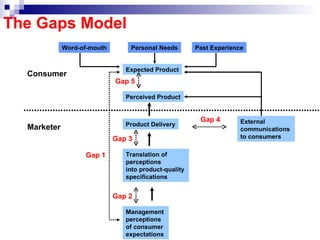
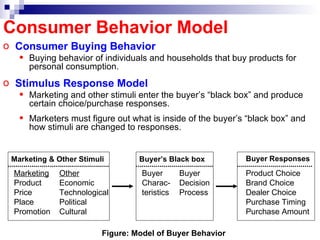
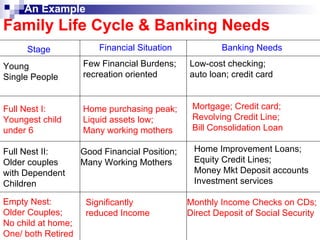
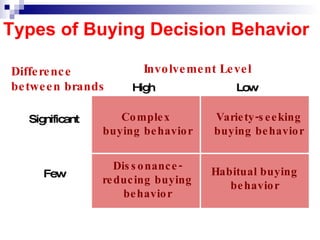
The document discusses consumer behavior and the buyer decision process. It outlines the gaps model of consumer expectations and marketer perceptions. It then describes the 5 stages of the buyer decision process - need recognition, information search, evaluation of alternatives, purchase decision, and post-purchase behavior. Finally, it discusses factors that influence consumer behavior such as cultural, social, personal and psychological characteristics.