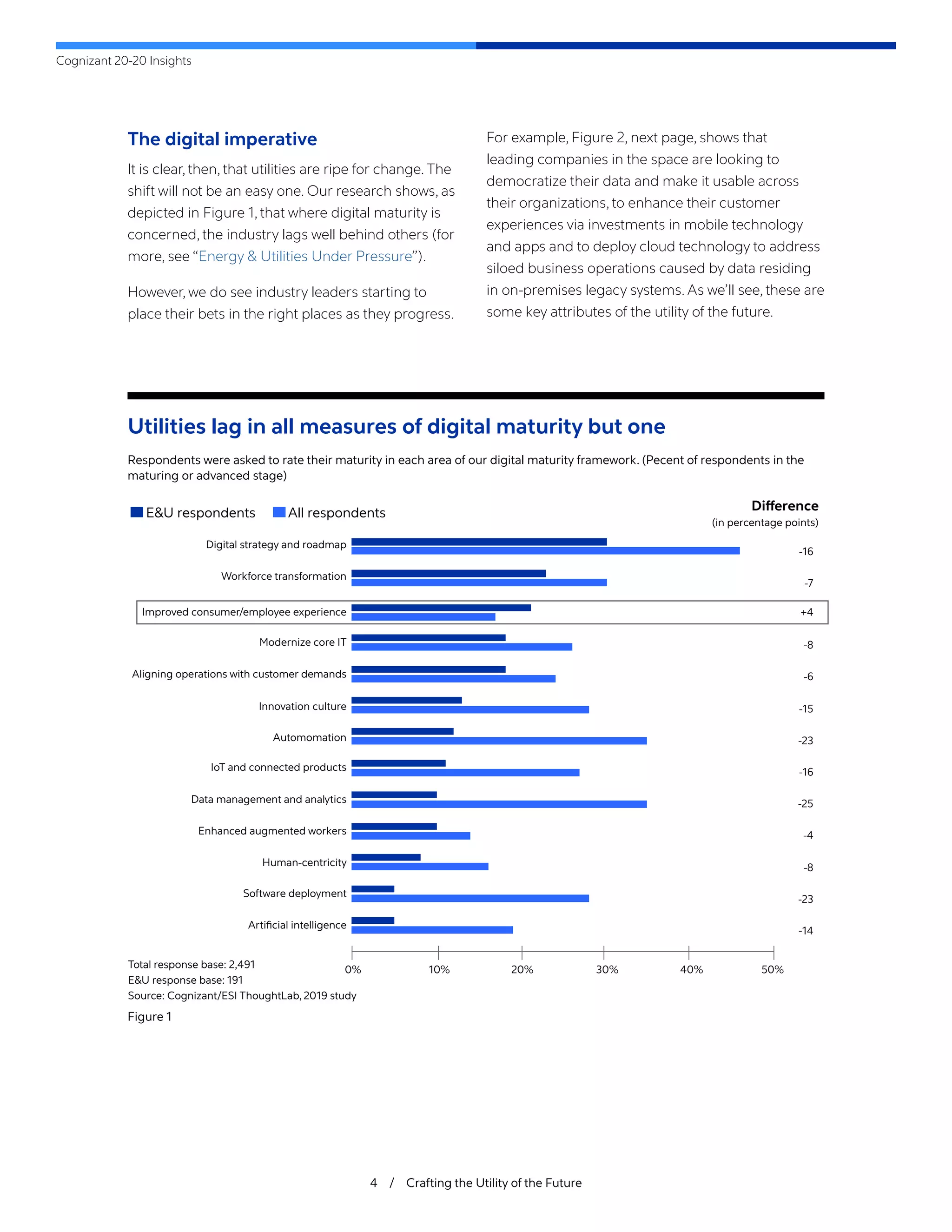
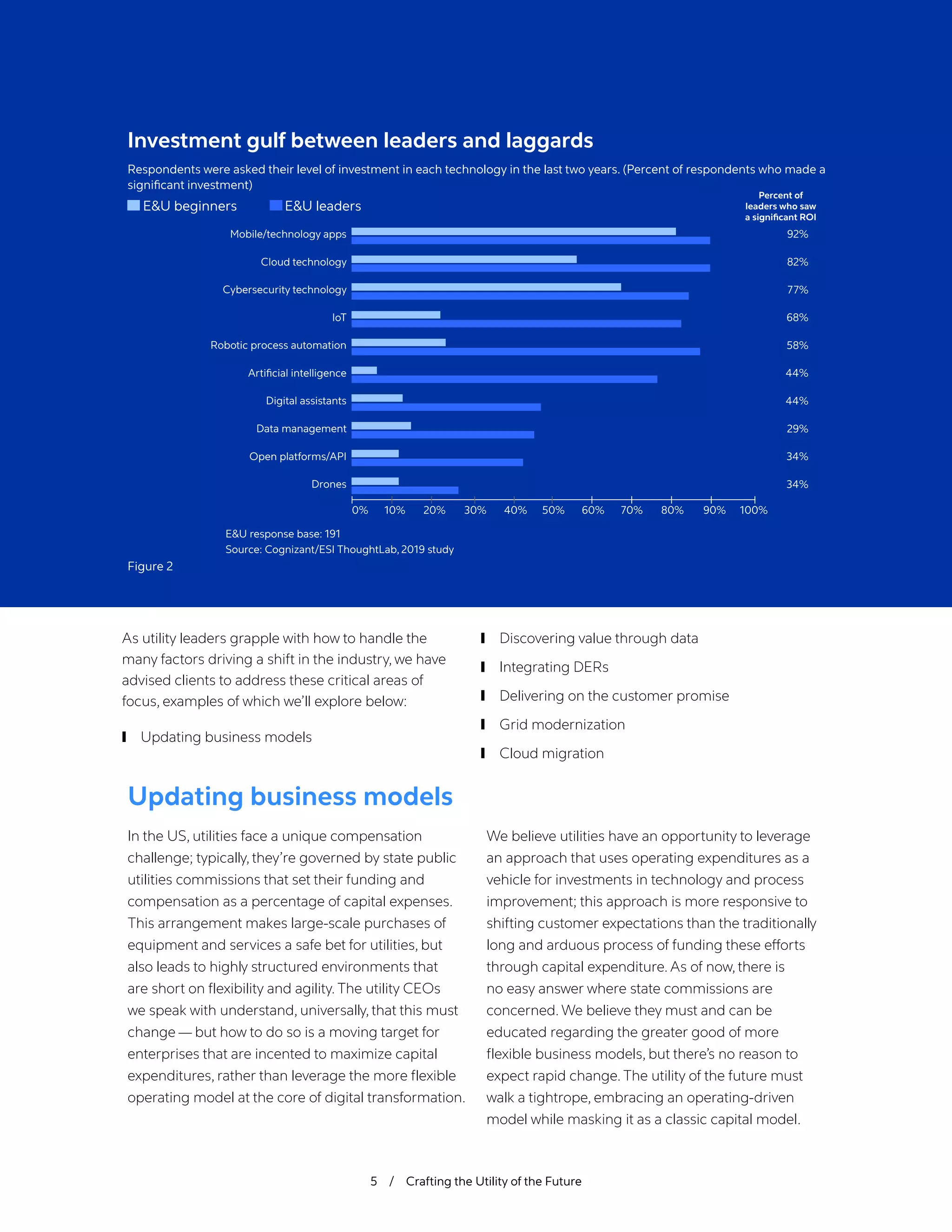
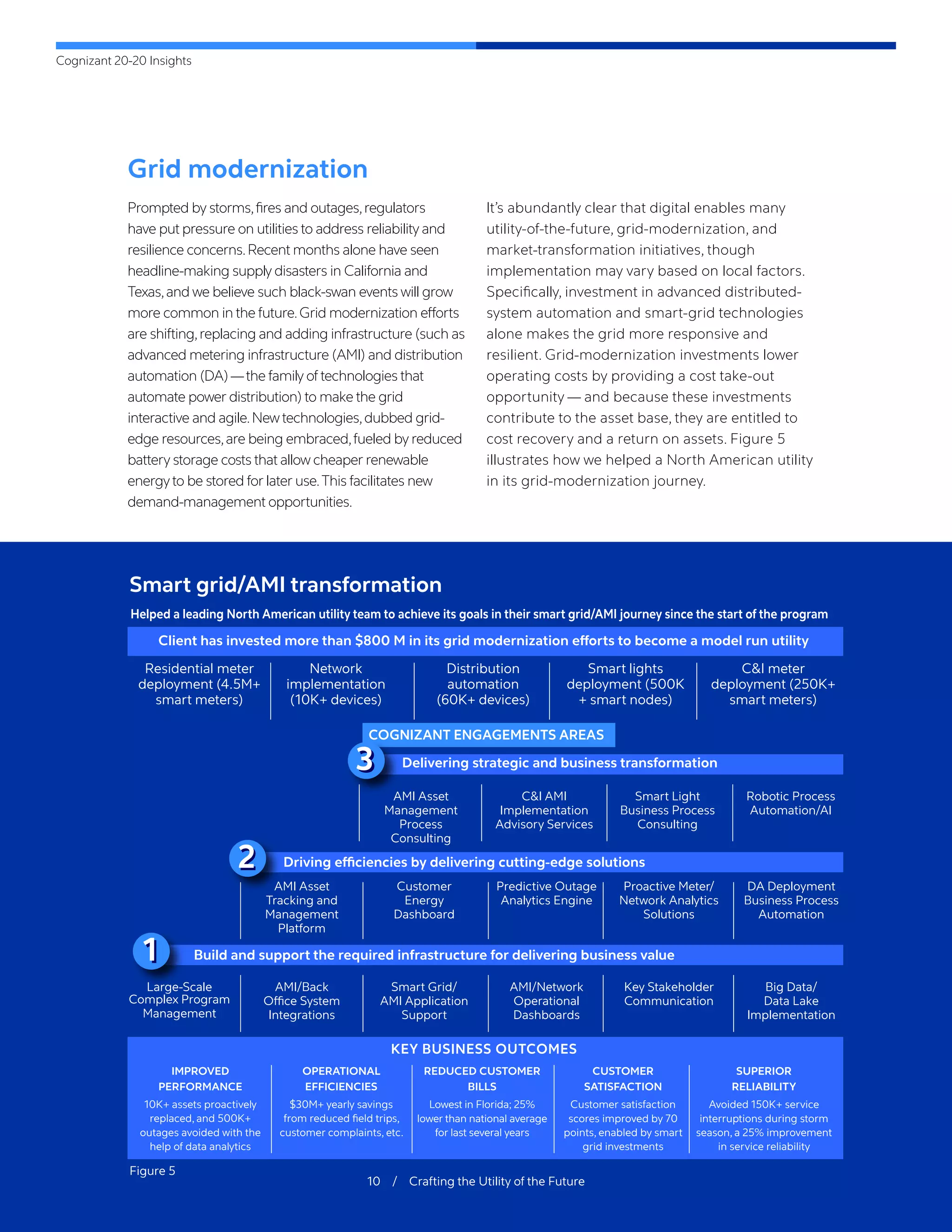
The document outlines the significant challenges facing the utility industry due to disruptions like decarbonization, decentralization, and digitization, which have been exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic. Utilities must adapt to changing consumer expectations and innovative technologies while dealing with operational difficulties, budget constraints, and a need for a more skilled workforce. It emphasizes the importance of modernizing business models, leveraging data, and enhancing customer engagement to secure a competitive future in an evolving energy marketplace.