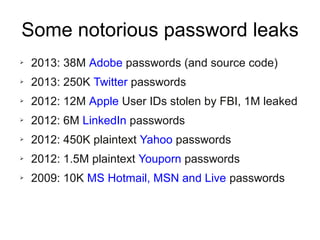
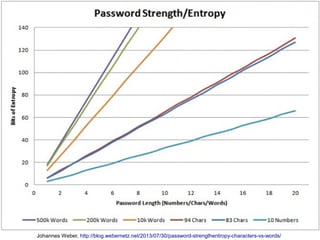
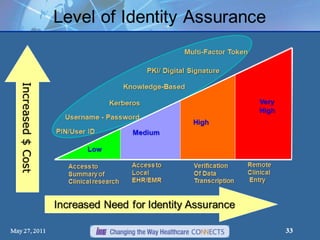
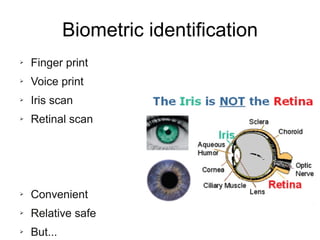
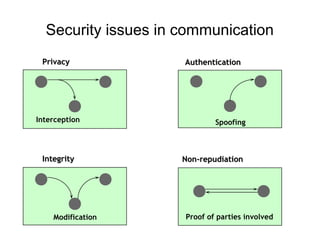
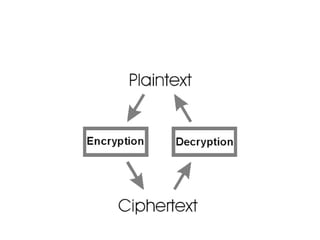
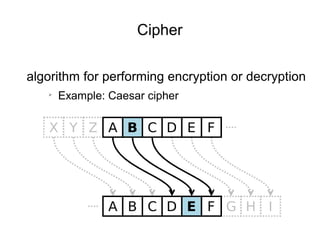
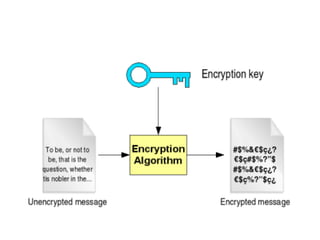
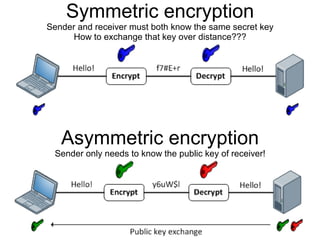
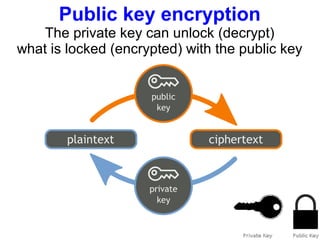
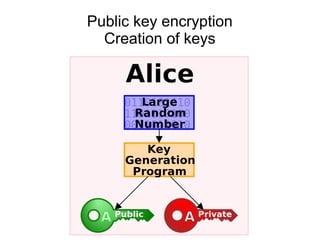
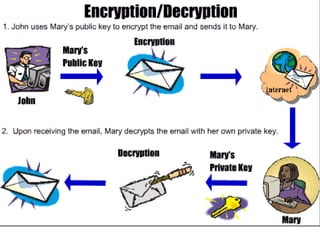
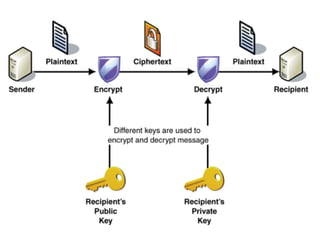
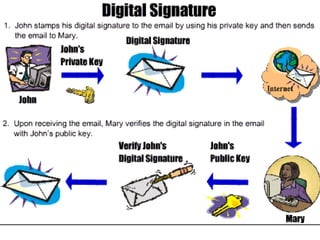
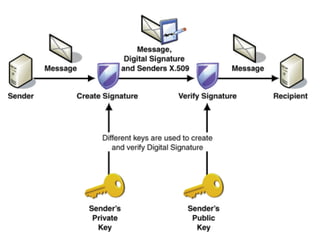
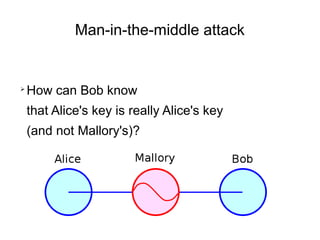
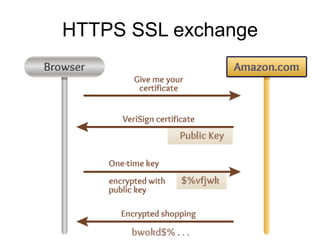
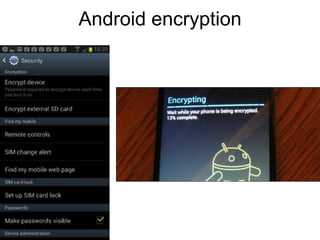
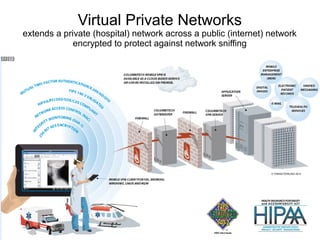
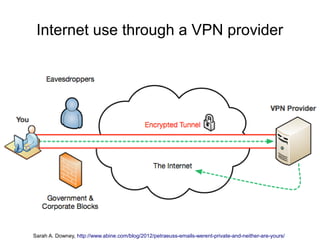
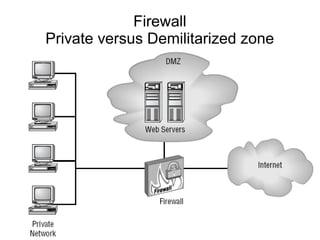
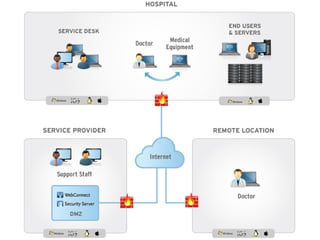
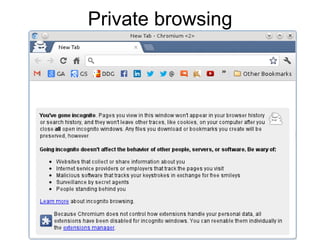
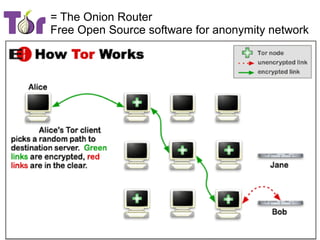
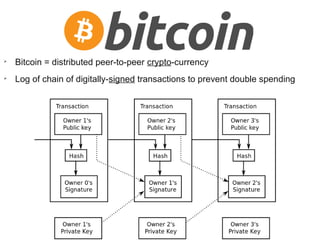
