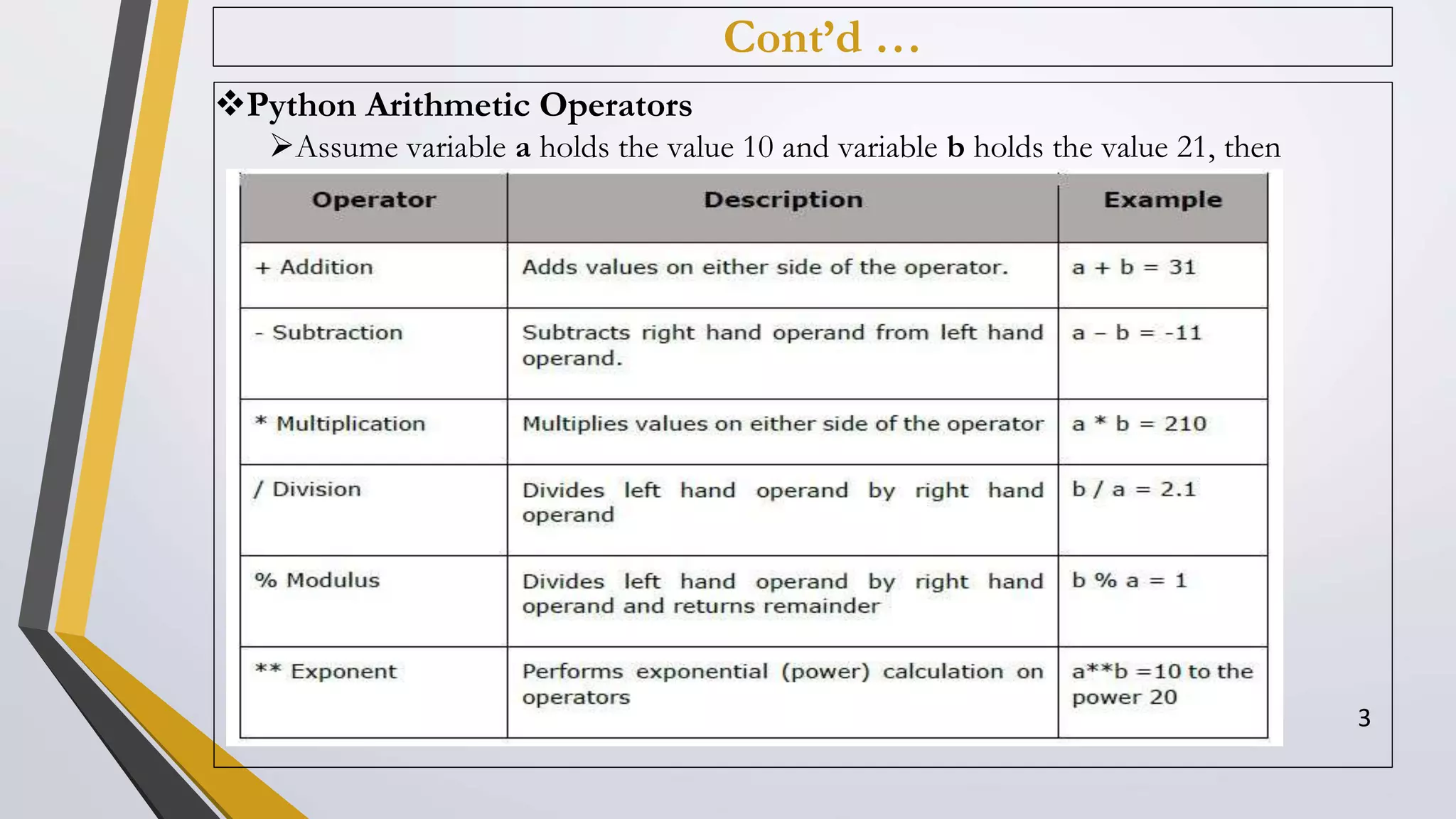
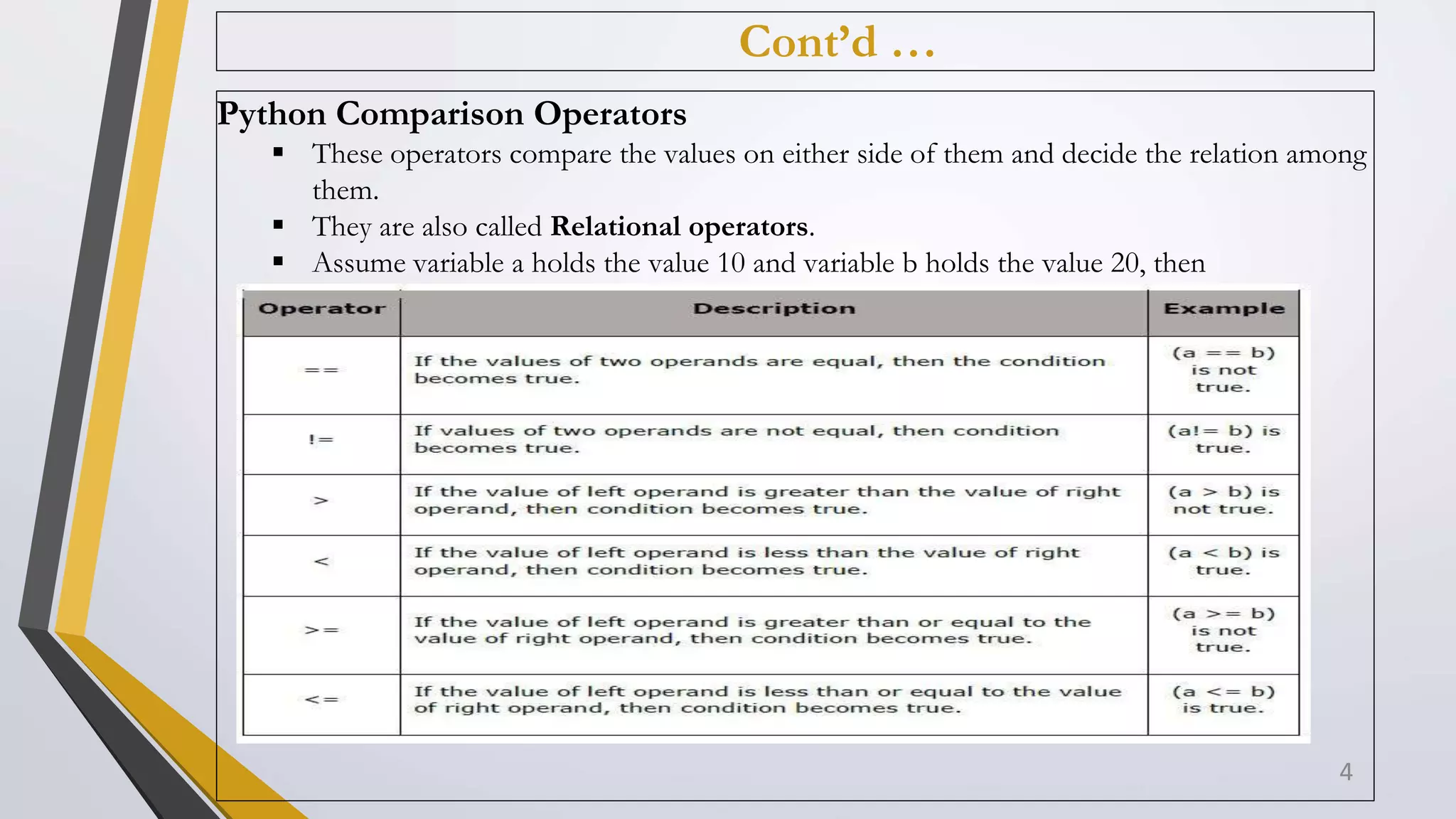
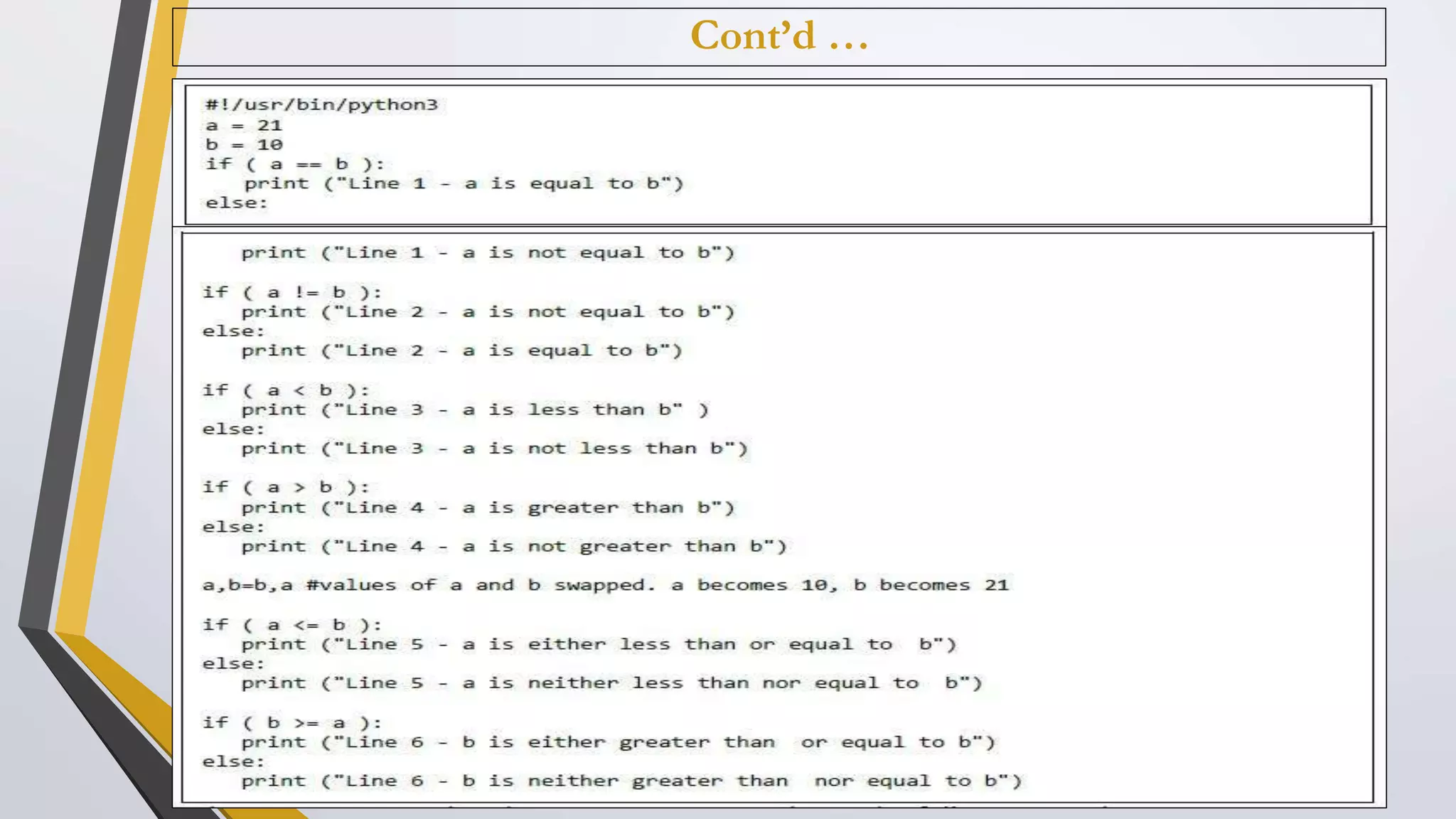
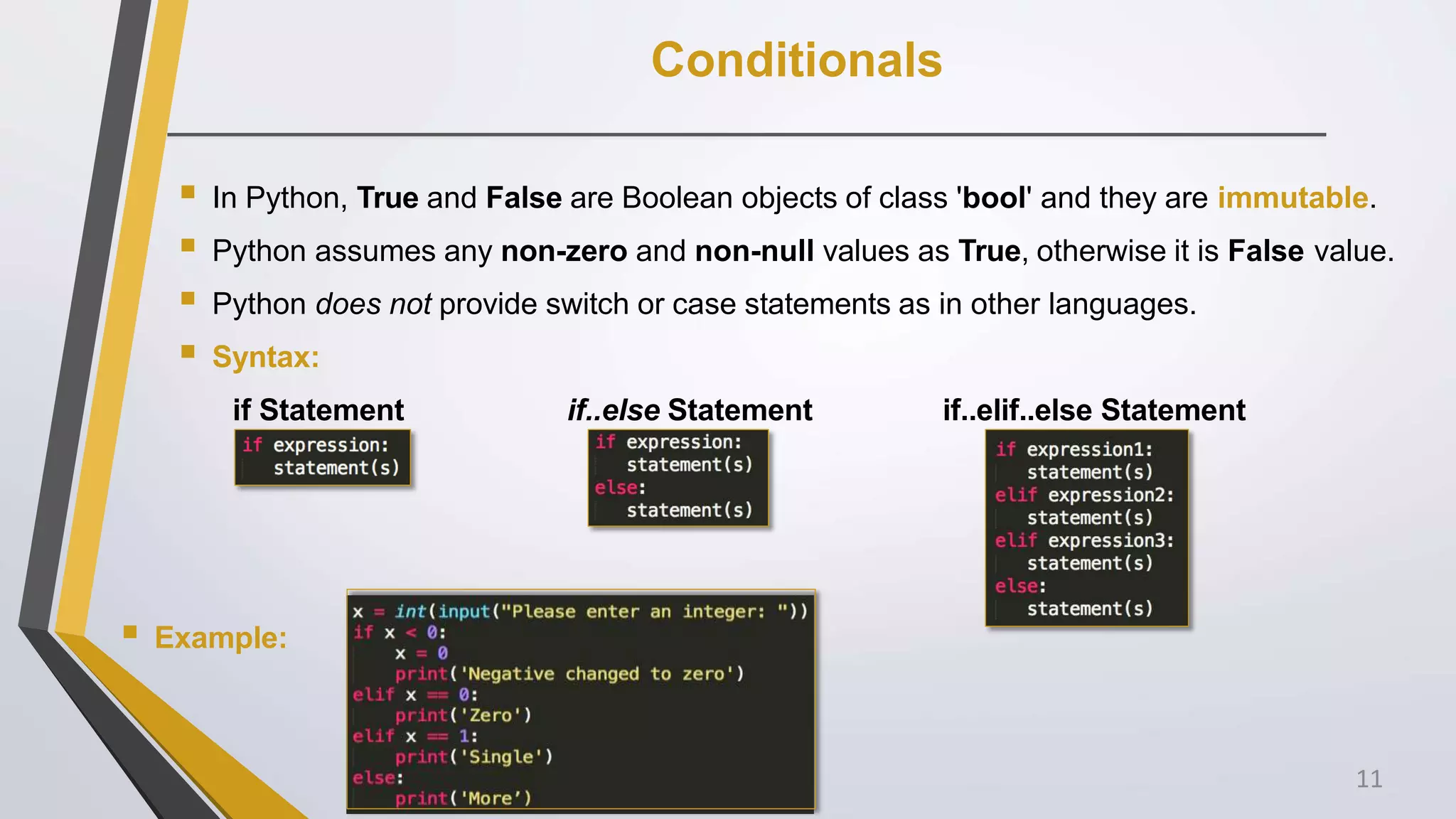
