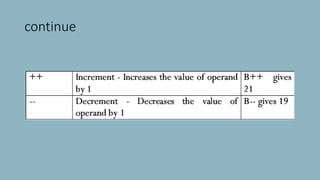
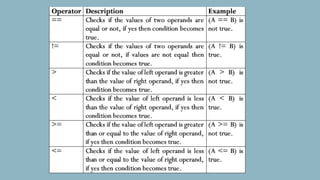
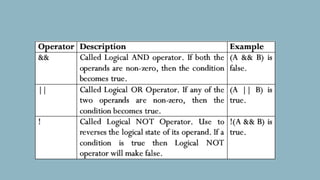
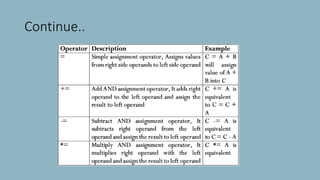
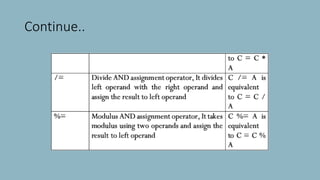
The document discusses different types of operators in Java including arithmetic, relational, bitwise, logical, assignment, and miscellaneous operators. It provides examples of using arithmetic operators like addition and subtraction on integer variables and using relational operators to compare values. Logical operators are described as evaluating Boolean expressions. Assignment operators are listed as supporting operations like assignment equal. The miscellaneous ternary operator is explained as evaluating a condition and assigning a value based on the result. Finally, operator precedence is covered as affecting how expressions are evaluated based on which operators have higher precedence over others.