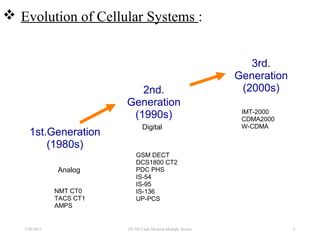
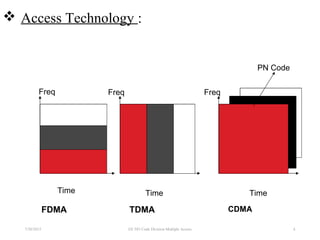
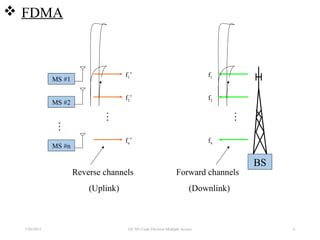
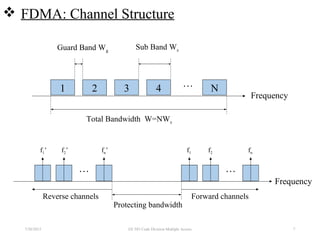
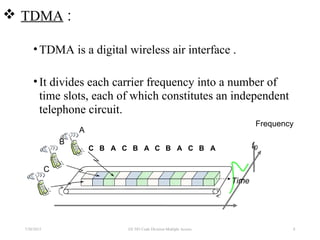
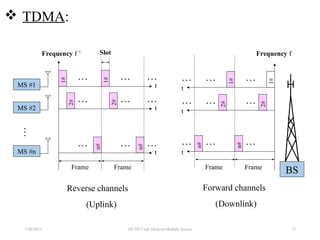
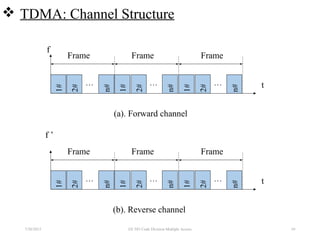
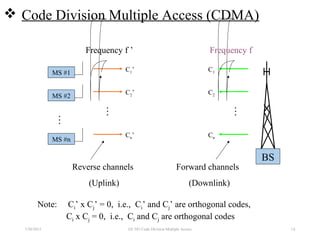
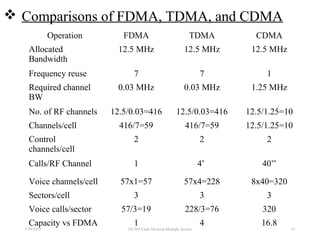
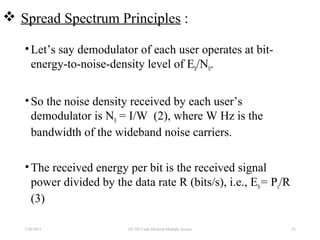
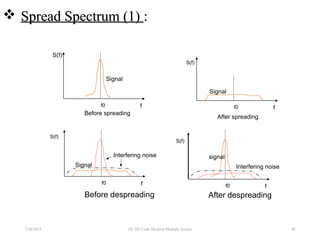
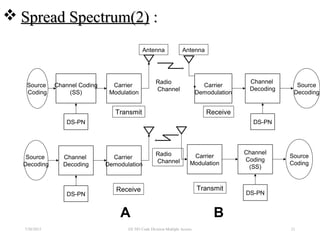
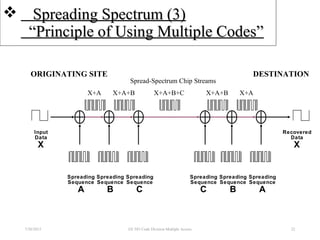
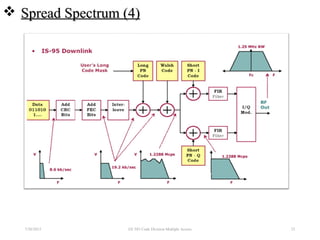
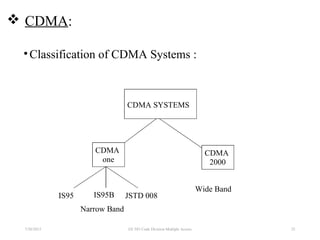
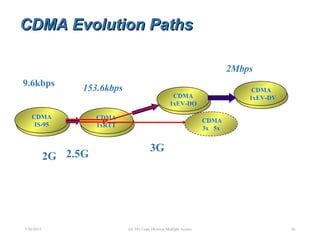
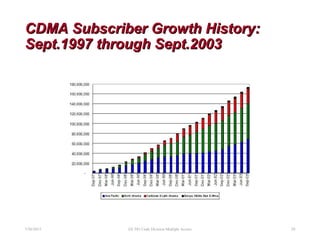
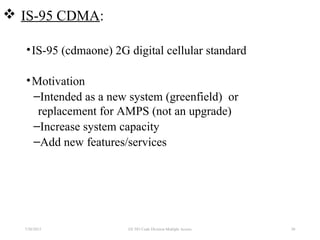
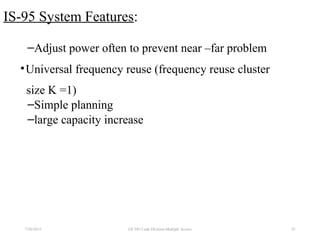
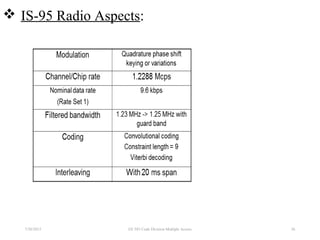
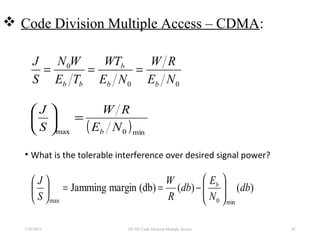
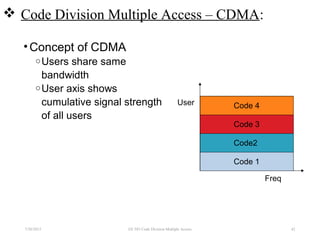
