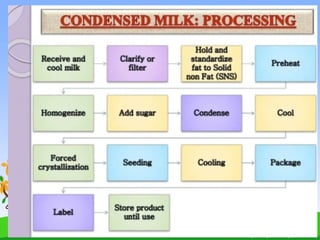
Condensed milk was invented in the 1850s by Gail Borden as a way to preserve milk for long periods. It involves evaporating water from milk to increase its concentration and shelf life. Sugar is often added to further preserve it. The processing involves standardizing, heating, condensing the milk in a vacuum, homogenizing, cooling and crystallizing it before packaging. Condensed milk can last up to a year unopened but only 2-3 weeks once opened. It is commonly used in desserts, drinks, ice cream and confectionaries due to its thickness and sweetness.