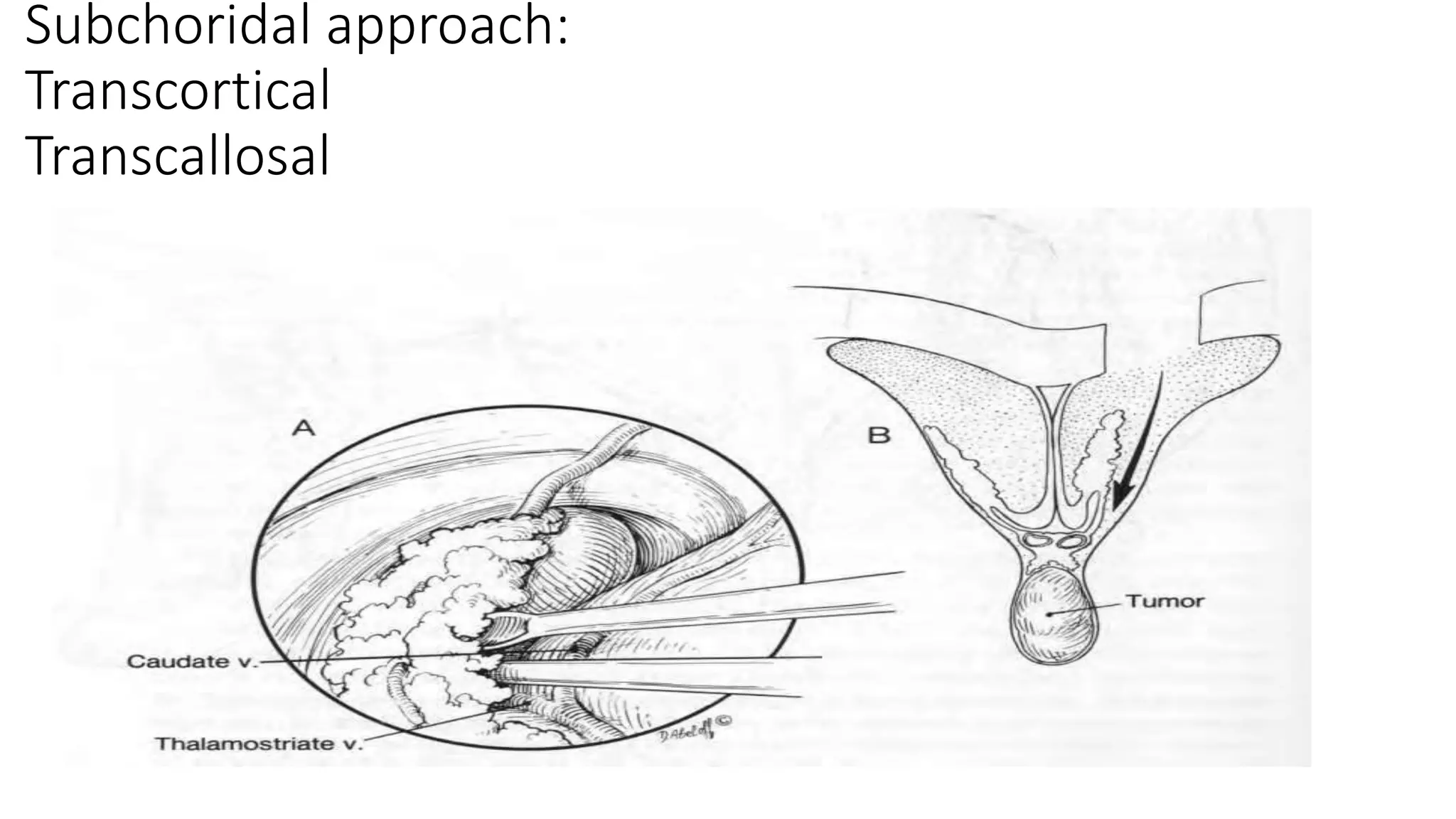
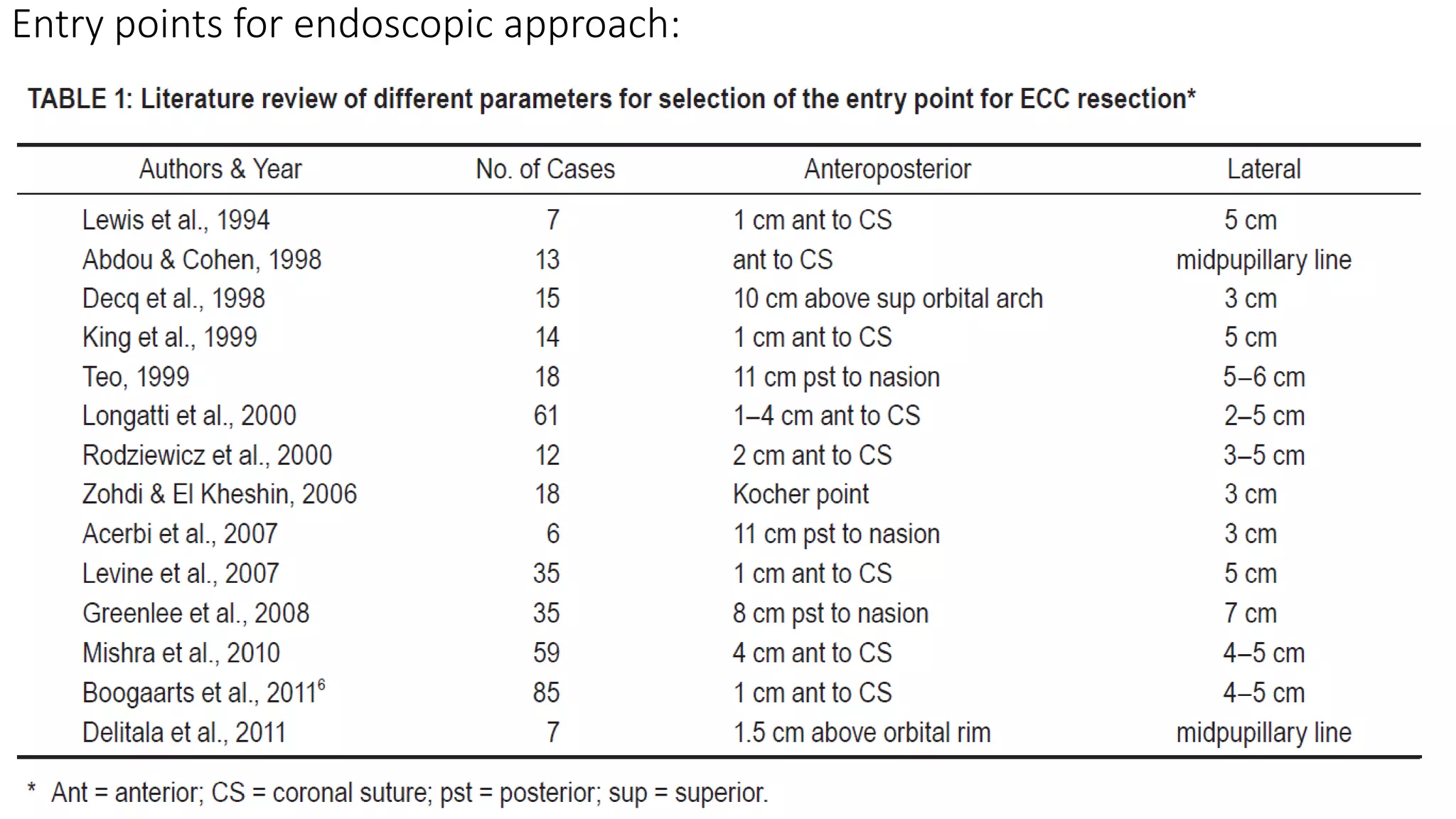
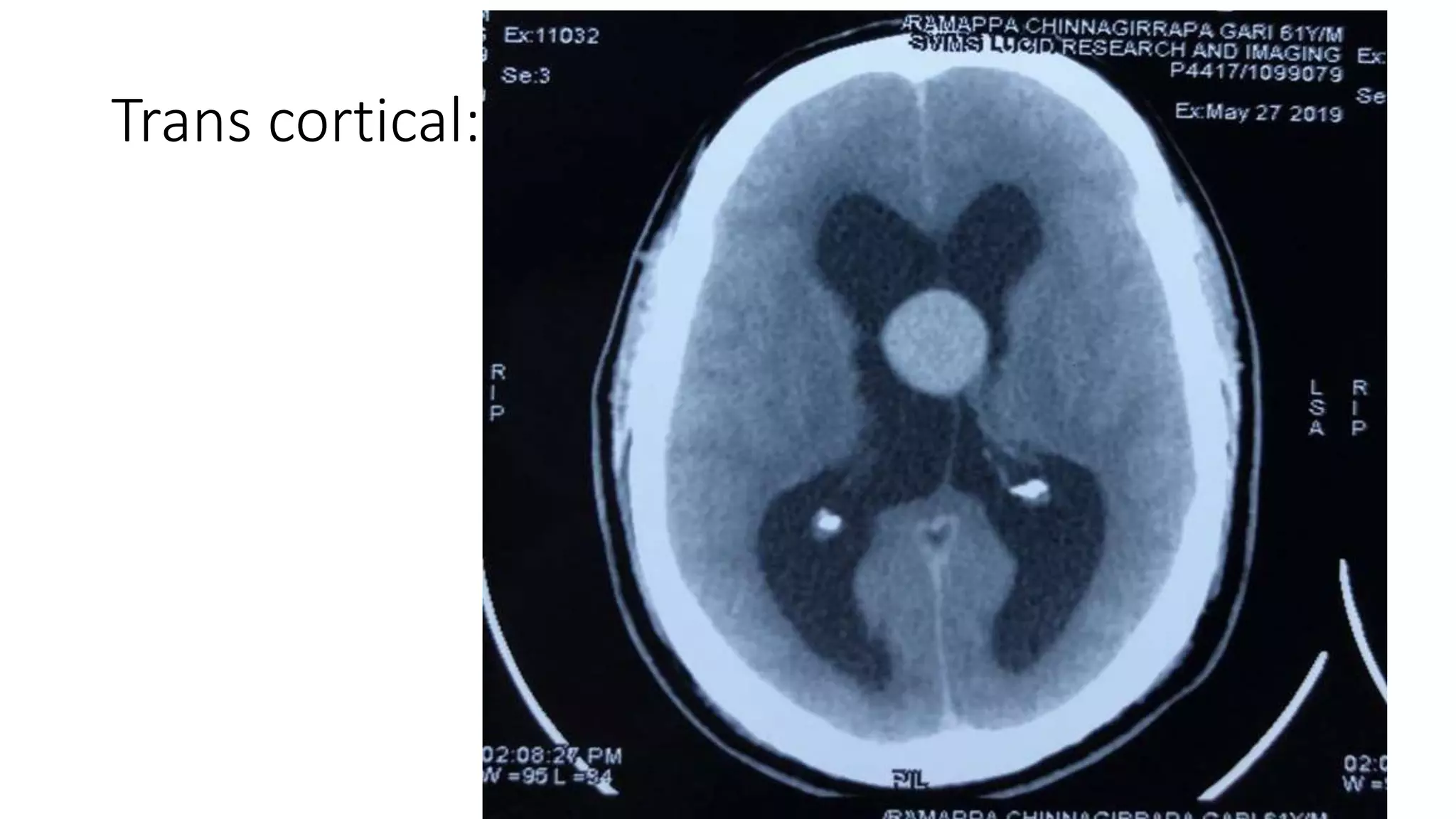
