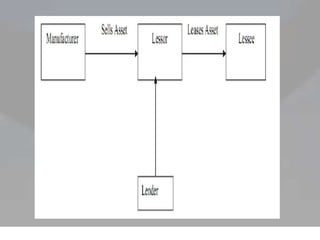
This document provides an overview of lease financing. It begins with introductions of the group members presenting. It then outlines the learning objectives which are to understand the definition of lease financing, its parties, characteristics, types, advantages and disadvantages, lease agreements, and decision making regarding lease financing. The document proceeds to define lease financing and its key parties. It describes the characteristics, types including finance lease, operating lease, leveraged lease, and sale and leaseback. It also covers the advantages and disadvantages as well as sources of lease financing and components of a lease agreement.