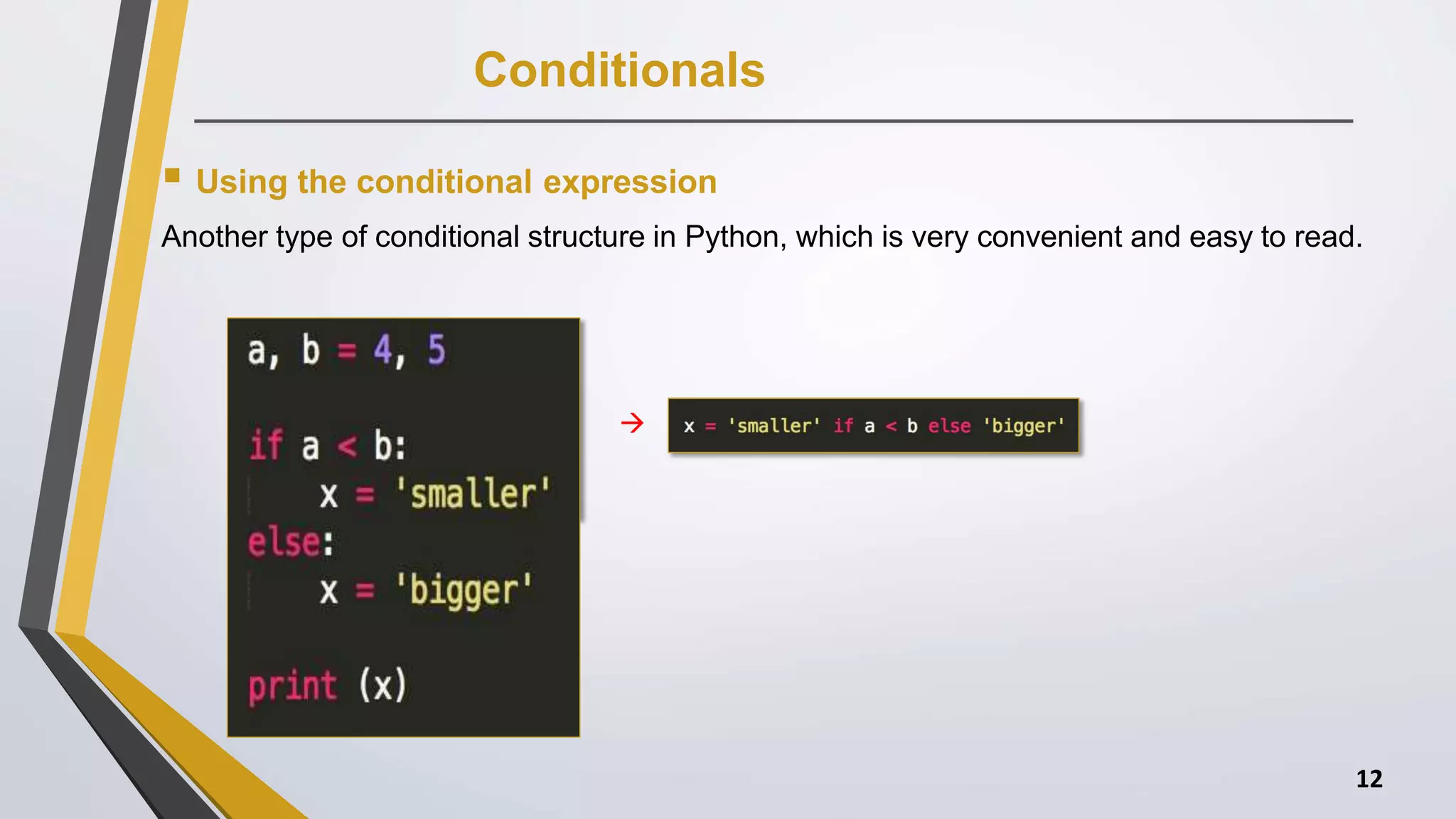
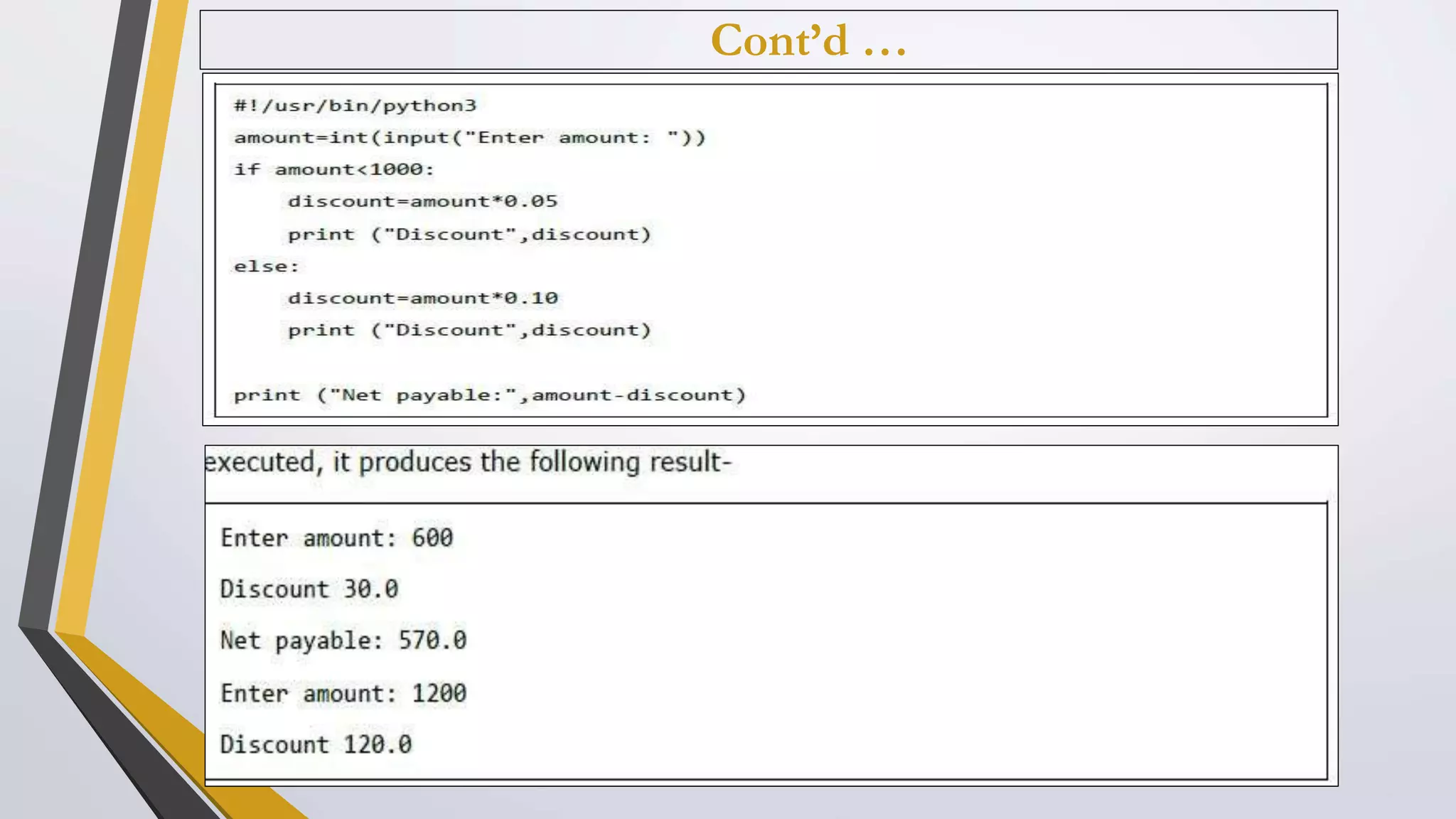
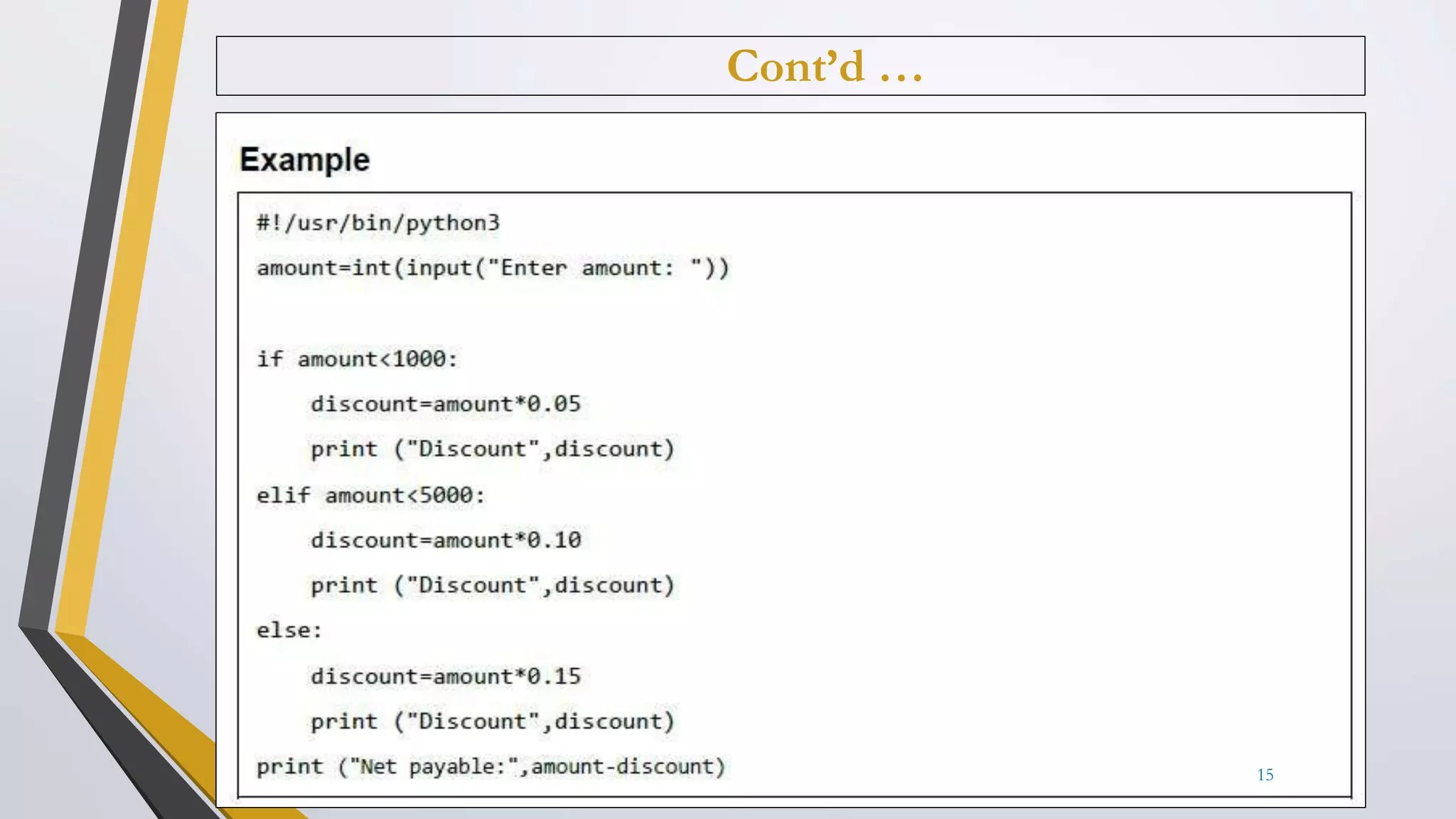
