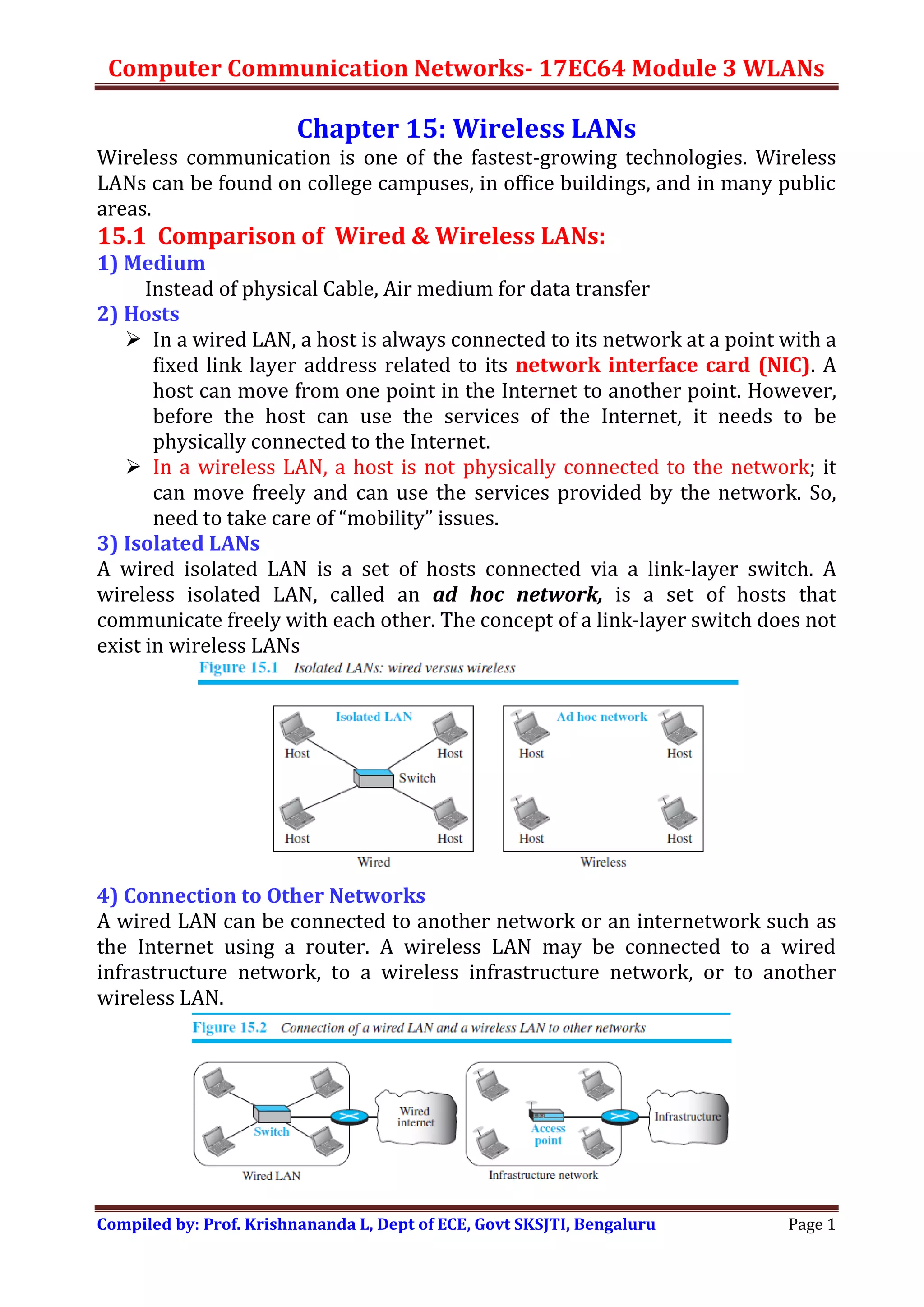
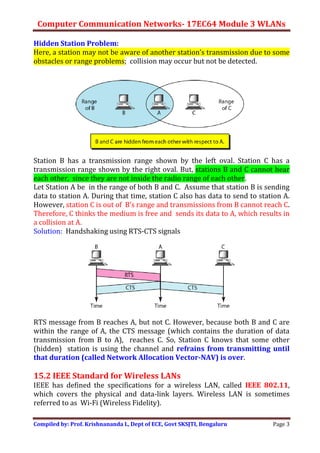
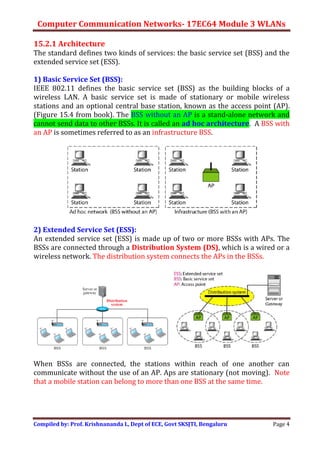
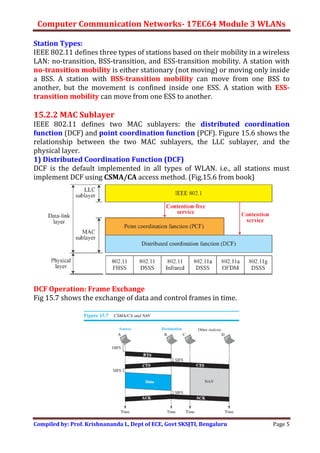
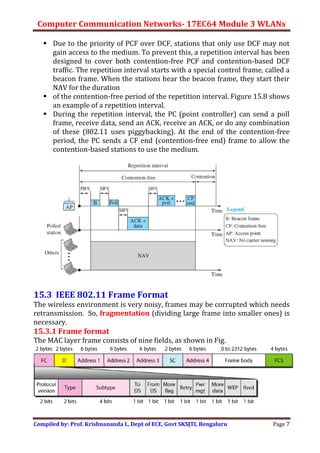
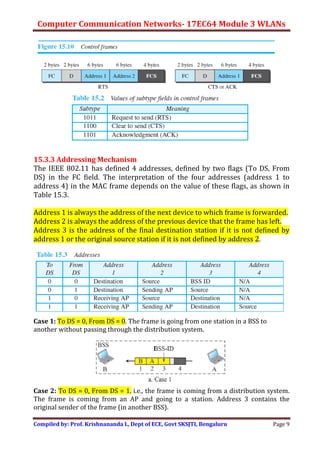
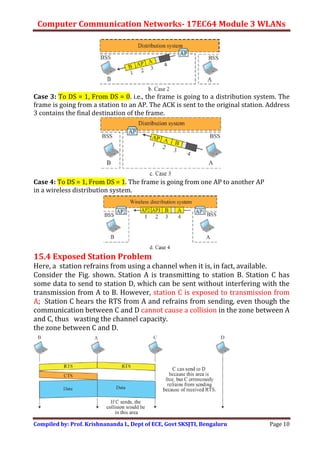
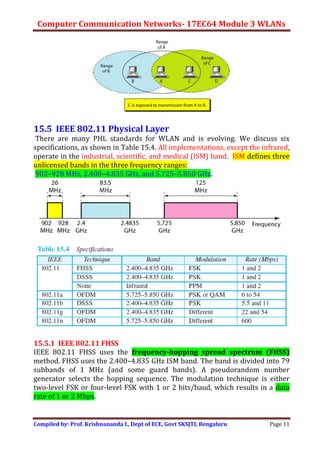
Wireless LANs allow hosts to connect to a network without being physically connected via cables. They use radio waves to transmit data through the air. Some key differences between wired and wireless LANs include the mobility of hosts in wireless LANs and the use of access points to connect wireless LANs to wired networks. Wireless LANs also face challenges from signal attenuation, interference, and multipath propagation that wired LANs do not. The IEEE 802.11 standard defines the specifications for wireless LANs, including using basic service sets and extended service sets to connect multiple wireless networks, and employing carrier sense multiple access with collision avoidance for medium access control.