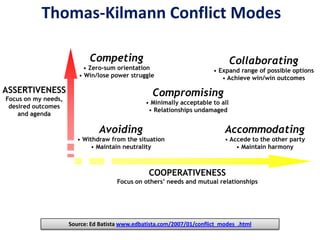
This document discusses conflict resolution basics and provides strategies for managing conflict effectively. It outlines five modes of conflict - avoiding, accommodating, competing, collaborating, and compromising. The most effective strategies include active listening, apologizing, compromising, humor, negotiating, and postponing, while the poor strategies are violence, running away, and whining. Throughout any culture, people communicate to be listened to and understood, and they respond to respect and disrespect. The key is to listen, be flexible, and be willing to change.