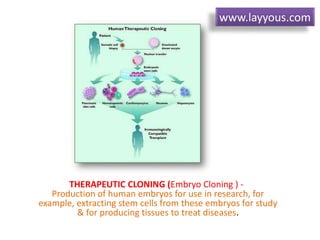
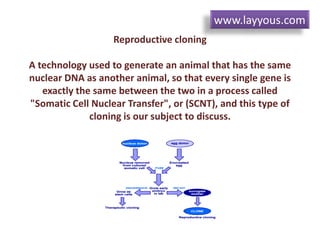
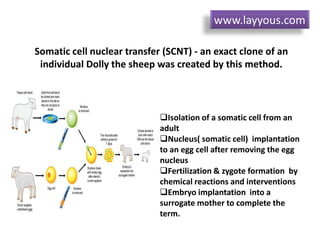
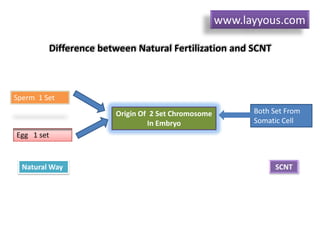
Cloning can be done through somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT) or artificial embryo twinning. SCNT involves transferring the nucleus of a somatic cell into an egg cell from which the nucleus has been removed. The embryo is then implanted into a surrogate mother. Dolly the sheep was the first mammal cloned using SCNT. Reproductive cloning has a high failure rate and cloned animals often have health issues. Alternatives like reproductive semi-cloning have been proposed to address ethical concerns while still helping infertility treatments.