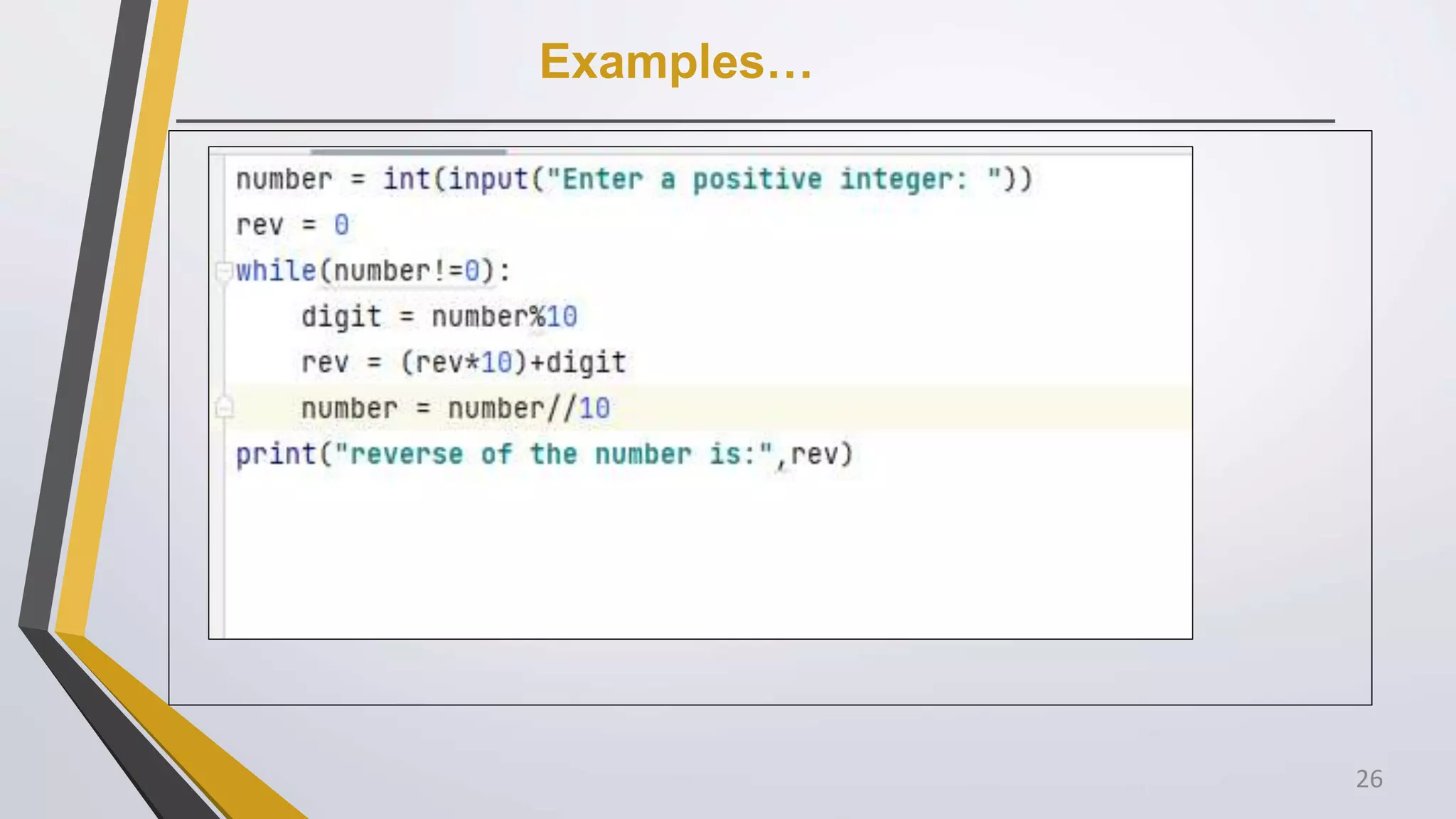
The document discusses Python operators and control structures. It covers various types of operators in Python like arithmetic, comparison, assignment, logical, bitwise, and membership operators. It provides examples of each operator type. The document also discusses conditional statements like if, elif, else and conditional expressions. It explains while and for loops in Python along with loop control statements like break, continue, and pass. The last section gives some examples of using operators and control structures in Python programs.






