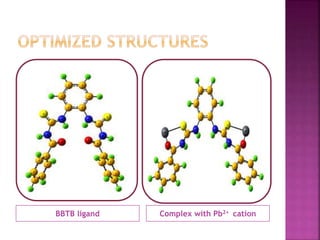
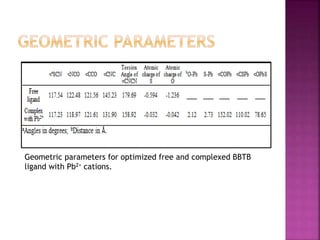
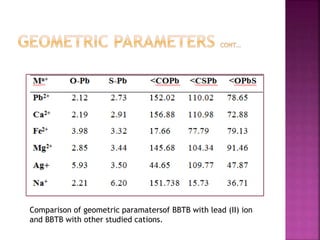
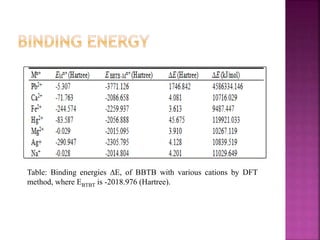
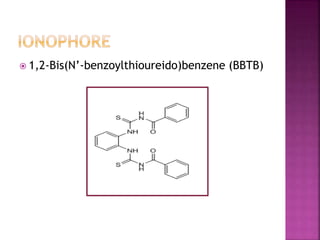
This document discusses the use of 1,2-Bis(N’-benzoylthioureido)benzene (BBTB) as an ionophore for detecting lead cations. Experimental studies using UV-Vis spectrophotometry showed that BBTB forms a 2:1 complex with lead, indicated by a breakpoint in the absorbance versus concentration plot. Theoretical DFT studies calculated binding energies and optimized structures, confirming complex formation between BBTB and lead cations. Overall, BBTB was found to selectively bind lead cations, demonstrating its potential as a selective ionophore sensor for lead quantification.





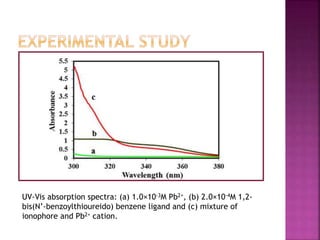
![UV-Vis absorption spectra of BBTB ligand (2.3×10-6 M) in 1:1 MeOH:AN
mixture in the presence of increasing concentration of lead(II) and
absorbance versus the [Pb2+]/[BBTB] molar ratio plots.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/complexationstudy-150122082113-conversion-gate02/85/Complexation-study-11-320.jpg)
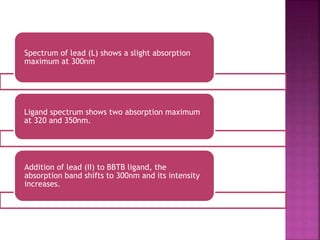
![The linear plot of absorbance versus the
molar ratio of [Pb2+]/[ BBTB] shows a
breaking point at 0.5
Formation of 2:1 [Pb: BBTB] complex.
BBTB + 2 Pb2+ BBTB(Pb)2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/complexationstudy-150122082113-conversion-gate02/85/Complexation-study-12-320.jpg)