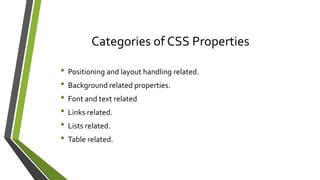
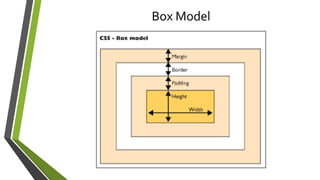
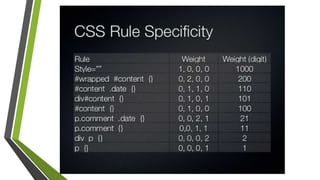
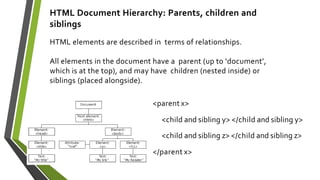
The document discusses various topics related to HTML, CSS, and client-side coding including: CSS selectors, properties, cascade, media queries, animations. It covers CSS syntax, selectors like type, ID, class, attribute, and pseudo selectors. It describes the box model and properties for text, background, positioning. It also explains cascade, specificity, inheritance in CSS and how media queries allow styling for different devices.




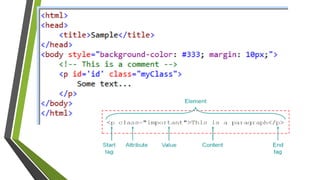








![CSSSelectors
p Type (element)
# ID
. Class
[] Attribute
* Universal](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/css-160127022557/85/CSS-15-320.jpg)

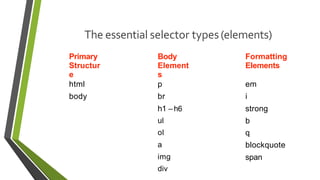


![Attribute selectors
Attribute selectors selects elements based upon the attributes present
in the HTMLTags and their value.
IMG[src="small.gif"] {
border: 1px solid #000;
}
will work for
<img src=“small.gif” />](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/css-160127022557/85/CSS-20-320.jpg)