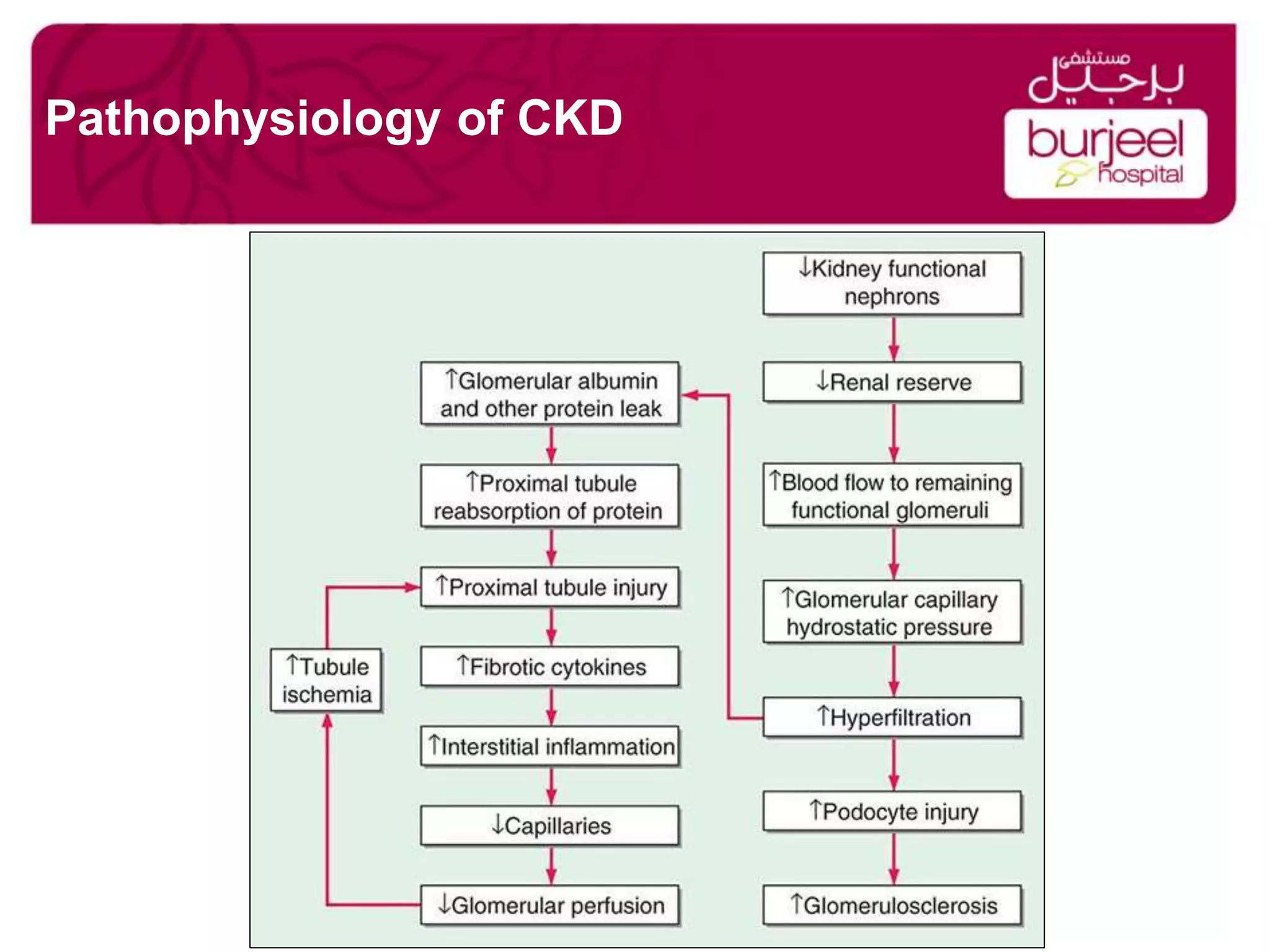
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is defined as abnormalities of kidney structure or function present for more than three months. It affects over 26 million Americans and is a major public health issue. The leading causes are diabetes and hypertension. As CKD progresses, kidney function declines and complications increase like anemia and bone disease. Cardiovascular disease risk also rises substantially. Inflammation, lipid abnormalities, and genetic factors can all contribute to CKD progression if not properly managed.