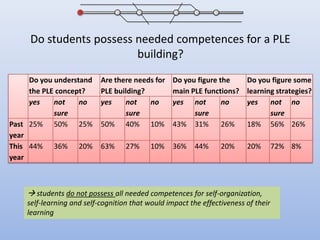
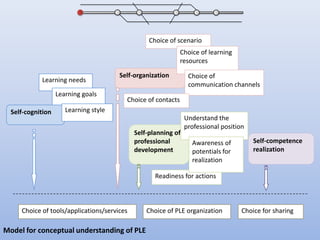
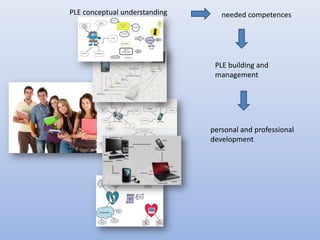
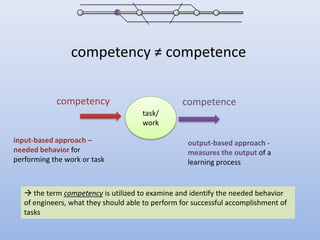
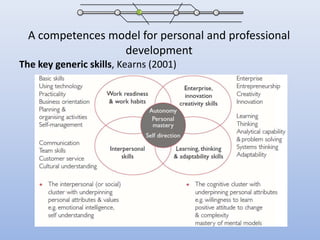
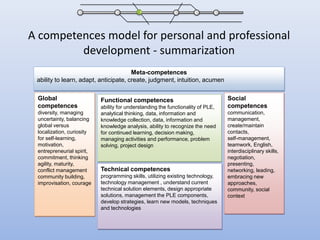
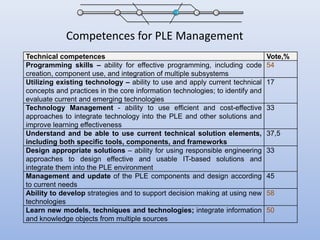
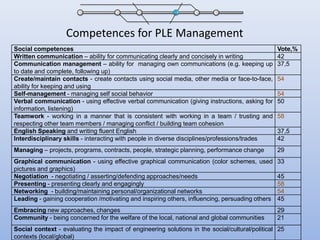
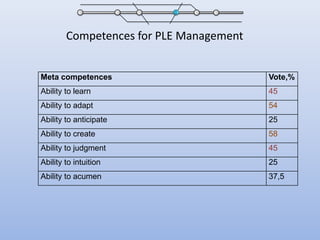
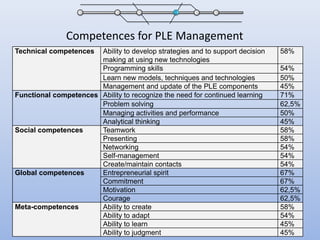
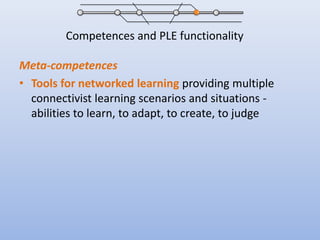
The document discusses competencies needed for personal learning environment (PLE) management and proposes a competencies model. It defines various competencies like technical, social, functional, and meta-competencies. It examines how PLE functionality can help develop these competencies, such as using tools to stimulate analytical thinking, manage activities, recognize the need for continuous learning, and develop programming skills. The document concludes that mapping competencies for PLE organization can support self-directed learning and identifies challenges in relating competencies to PLE functionalities.