![QUIZ(5%)
1) Write python code that Accept two numbers from the user and calculate multiplication
,subtraction and addition.
2) Given a Python list of numbers. Turn every item of a list into its square
List = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
Expected Output: [1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49]
3) Reverse the given” List = [100, 200, 300, 400, 500]” in Python.
Expected Output: [500, 400, 300, 200, 100]
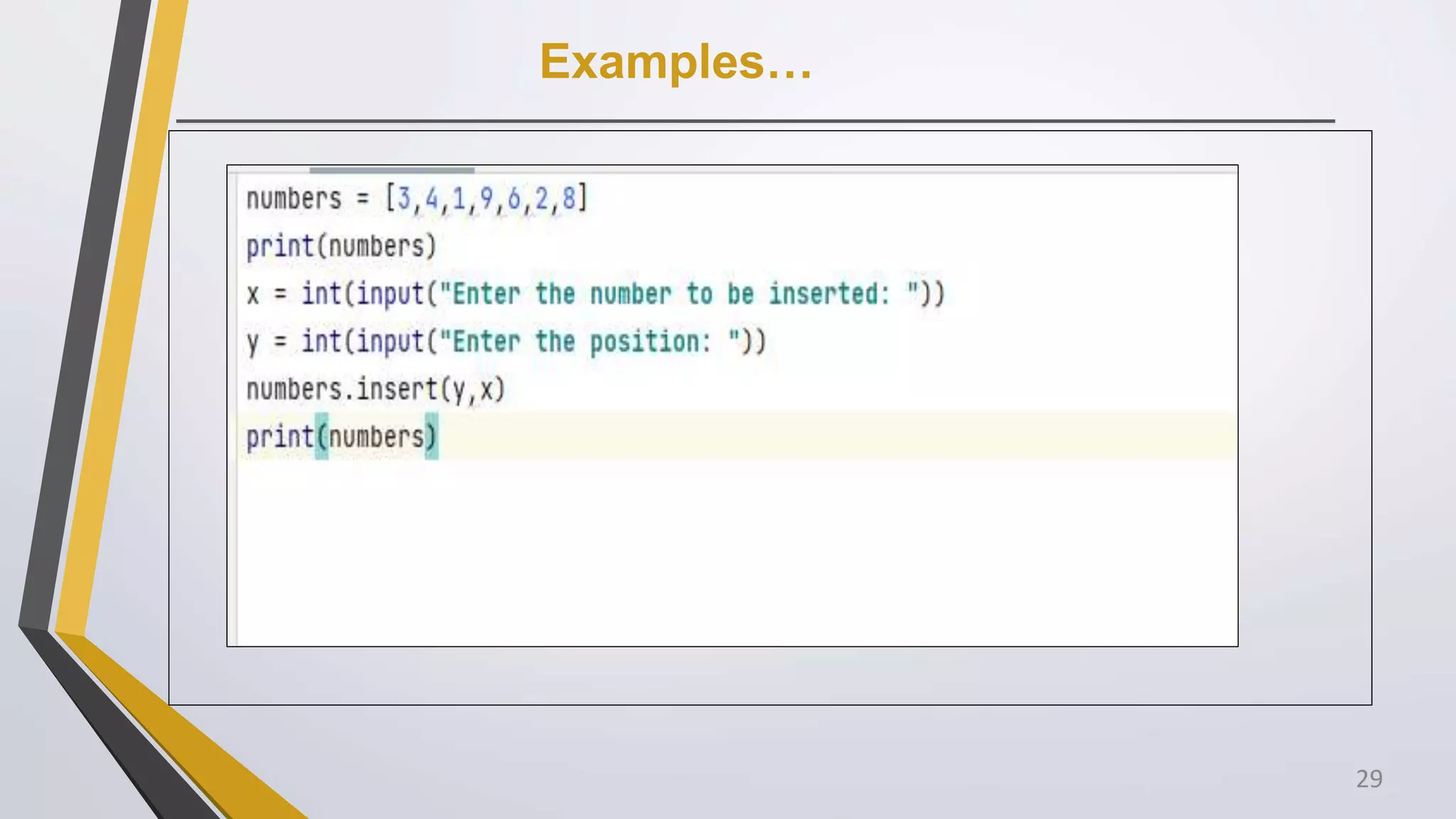
