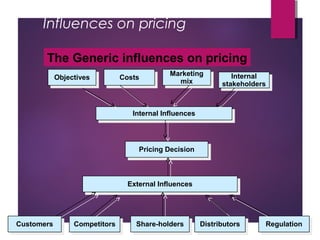
This document discusses influences on pricing decisions for products and services. It identifies key objectives, costs, marketing mix factors, internal and external stakeholders that influence pricing. Objectives include profit maximization and market share. Costs like fixed and variable must be considered. The marketing mix and brand positioning also affect price. Internally, different departments have different pricing priorities. Externally, customers, competitors, distributors, regulations are pricing factors. The document also discusses challenges in pricing financial services and different pricing strategies like explicit, implicit, spread, fixed fee, transaction charges, and two-part tariffs.