This document discusses an introductory chapter on cascading style sheets (CSS) that covers key concepts such as:
- The evolution of style sheets from print to web and advantages of using CSS
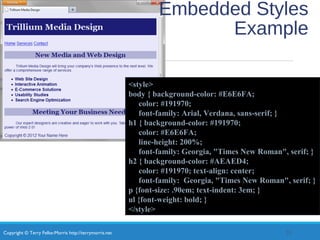
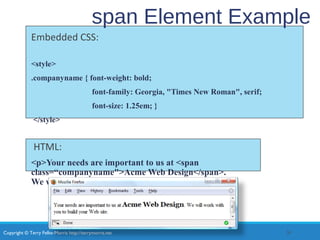
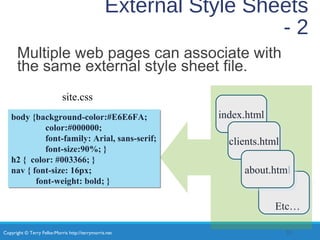
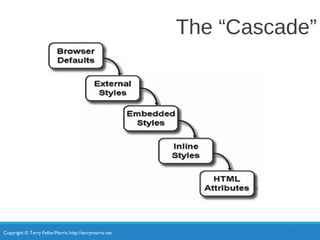
- Types of CSS like inline, embedded, and external styles
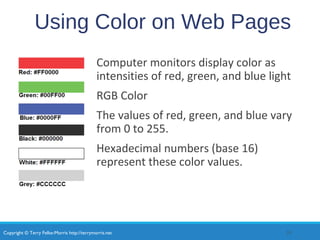
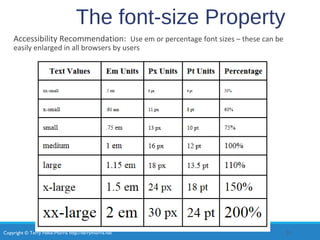
- Common CSS properties for configuring color, text, and formatting
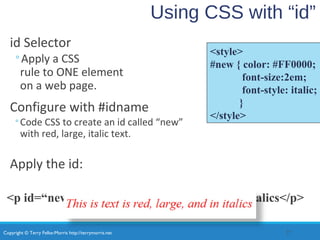
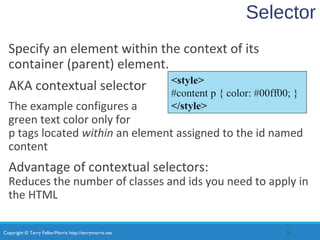
- Using CSS selectors like classes, IDs, and contextual selectors to target specific elements
- Validating CSS styles and ensuring sufficient color contrast for accessibility