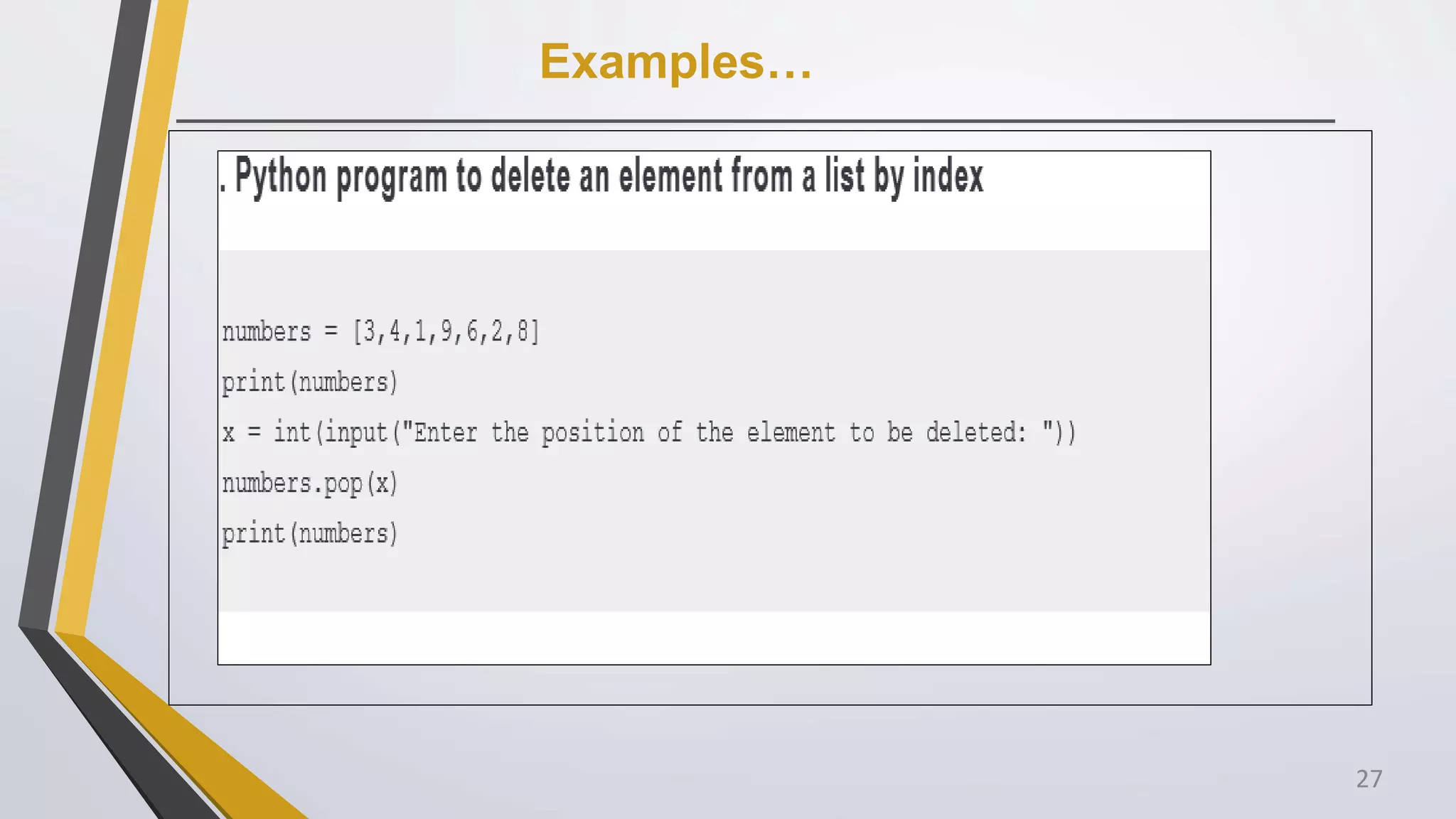
4. Write Python program to insert a number to any position in a list.
for example numbers = [3,4,1,9,6,2,8]
5. Write a program in Python to print number ranging from 1 to 25 but excluding number
which is the multiples of 5.
6. Write a program to filter even and odd number from a list.
Hint 1
Given x = [10, 23, 24, 35, 65, 78, 90] 28](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter-3-230122114006-319b9511/75/Chapter-3-pptx-28-2048.jpg)