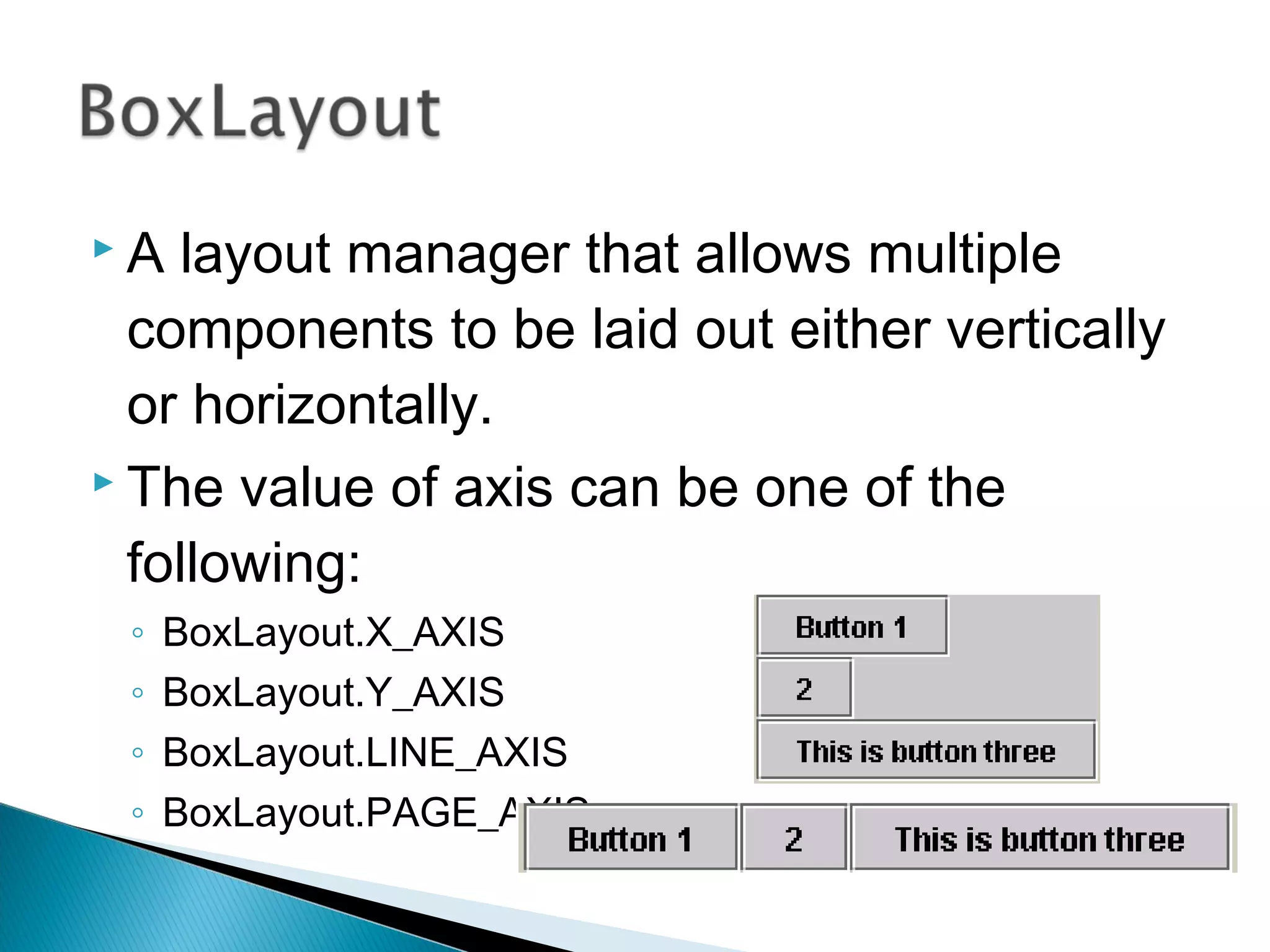
