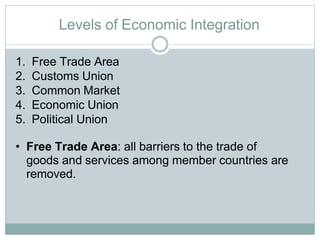
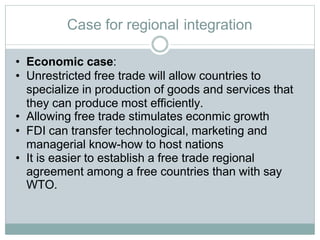
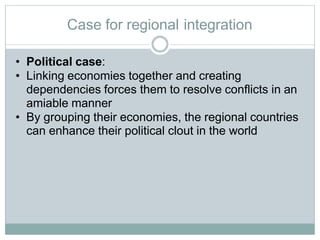
Regional economic integration refers to agreements among countries in a geographic region to reduce and ultimately remove tariffs and non-tariff barriers to trade. There are various levels of integration including free trade areas, customs unions, common markets, economic unions, and political unions. The document discusses the case for and disadvantages of regional integration. Key benefits include increased specialization and economic growth from free trade, as well as greater political cooperation and foreign investment attraction. History and structures of economic unions like the EU, NAFTA, and ASEAN are also outlined.