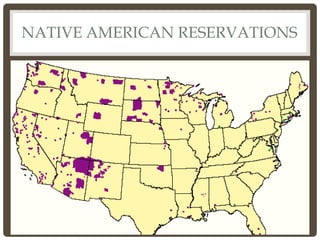
The document summarizes Western expansion in the mid-19th century United States. It discusses key events like the annexation of Texas, Oregon Territory, and Mexican Cession that expanded U.S. territory westward. It also describes cultural clashes as European, Mexican, African American, Chinese, and Native American groups interacted in the expanding West. Ranching, farming, mining, and the transcontinental railroad transformed the economy and society of the Western territories during this period of rapid growth and conflict. Farmers organized cooperatives and the Populist movement in response to economic difficulties in the late 1800s.