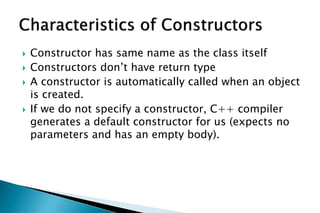
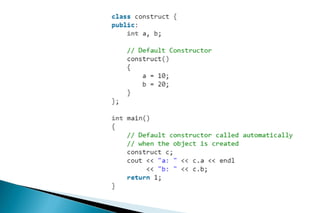
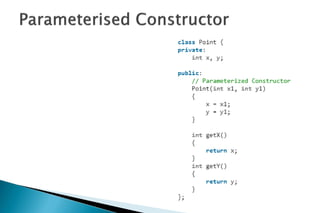
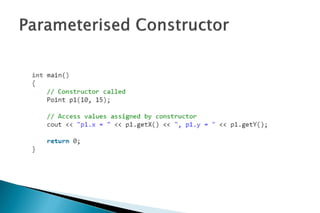
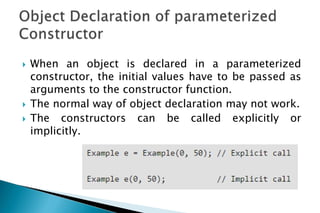
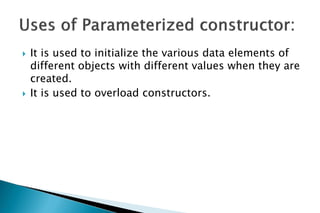
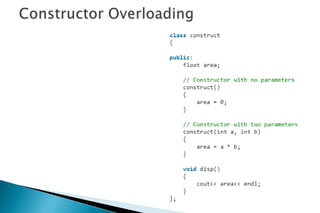
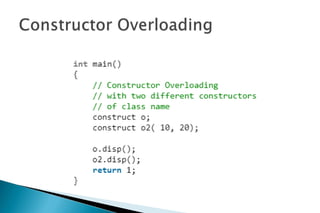
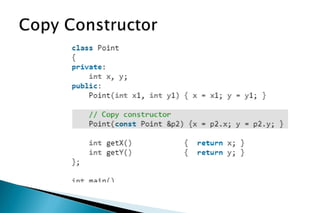
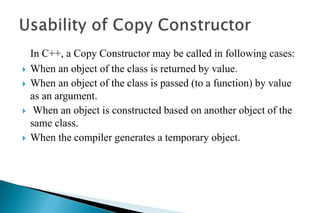
A constructor is a special member function that initializes objects of a class. Constructors are automatically called when an object is created. There are different types of constructors like the default constructor, parameterized constructor, copy constructor, and dynamic constructor. A destructor is used to destroy objects and is called automatically when an object goes out of scope.