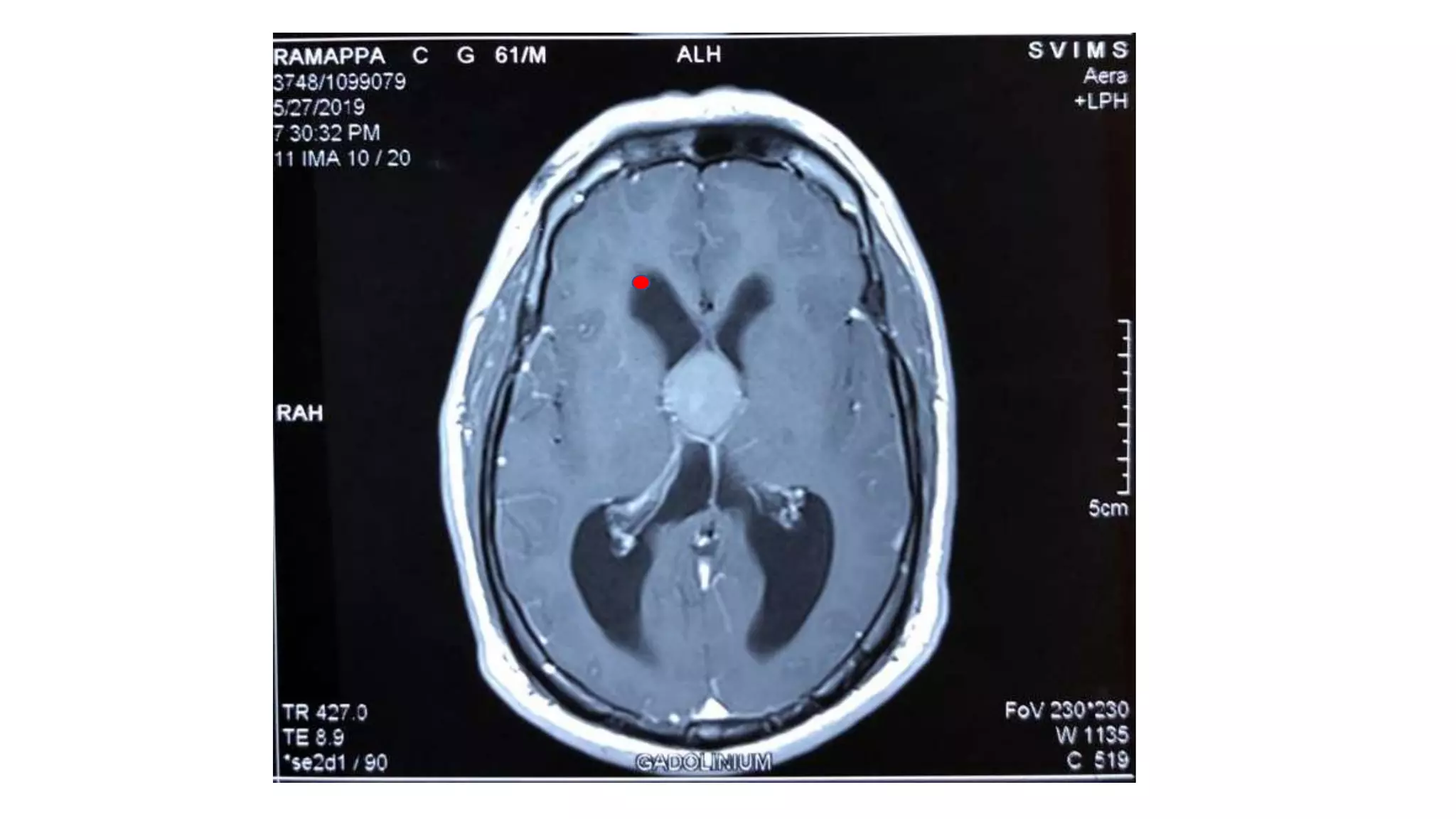
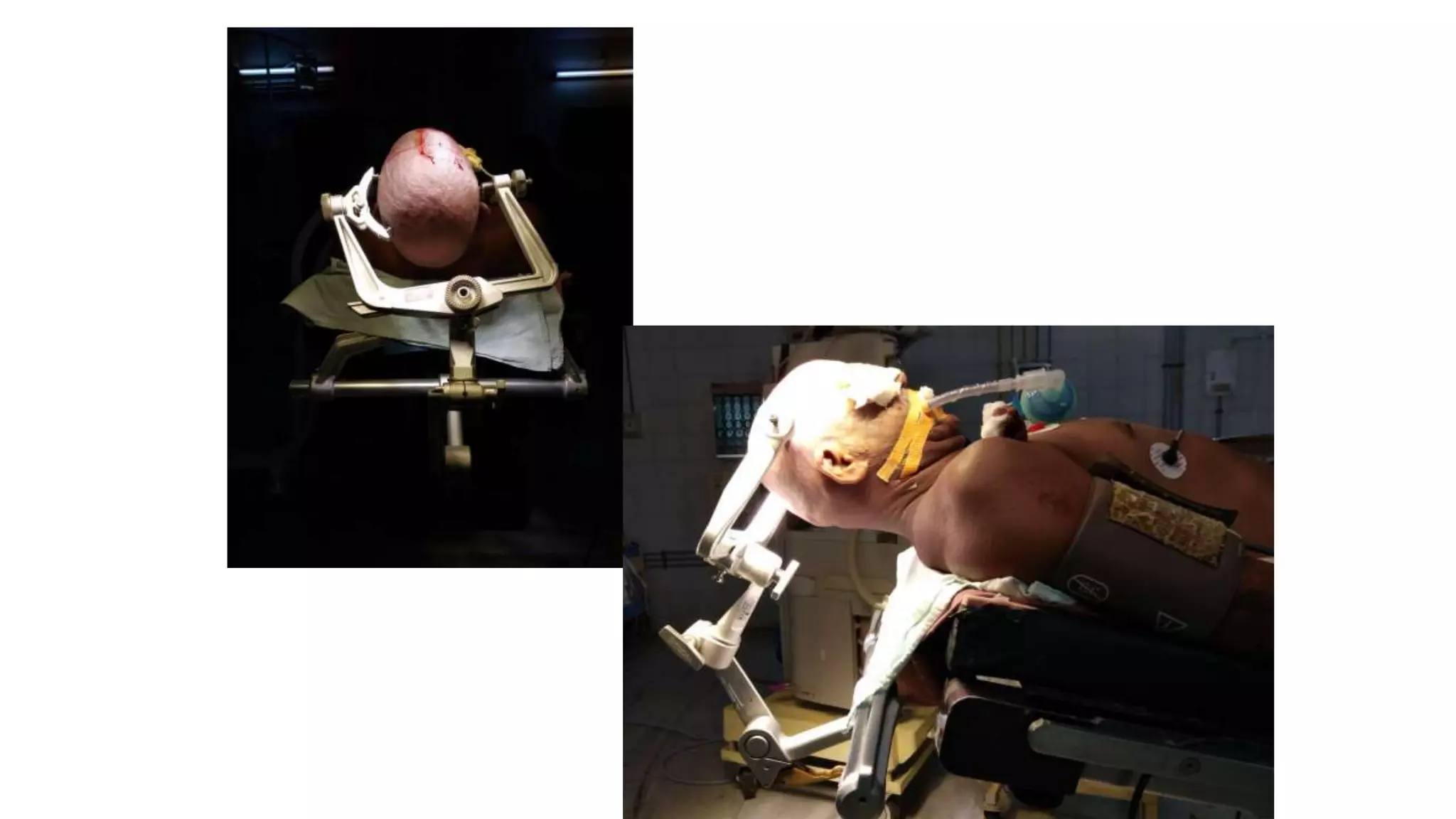
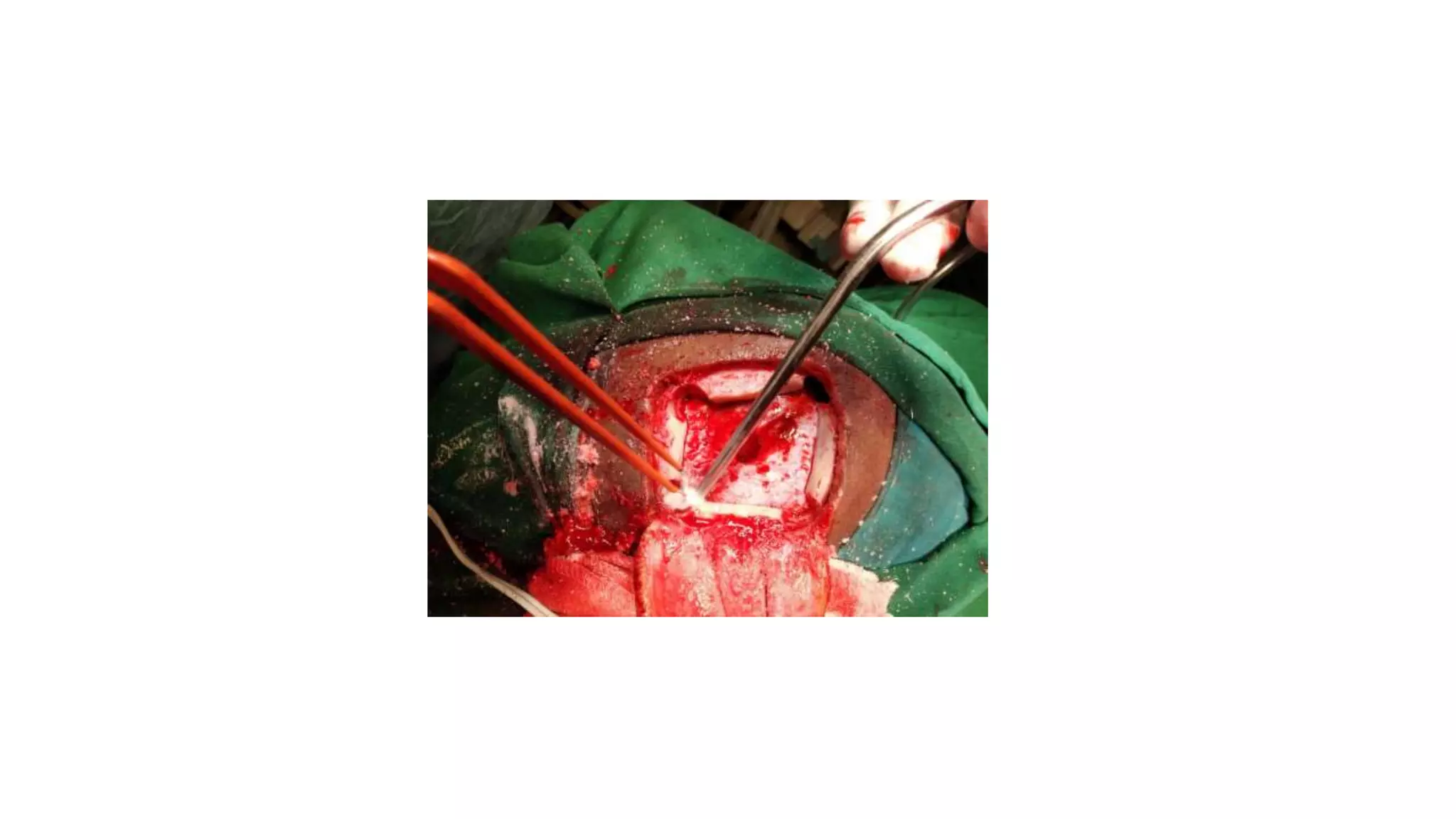
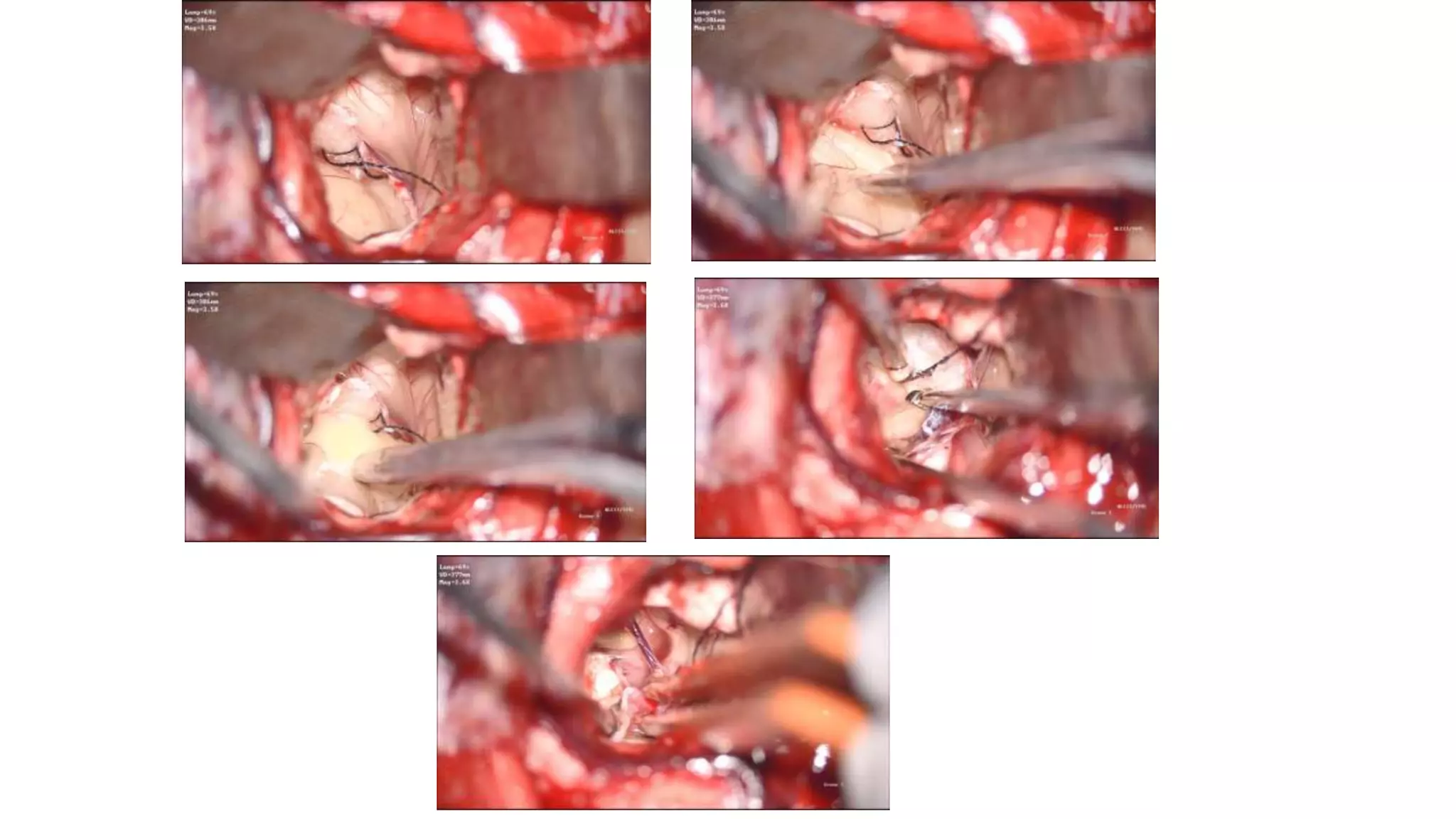
