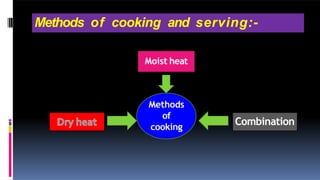
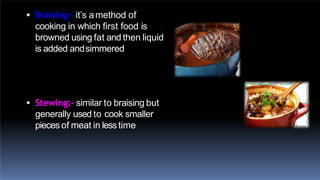
This document discusses cooking methods and food preservation techniques. It defines cooking as preparing food using heat and describes various heat transfer methods like conduction, convection, and radiation. It explains different moist and dry cooking techniques such as boiling, simmering, steaming, roasting, baking, and frying. It also covers combination methods like braising and stewing. The document emphasizes the importance of proper food handling and storage to prevent toxicity and nutrient loss. It outlines traditional food preservation methods including drying, cooling, salting, and smoking.