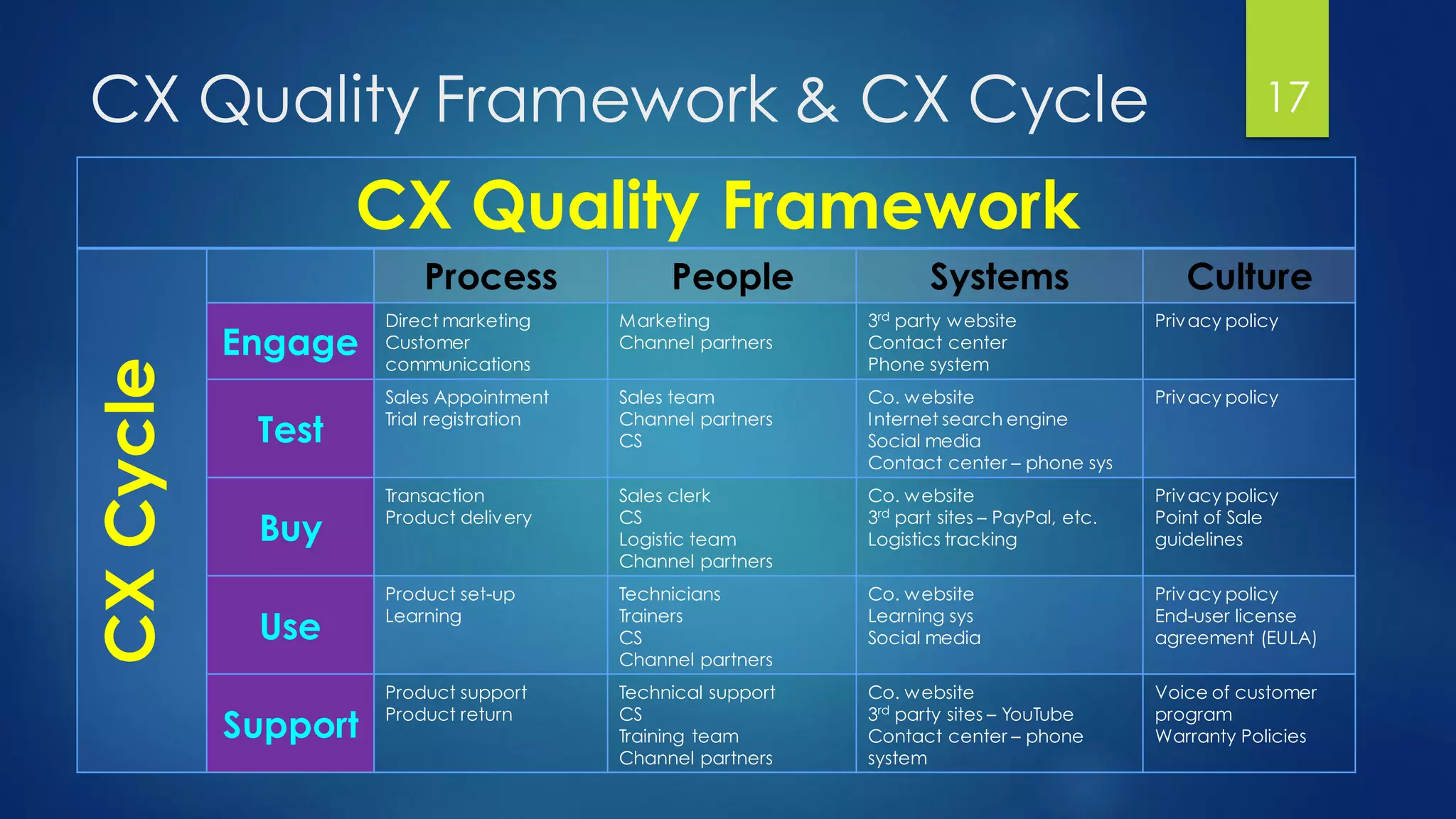
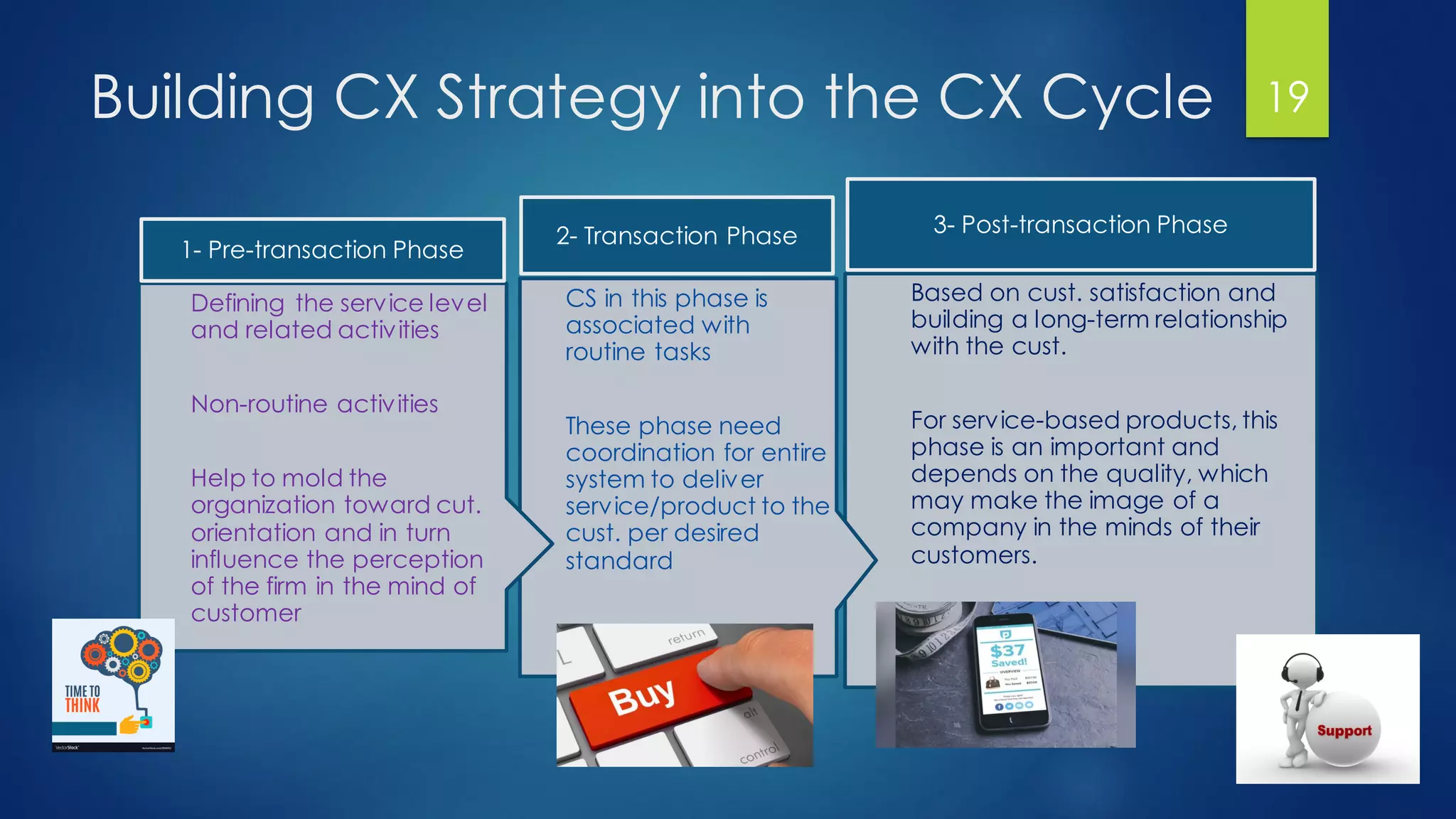
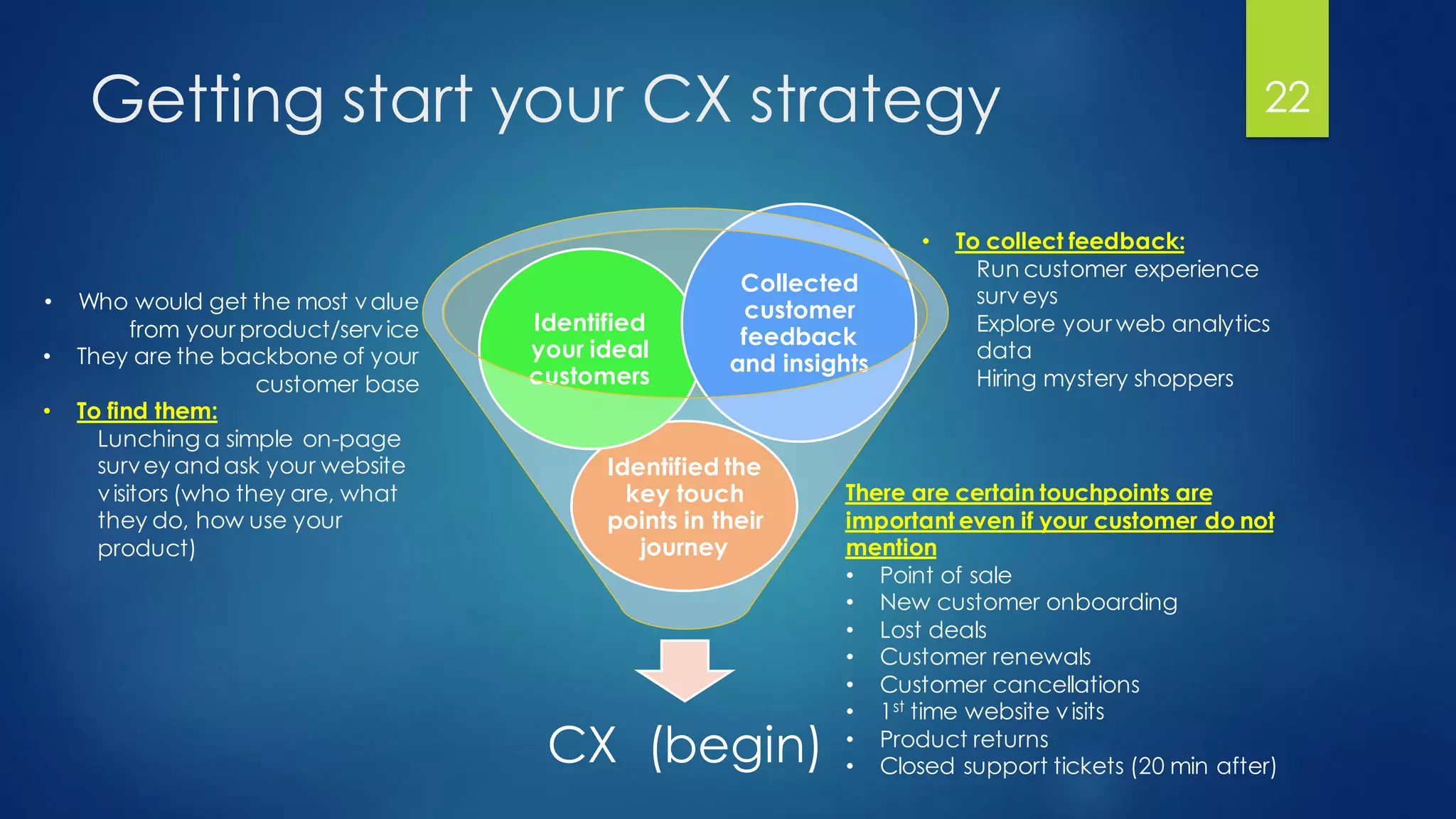
The document outlines a presentation on customer experience (CX) led by Dr. Ramadan Babers, covering the evolution of marketing, the definition and importance of CX, and its benefits for businesses. It emphasizes the distinction between customer service (CS) and CX and discusses strategies for improving customer interactions and measuring satisfaction. The presentation advocates using customer feedback to refine CX strategies and detailed methods for conducting effective CX surveys.