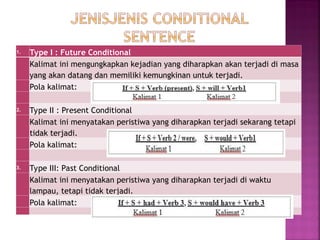
Dokumen ini menjelaskan tentang kalimat pengandaian (conditional sentence) yang terdiri dari dua klausa yaitu main clause dan if clause, serta berbagai jenisnya: type I, II, dan III. Setiap jenis conditional menyatakan keadaan yang berbeda, seperti masa depan, saat ini, dan masa lalu, dengan pola tertentu untuk mengekspresikan kondisi yang mungkin terjadi. Contoh juga diberikan untuk membantu pemahaman tentang penerapan kalimat pengandaian.