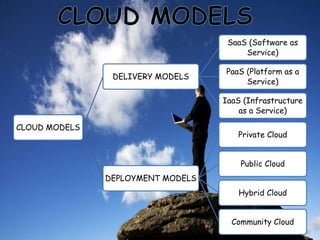
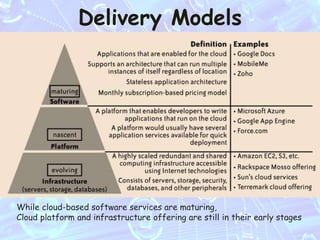
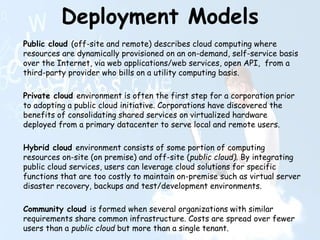
Cloud computing involves using the internet and remote servers run by third-party providers to access and store data and applications. It allows users to access software and data storage over the internet rather than locally. There are different types of cloud services including Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). Cloud computing provides benefits like lower costs, flexibility, and scalability but also risks around security, control and reliability if internet access is lost.