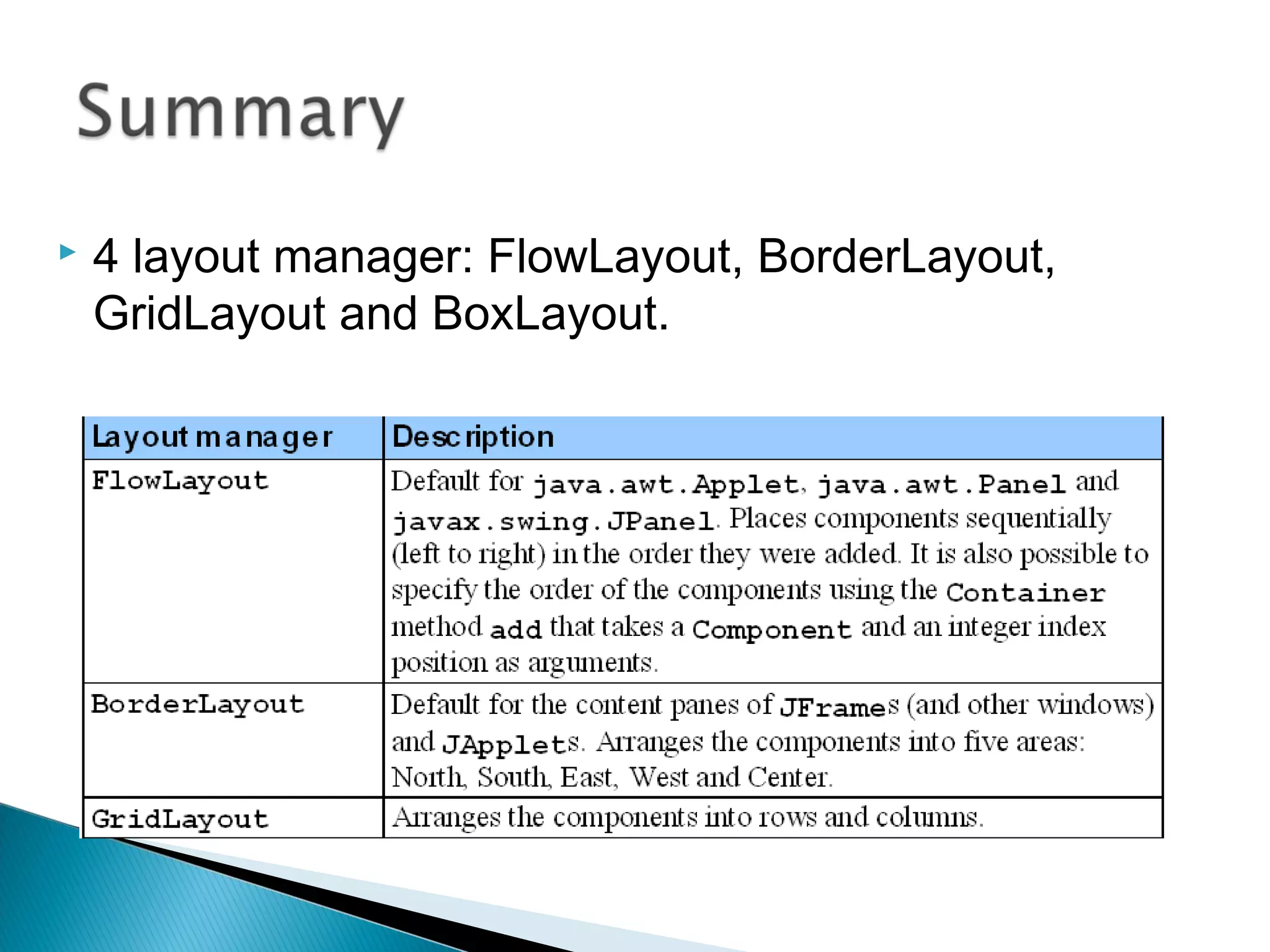