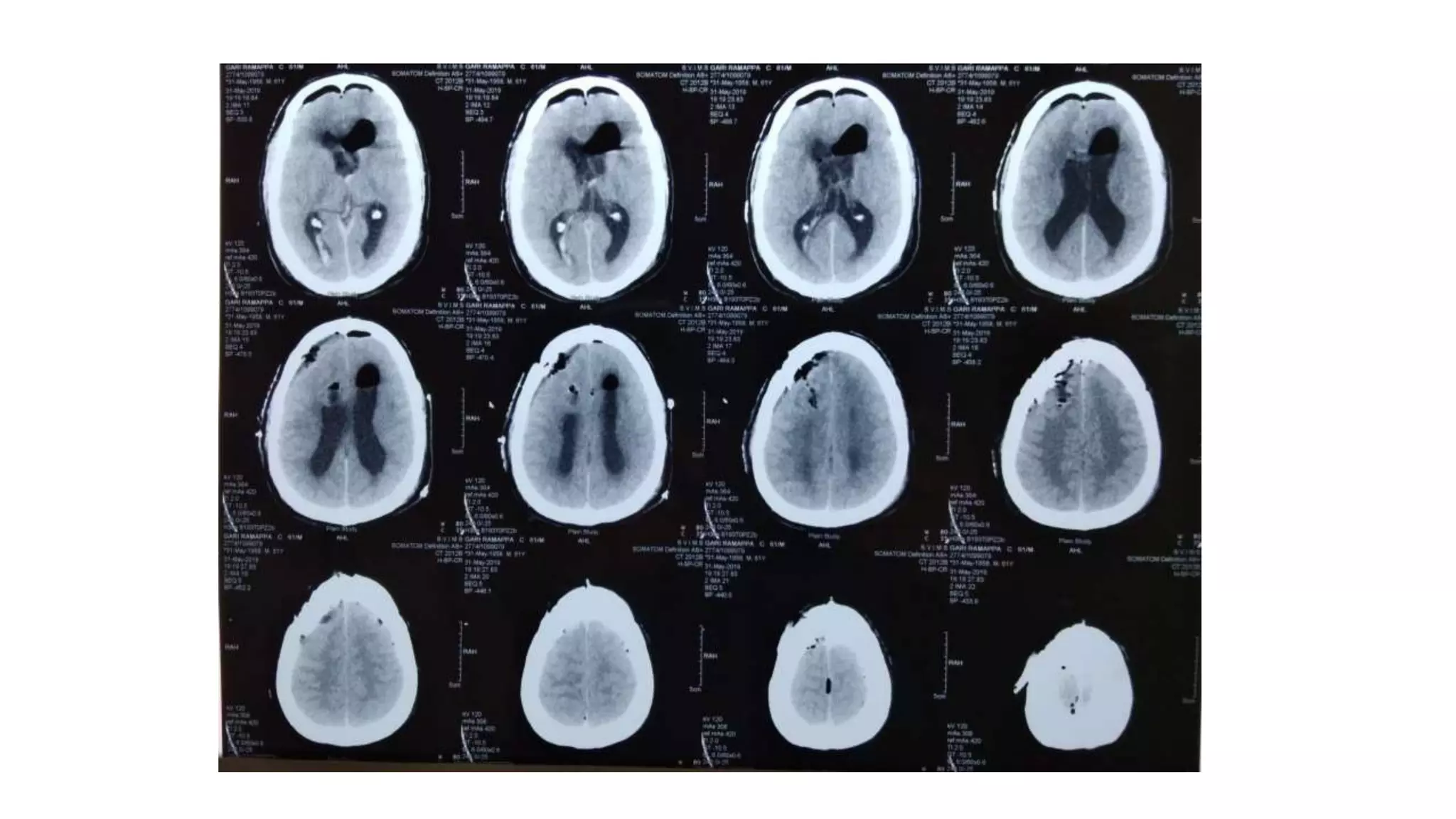
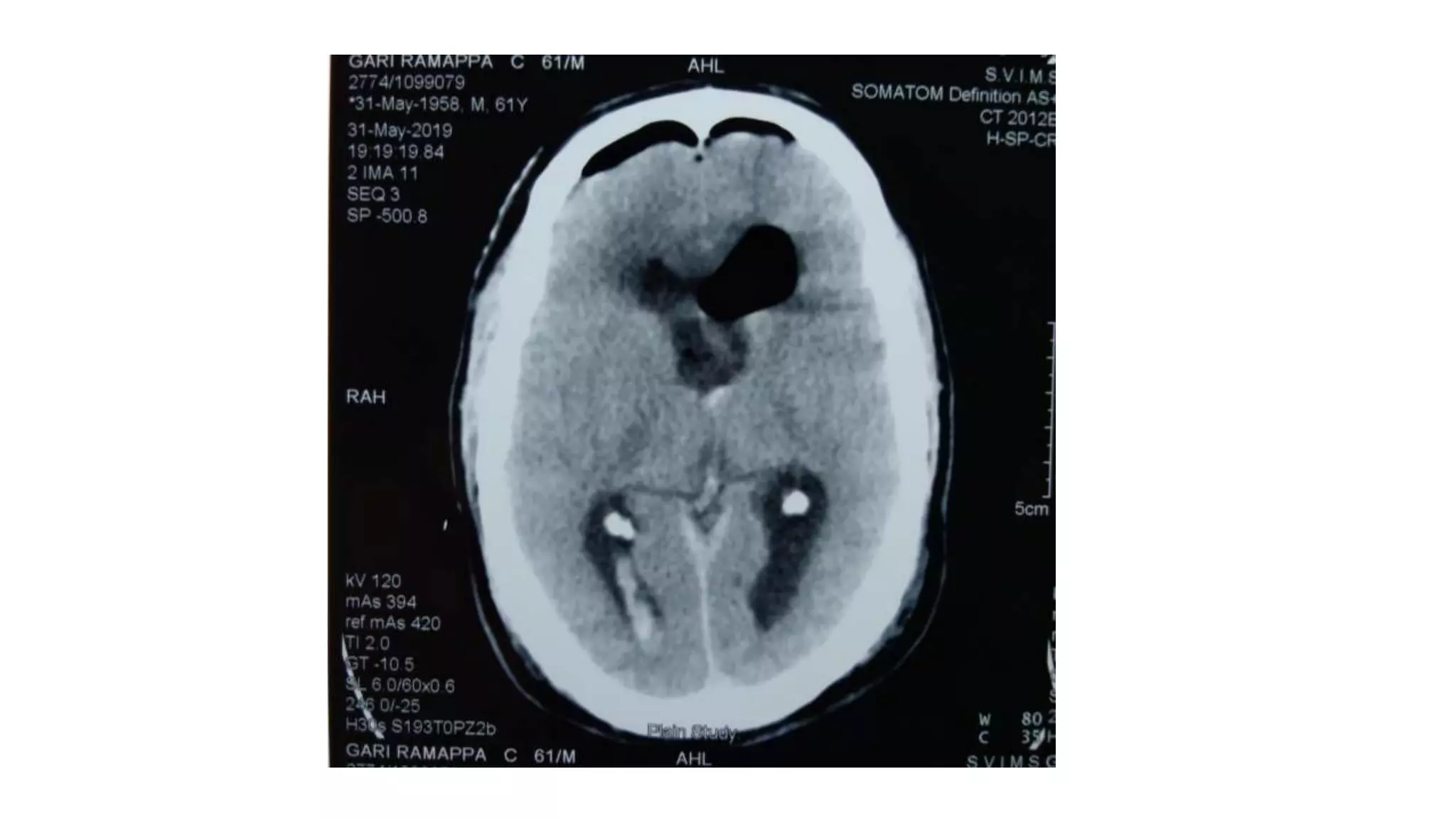
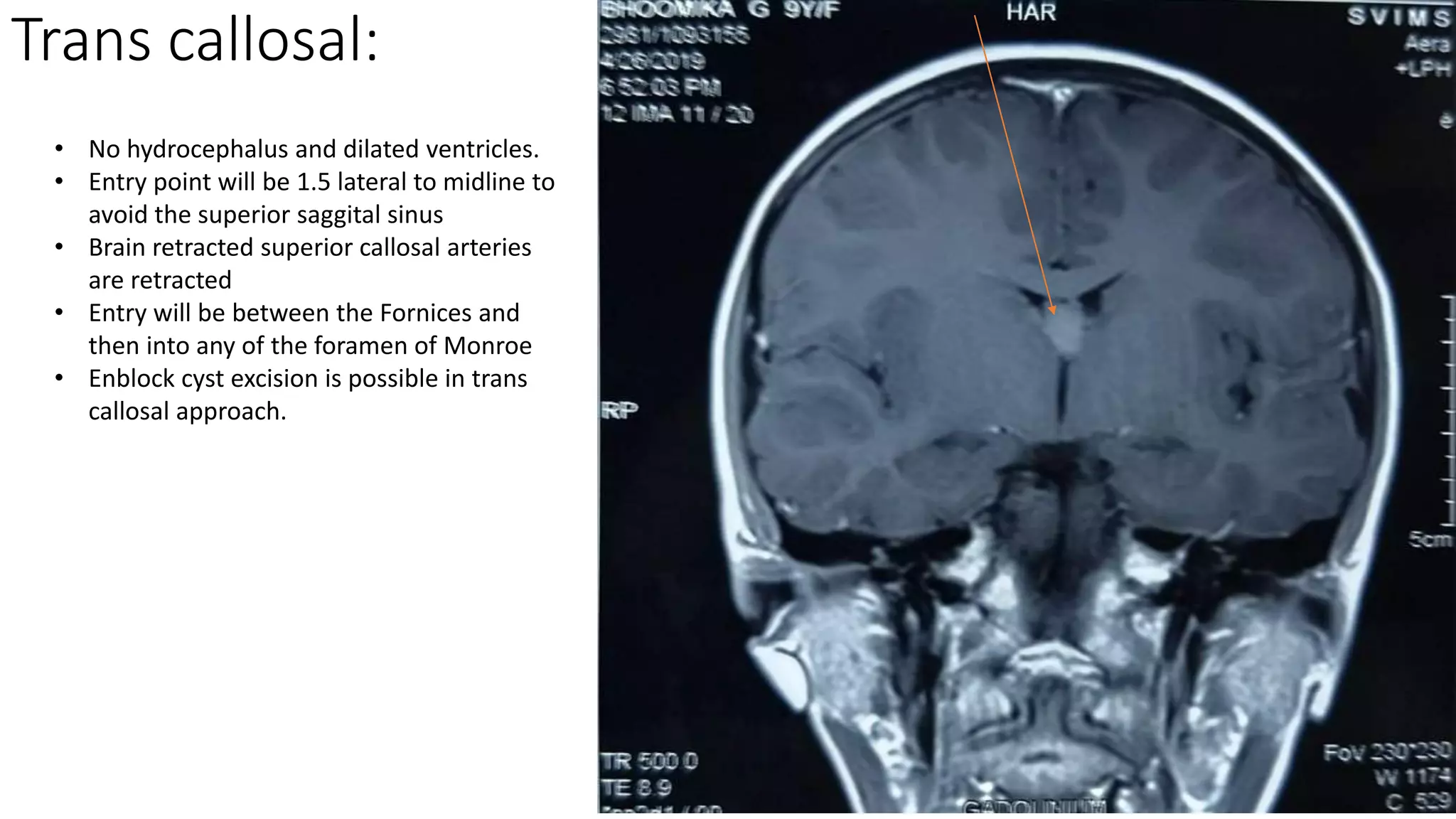
