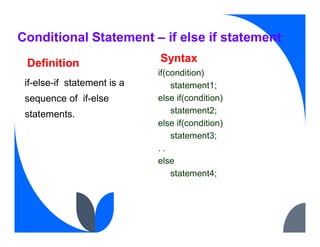
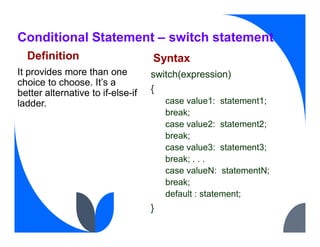
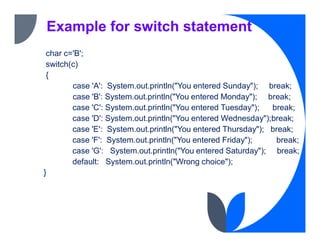
The document provides an overview of control flow statements in Java, which enable programmers to make decisions about the execution of code. It outlines four main categories: conditional statements, loops, exceptions, and branching, detailing various types of conditional statements such as 'if', 'if-else', 'nested if', 'if-else if', and 'switch' statements, along with their syntax and examples. This information is crucial for understanding how to manipulate the flow of a program based on different conditions during runtime.