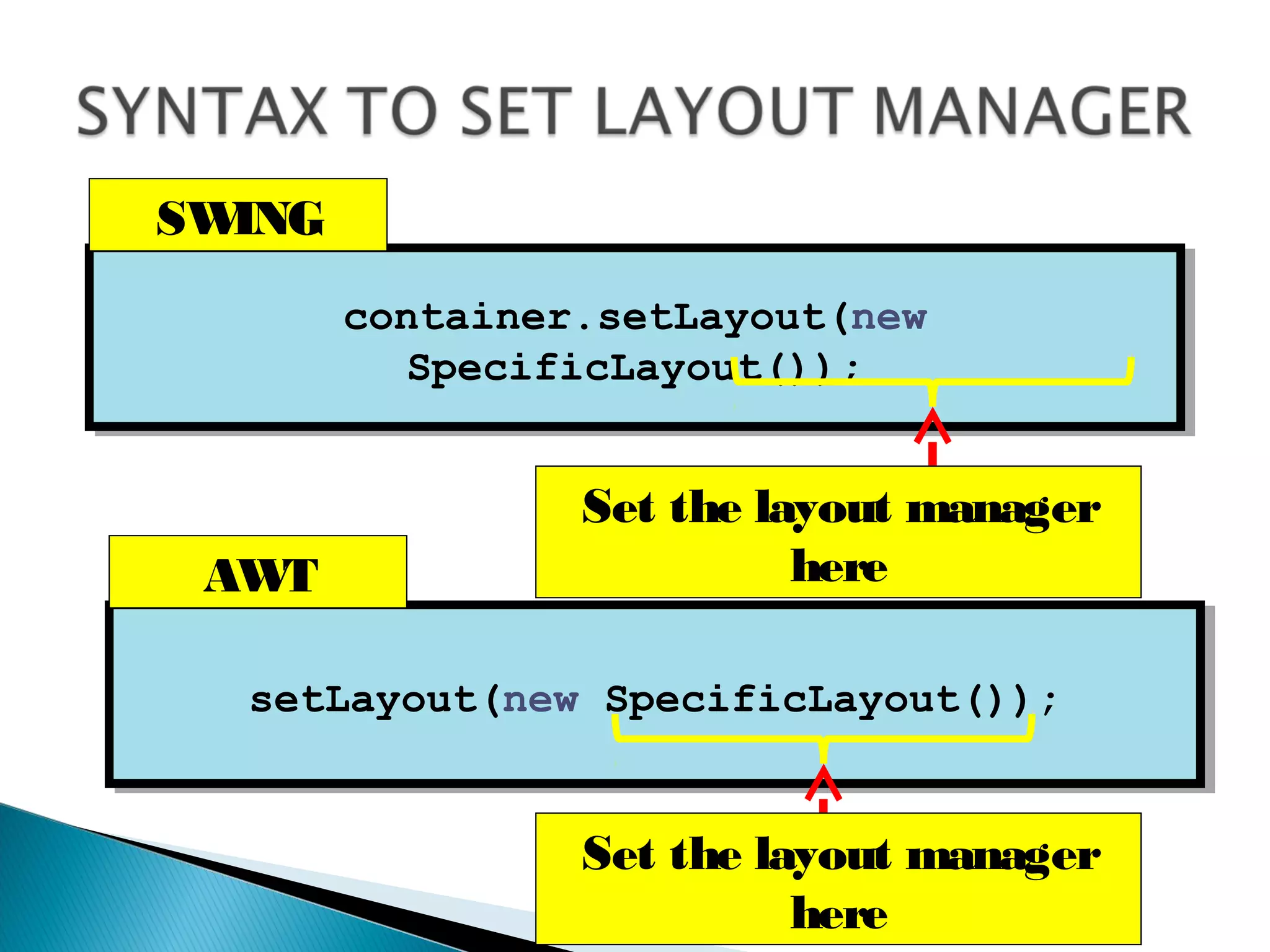
