This chapter discusses interpersonal behavior in organizations. It covers conflict, assertiveness, power, and politics. The key topics are:
- Conflict can arise from disagreements over goals/methods, task interdependence, roles/rules, and personality differences.
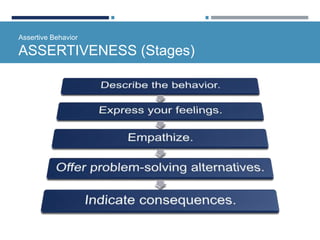
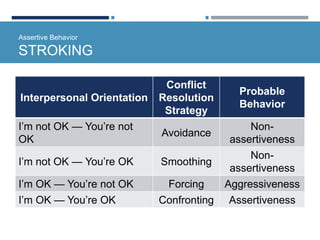
- Assertiveness involves expressing feelings and giving honest feedback. Different interpersonal orientations exist such as dominance.
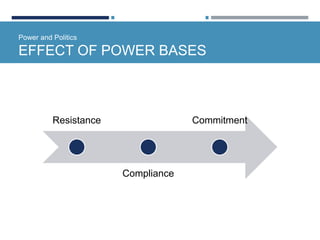
- Power is the ability to influence others and events. Types of power include personal, legitimate, expert, reward, and coercive power.
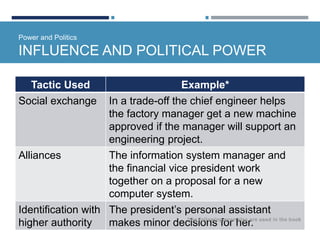
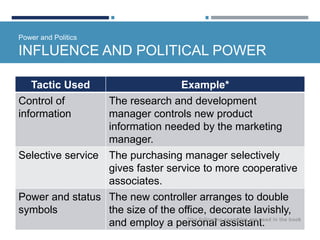
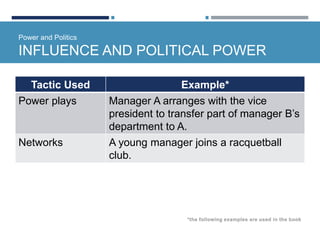
- Organizational politics involves intentional behaviors to enhance influence through tactics like social exchange, alliances, and controlling information.