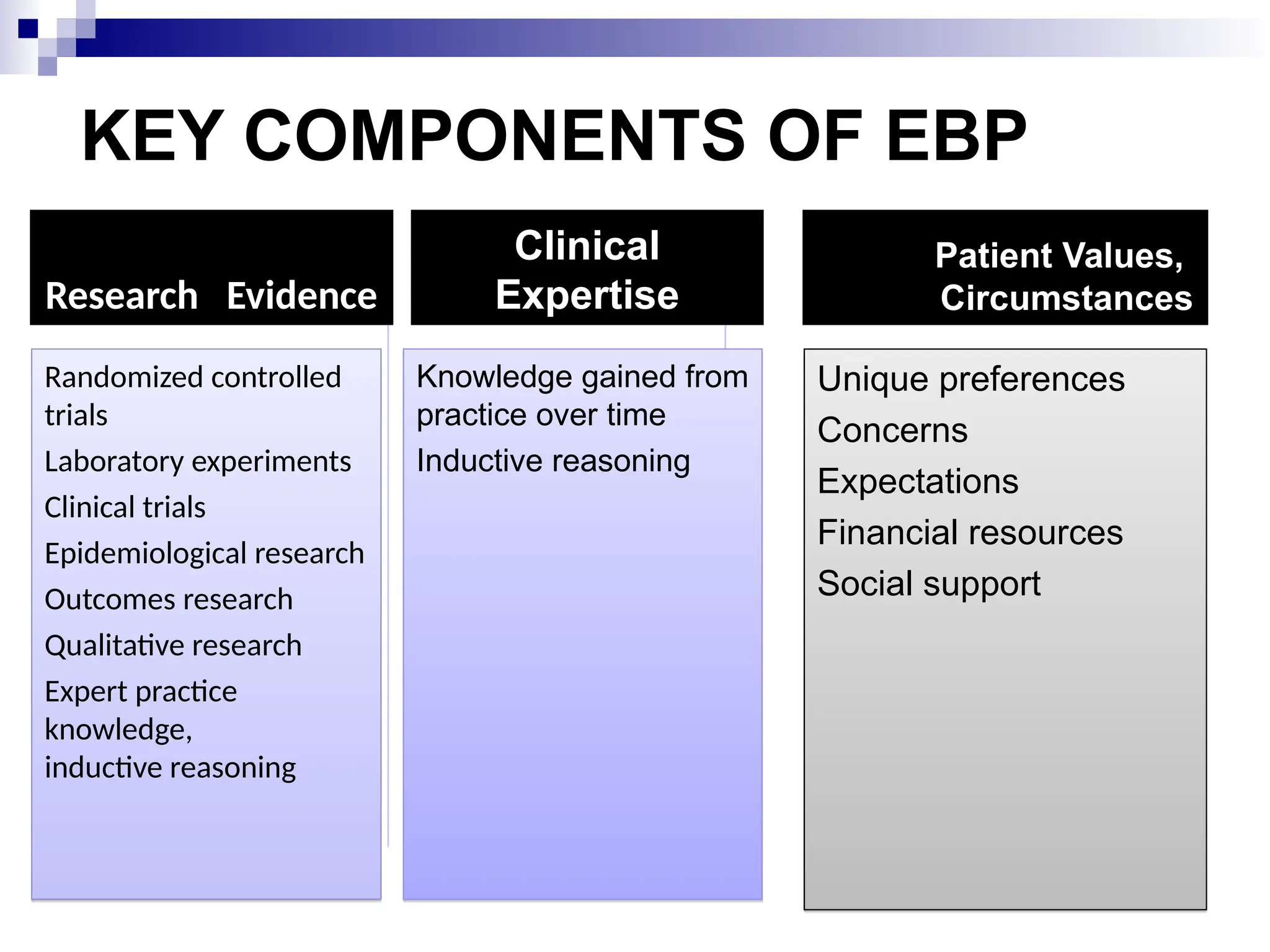
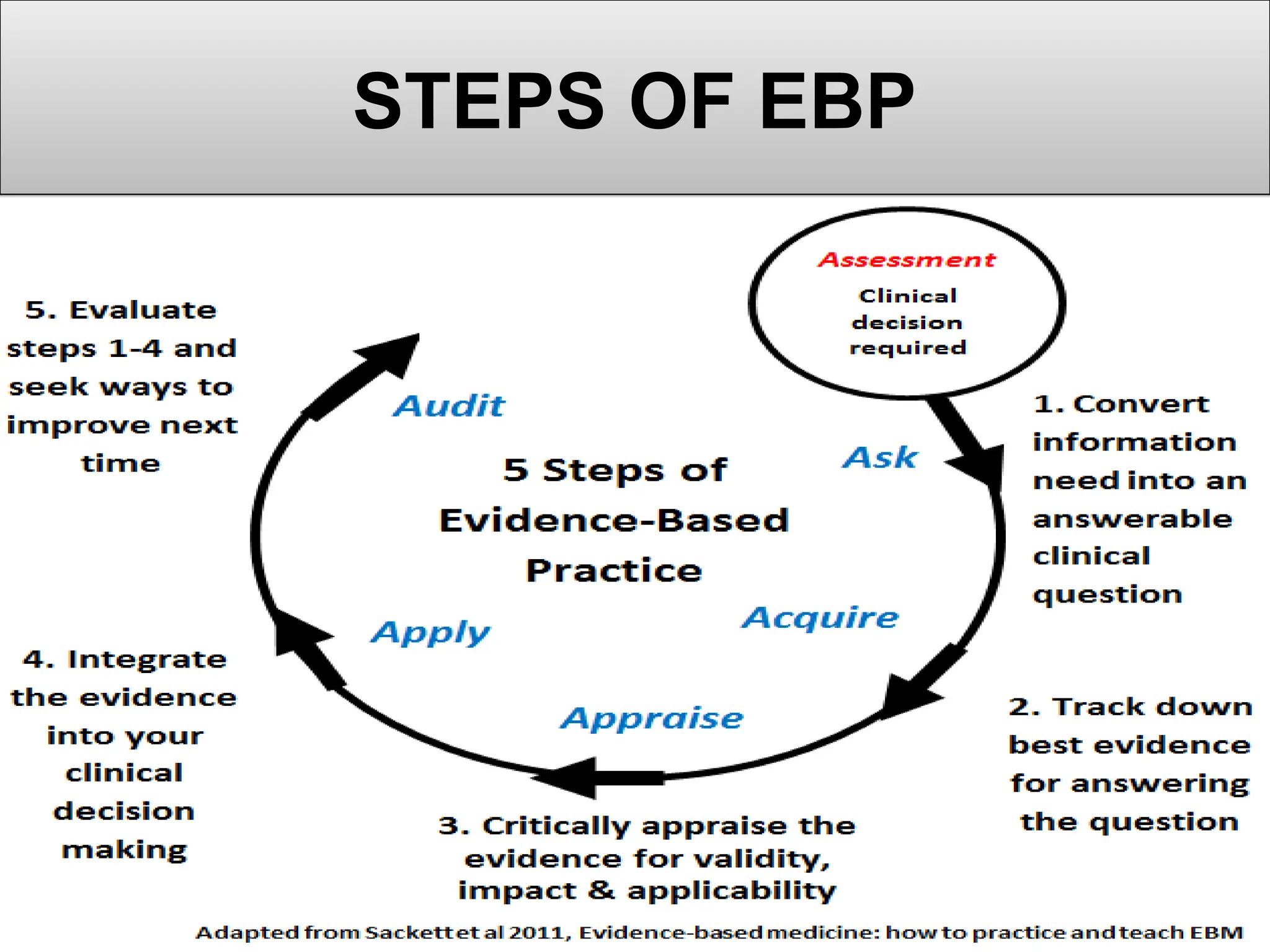
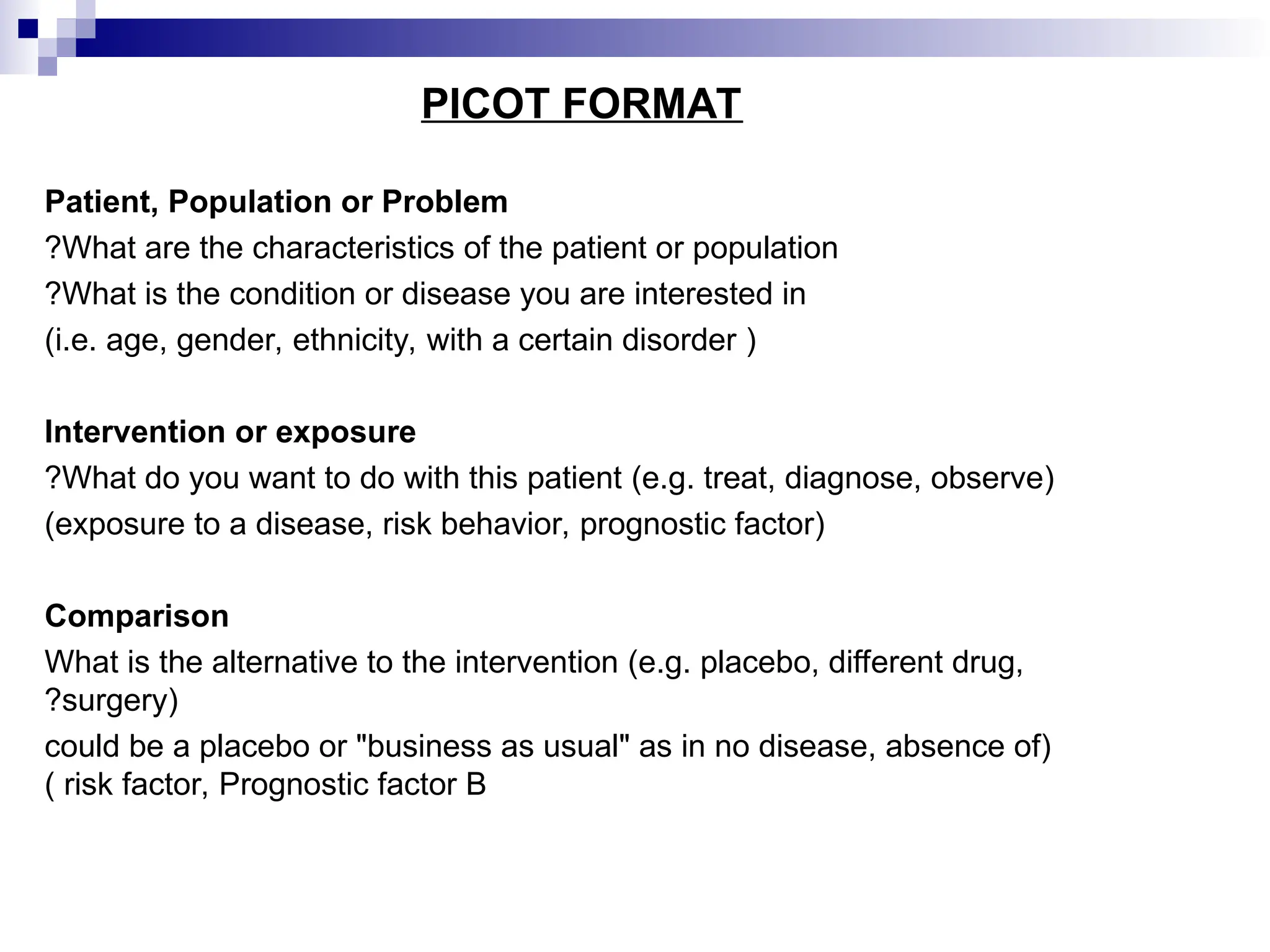
Evidence-based practice (EBP) integrates the best clinical evidence, patient values, and clinician expertise to improve healthcare outcomes. Key components of EBP include research evidence, clinical expertise, and patient preferences, with structured steps to formulate questions, collect, and appraise evidence for practical application. The role of nurses in EBP emphasizes decision-making, knowledge transfer, resource management, and fostering an environment conducive to research and collaboration.