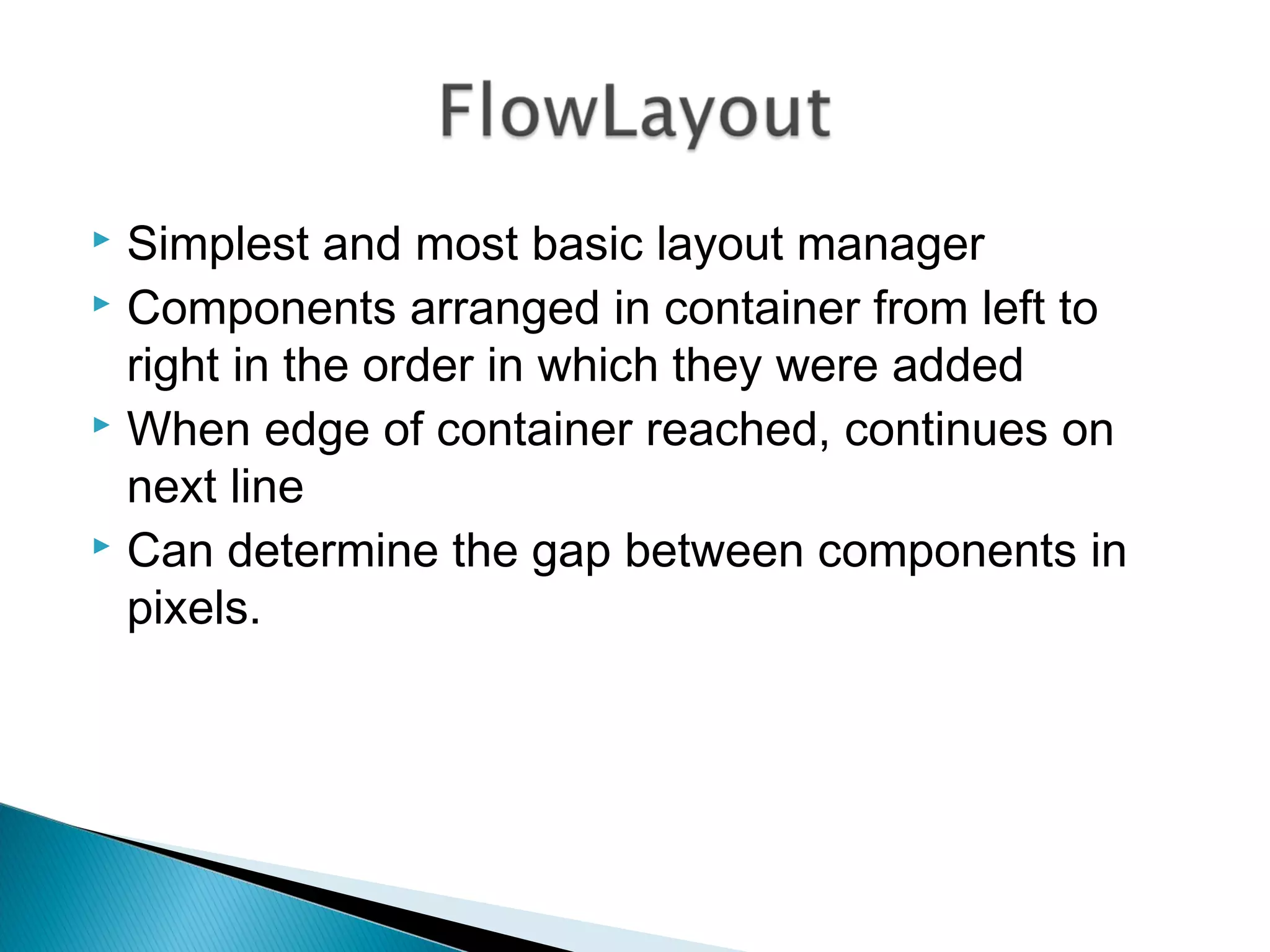
