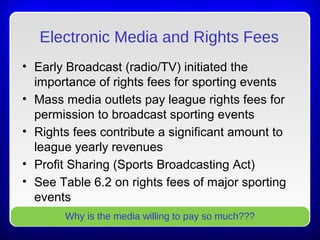
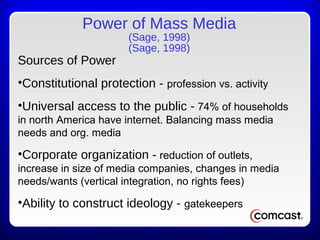
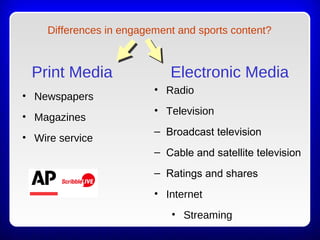
This chapter discusses the relationship between sport organizations and mass media. It defines mass media and notes the significance of rights fees in the success of sport organizations. Sport organizations have adapted to accommodate television by changing rules and scheduling. Historically, sport organizations used newspapers to promote athletes and build fan bases. The evolution of electronic media increased the importance of rights fees, which now contribute significantly to league revenues. The relationship between sport and media is symbiotic, with each partner helping to deliver sport content to consumers.