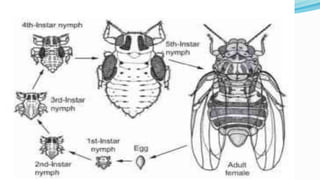
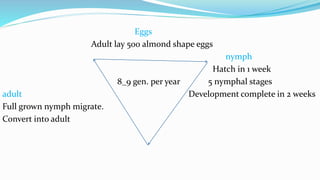
The document describes the Asian citrus psyllid (Diaphorina citri), a pest affecting citrus trees across various countries. It details its life cycle, including egg laying, nymph and adult stages, and the damage it causes, such as plant wilting and virus spread. Control measures include biological, chemical, and cultural methods to manage this significant pest.