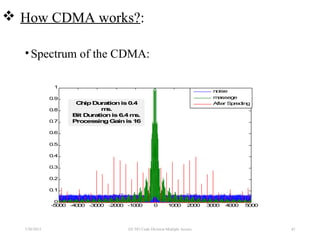
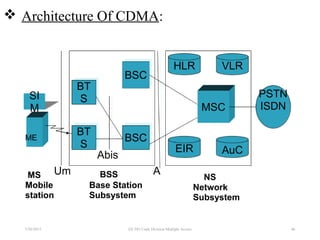
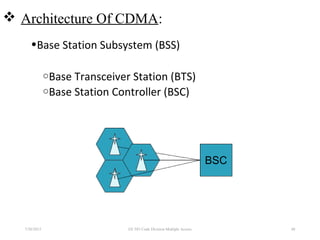
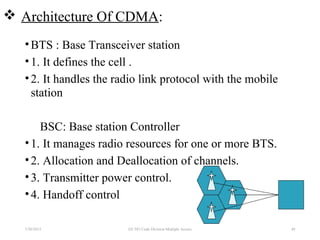
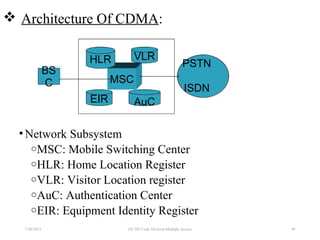
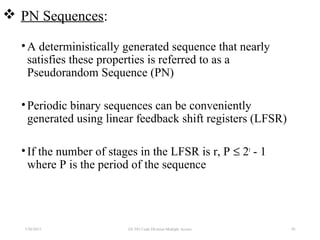
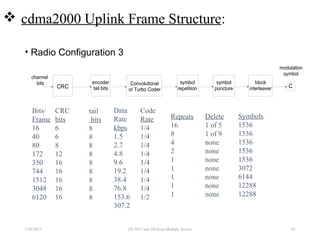
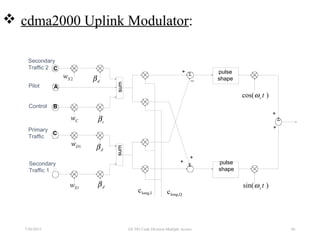
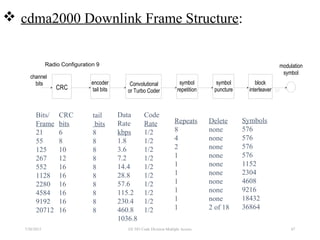
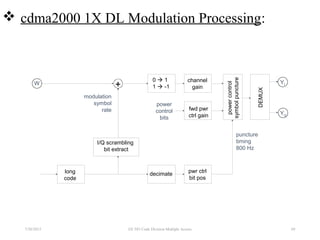
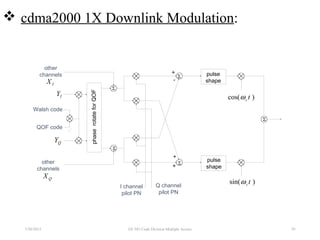
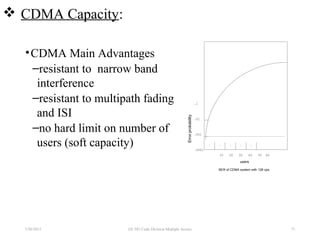
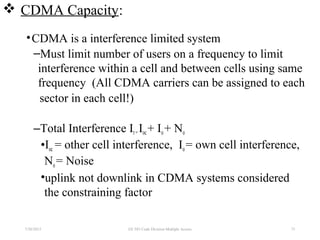
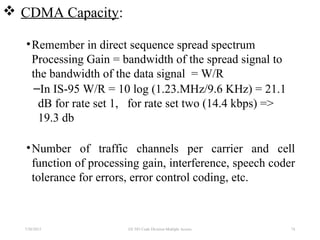
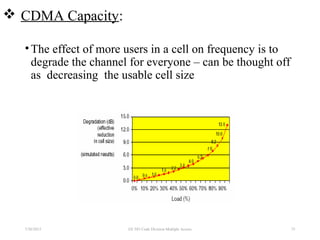
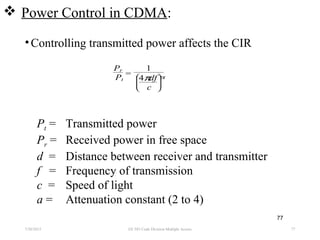
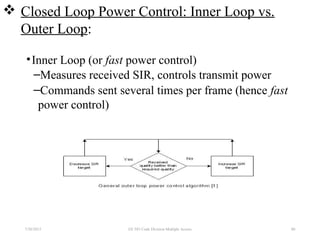
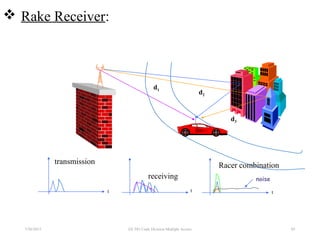
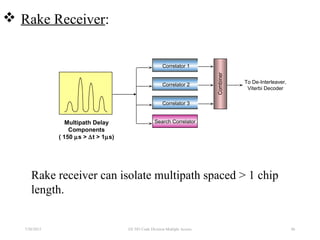
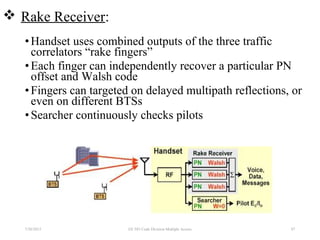
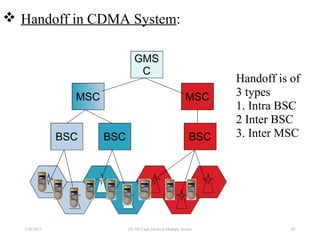
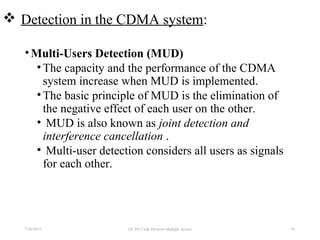
