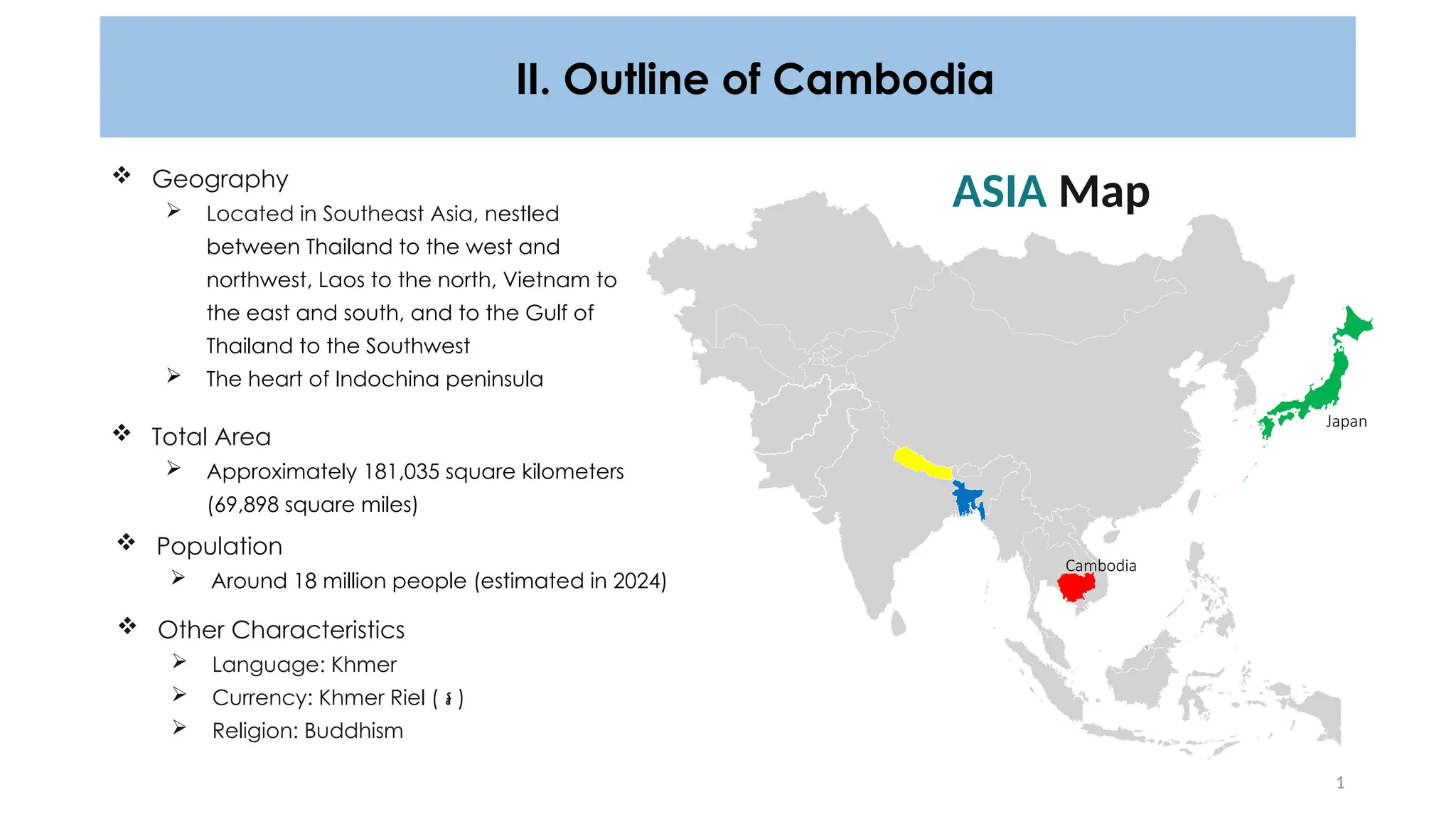
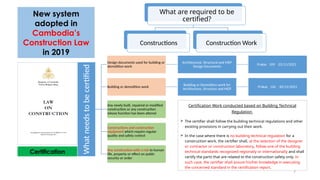
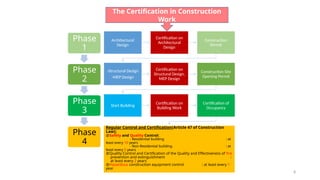
Cambodia is located in Southeast Asia, bordered by Thailand, Laos, and Vietnam, with a population of approximately 18 million and notable cities like Phnom Penh and Siem Reap. The document discusses risks associated with construction, including potential disasters like fires and building collapses, emphasizing the need for certified design documents and compliance with new construction laws. Challenges in the construction sector are highlighted, including lack of permits, inspections, and adherence to technical regulations.