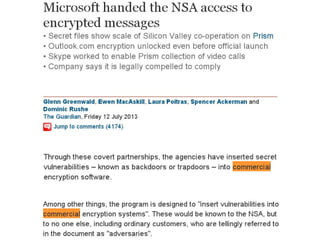
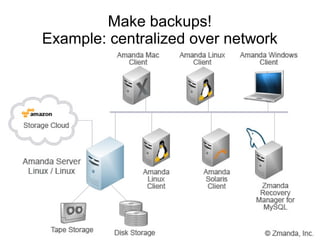
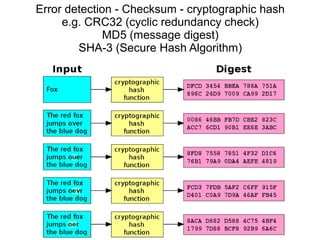
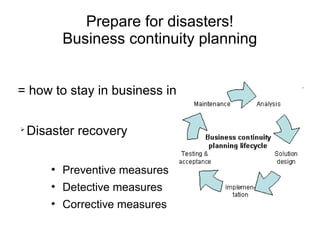
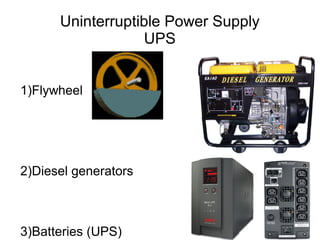
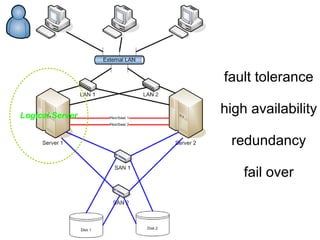
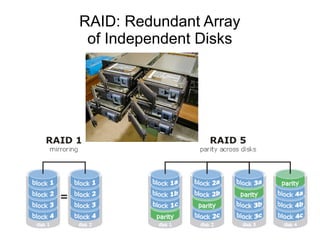
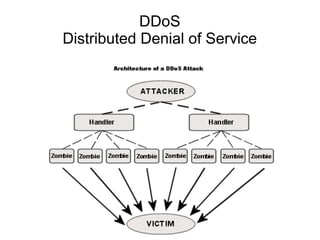
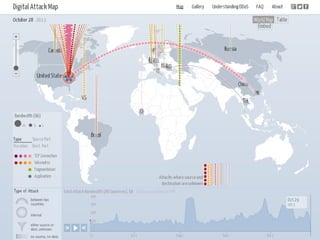
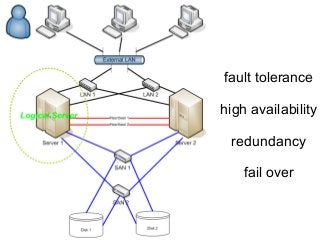
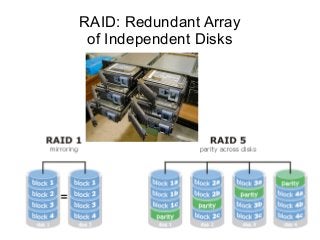
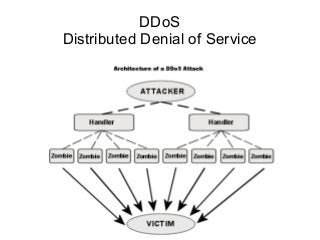
The document presents a workshop on computer security, outlining key objectives such as confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data. It discusses various risks that may compromise computer security including human errors, malware, and environmental issues, along with strategies to mitigate these risks. Tools for maintaining security, including encryption, firewalls, and backup systems, are emphasized, alongside the importance of open-source software for reliable security measures.