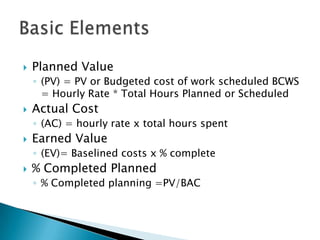
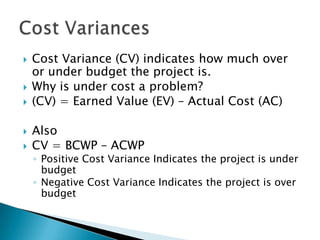
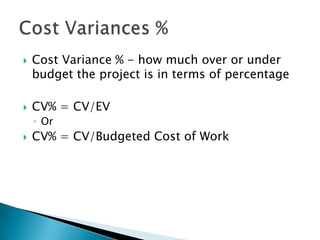
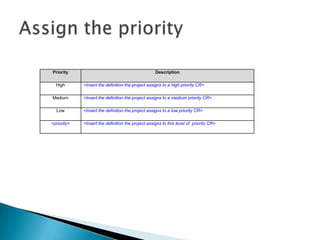
Here are two examples of change requests that could arise from the situations described:
1. MC Change Request
Title: Replace Volunteer MC with Professional
Description: The original volunteer MC is no longer available. This request is to hire a professional MC to ensure the event runs smoothly.
Impact: Additional $500 in budget for professional fees. May require schedule adjustment.
2. Access Change Request
Title: Ensure Event Complies with Access Policy
Description: Confirm event plans like venue access, signage, seating accommodate disabilities.
Impact: May require venue changes, additional signage or support. Access officer to review plans and confirm compliance.