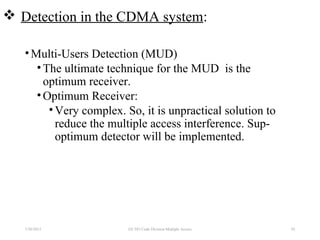
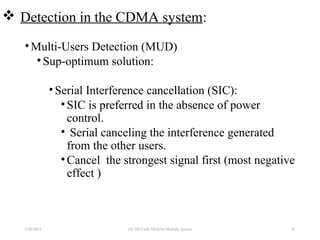
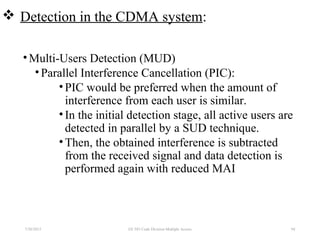
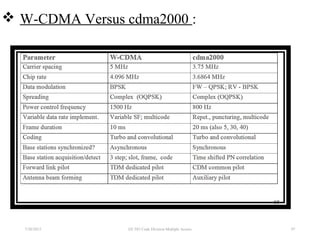
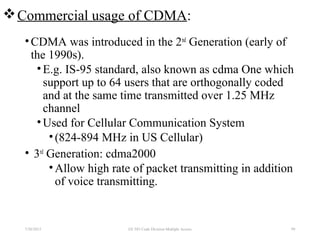
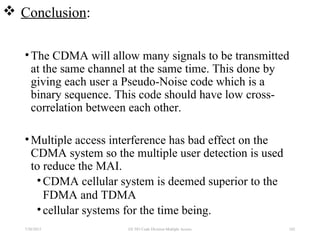
CDMA is a digital cellular standard that allows multiple users to access the same radio frequency channel simultaneously through the use of unique code sequences. Users are separated by spreading their transmitted signals across the frequency band using pseudo-random codes. CDMA provides advantages over other multiple access techniques like FDMA and TDMA such as increased capacity, soft handoffs between cells, and covert operation due to its noise-like signals. The IS-95 standard introduced CDMA to cellular networks and specified the use of orthogonal codes to separate signals and a 1.25 MHz channel bandwidth to support multiple simultaneous voice calls.