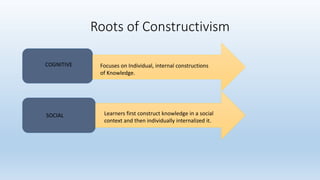
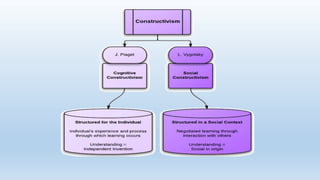
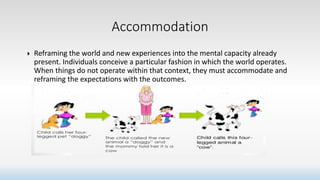
Constructivism is a theory of learning that claims individuals construct their own understanding and knowledge of the world through experiencing things and reflecting on those experiences. According to constructivism, learning is an active process where learners build new ideas upon existing knowledge. Learners are not blank slates but rather active creators of their own knowledge who assimilate new information through existing mental frameworks developed from prior experiences. Constructivism asserts that knowledge is constructed in social contexts through interactions, not acquired, and places importance on collaboration and social activities in the learning process.