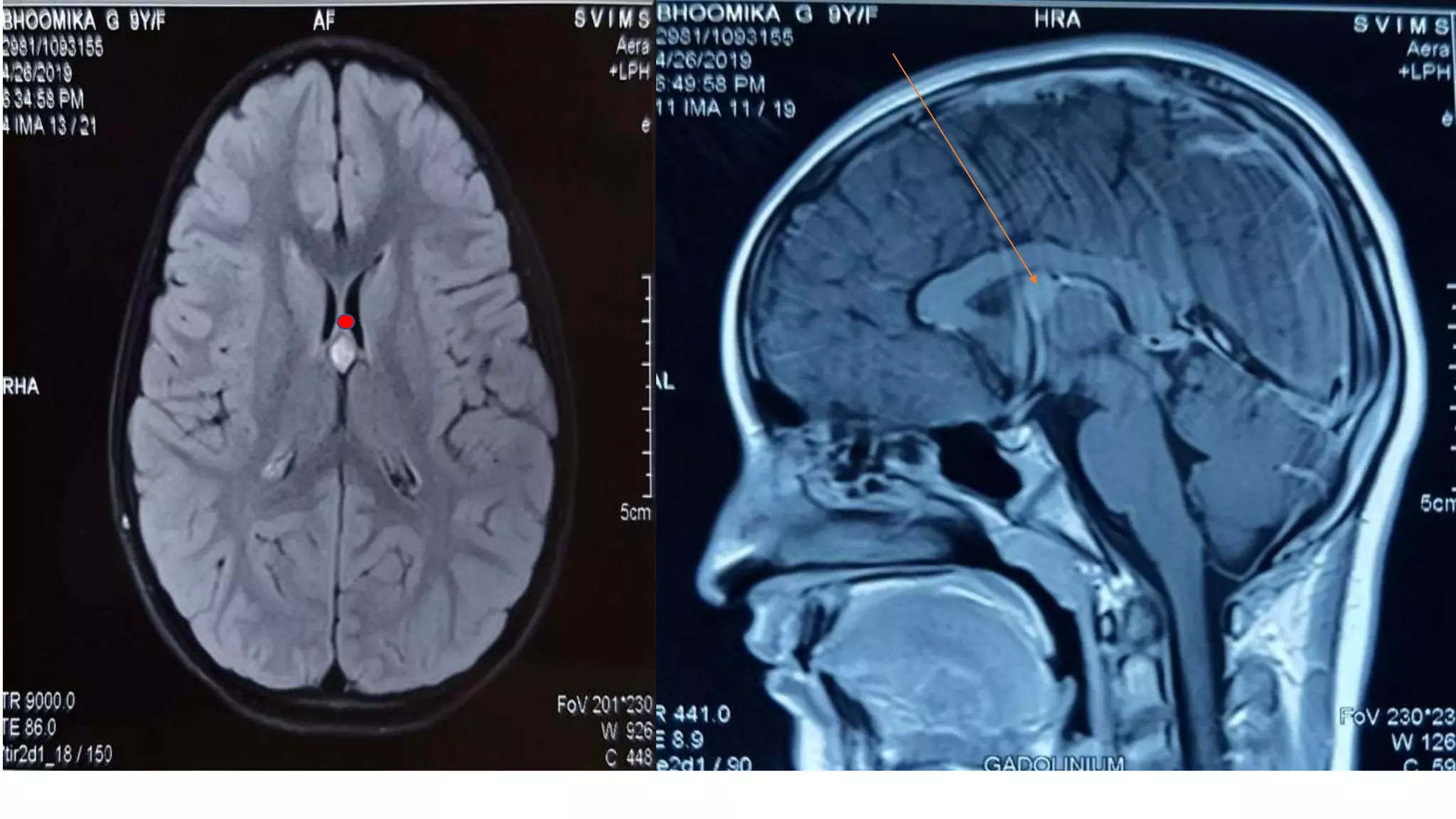
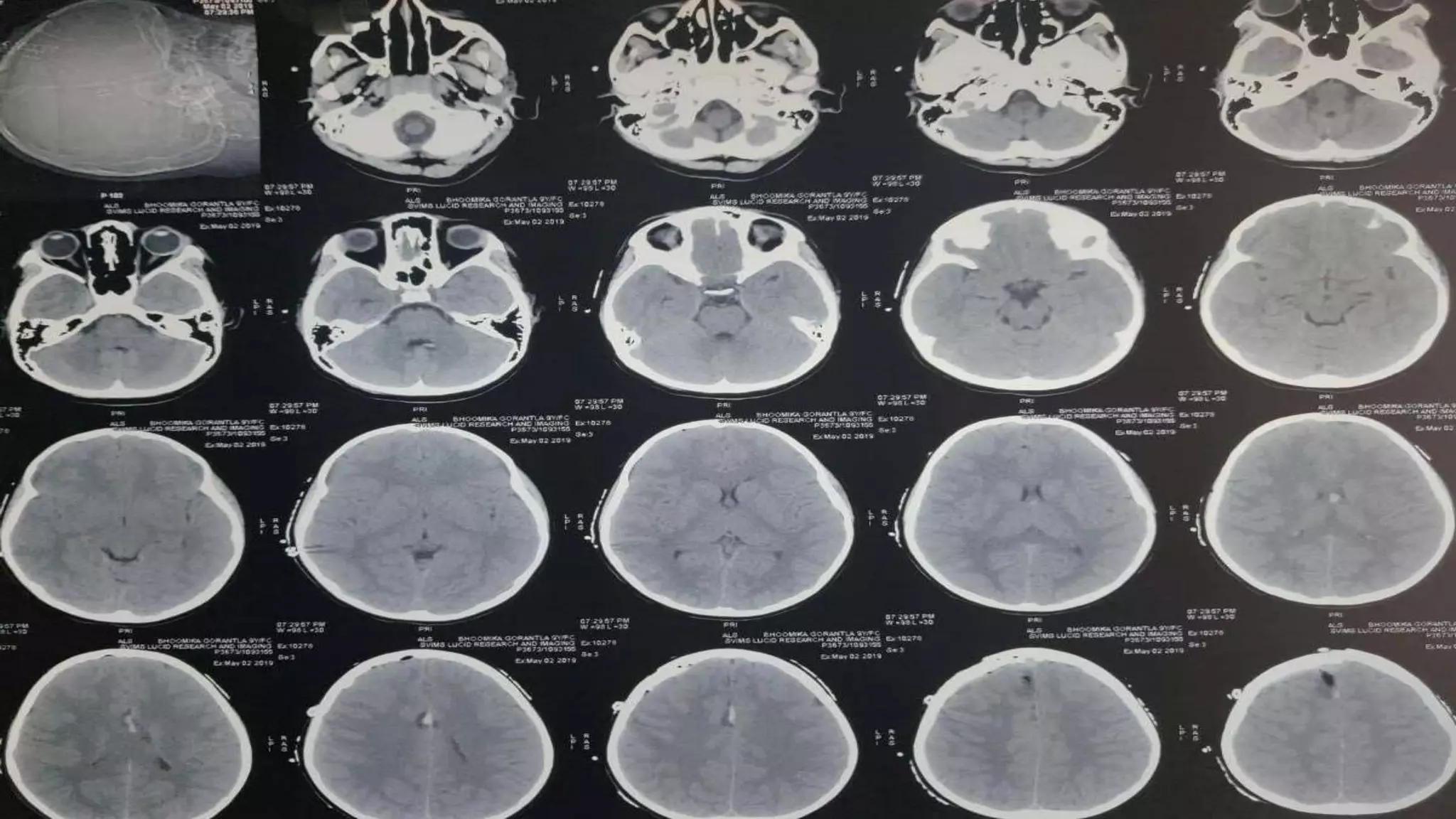
This document discusses the management of colloid cysts, specifically comparing microsurgical and endoscopic approaches. It notes that microsurgical resection leads to better gross total removal rates but higher risks of complications like memory deficits and hydrocephalus. Meanwhile, the endoscopic approach has fewer complications overall but a higher risk of incomplete resection and recurrence. The document provides details on the transcortical, transcallosal, and endoscopic techniques as well as factors to consider in surgical approach selection for individual patients and cyst characteristics.