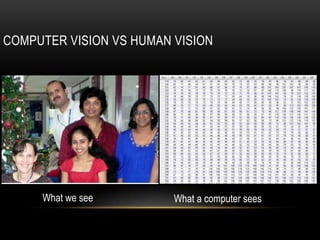
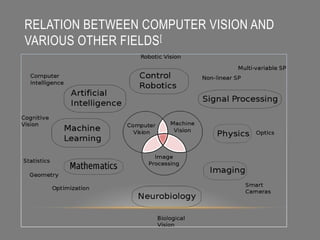
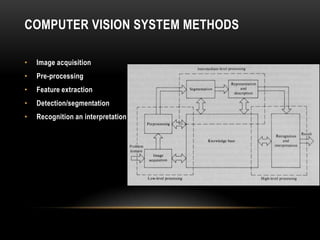
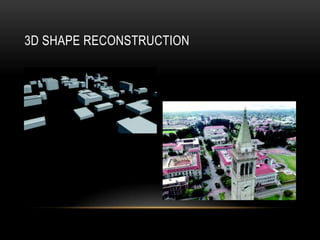
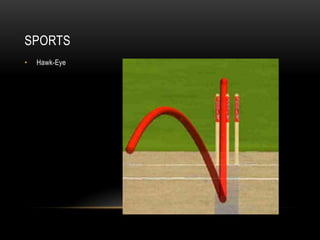
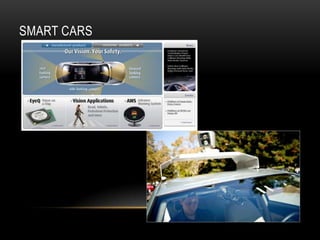
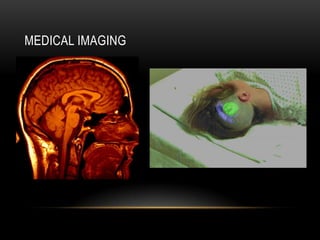
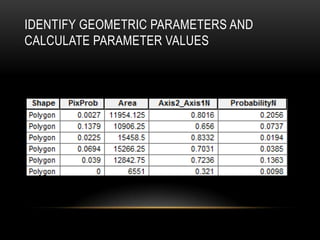
Computer vision is a field that uses techniques to electronically perceive and understand images. It involves acquiring, processing, analyzing and understanding images and can take forms like video sequences. Computer vision aims to duplicate human vision abilities through artificial systems. It has applications in areas like manufacturing inspection, medical imaging, robotics, traffic monitoring and more. Some techniques used in computer vision include image acquisition, preprocessing, feature extraction, detection, recognition and interpretation.