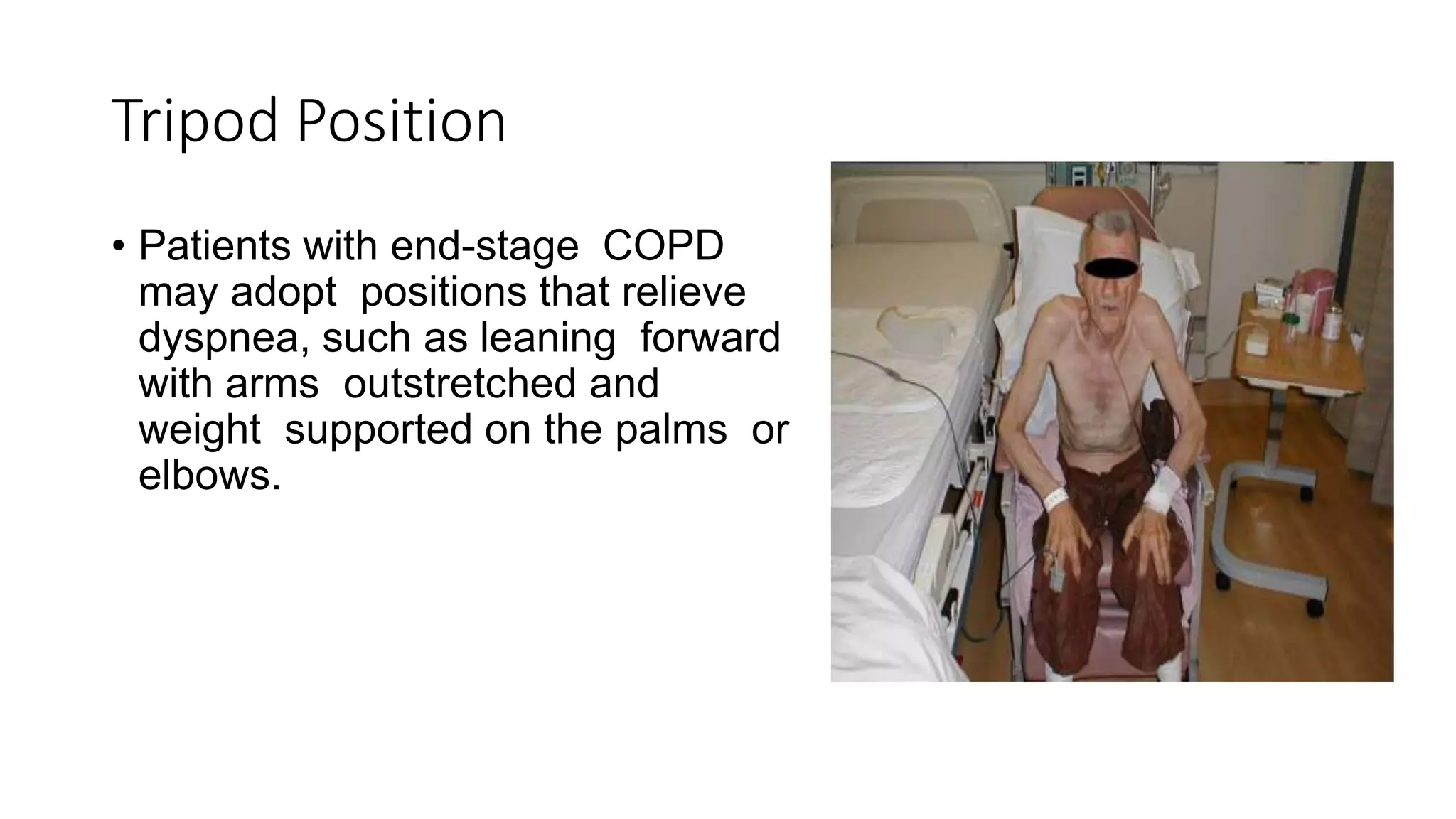
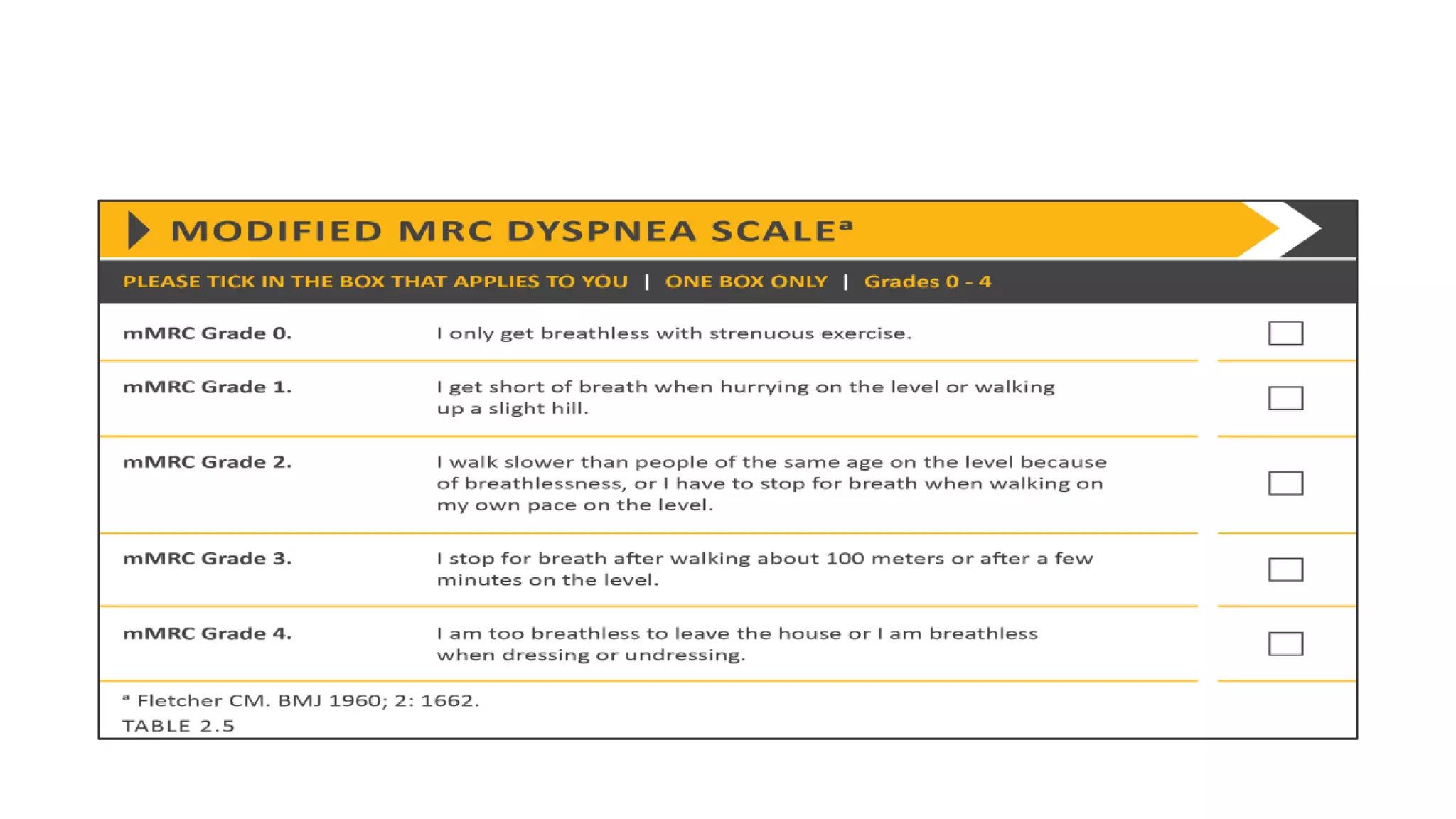
COPD is a common lung disease characterized by airflow limitation caused by exposure to noxious particles. It includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema. Globally, COPD affects over 300 million people and causes over 3 million deaths annually. The major risk factor is tobacco smoking. Symptoms include dyspnea, cough, and sputum production. Exacerbations are defined as worsening of symptoms and require treatments like bronchodilators, antibiotics, corticosteroids, and sometimes noninvasive ventilation. Management involves smoking cessation, vaccinations, pulmonary rehabilitation, and surgery in severe cases.