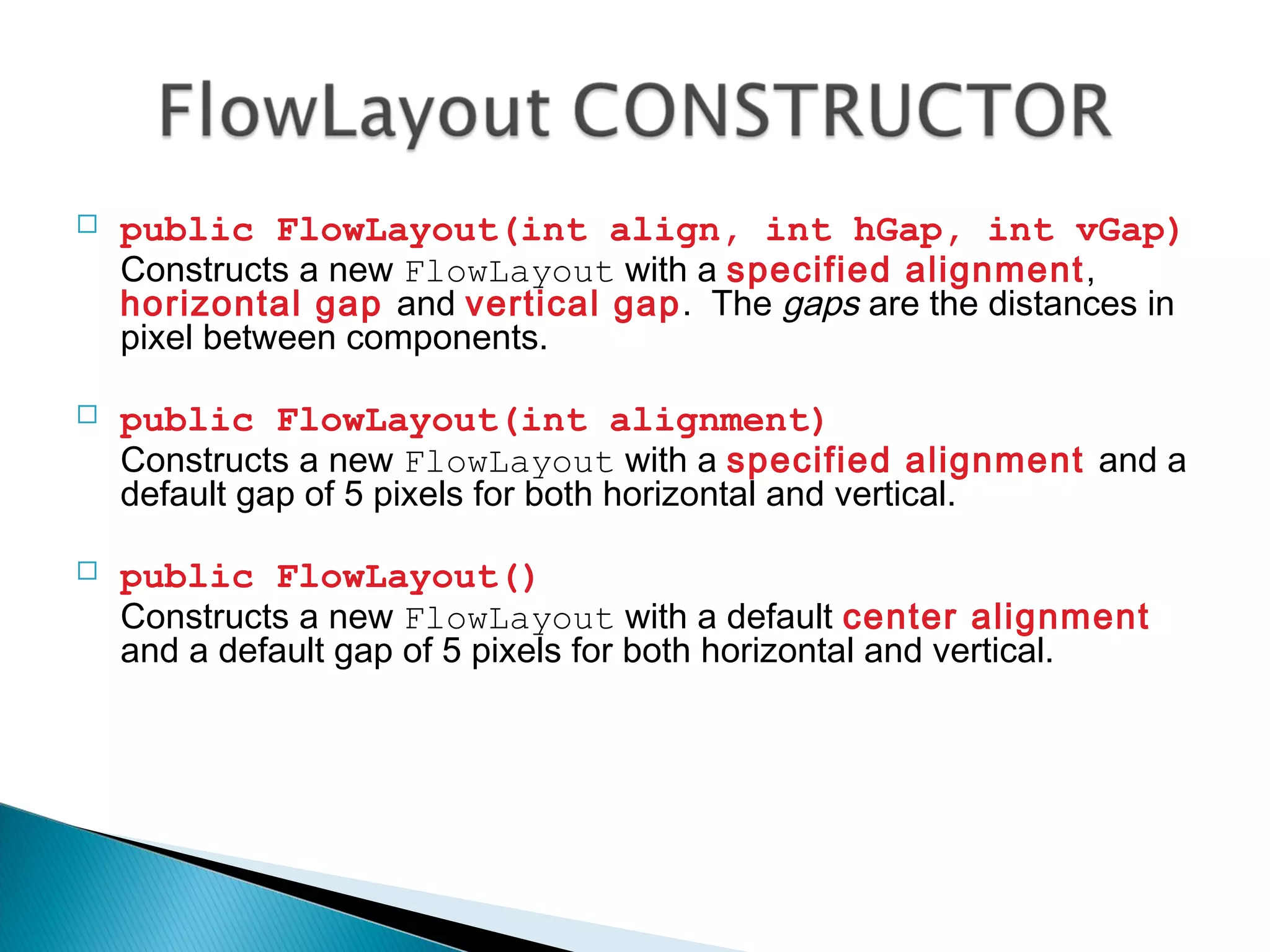
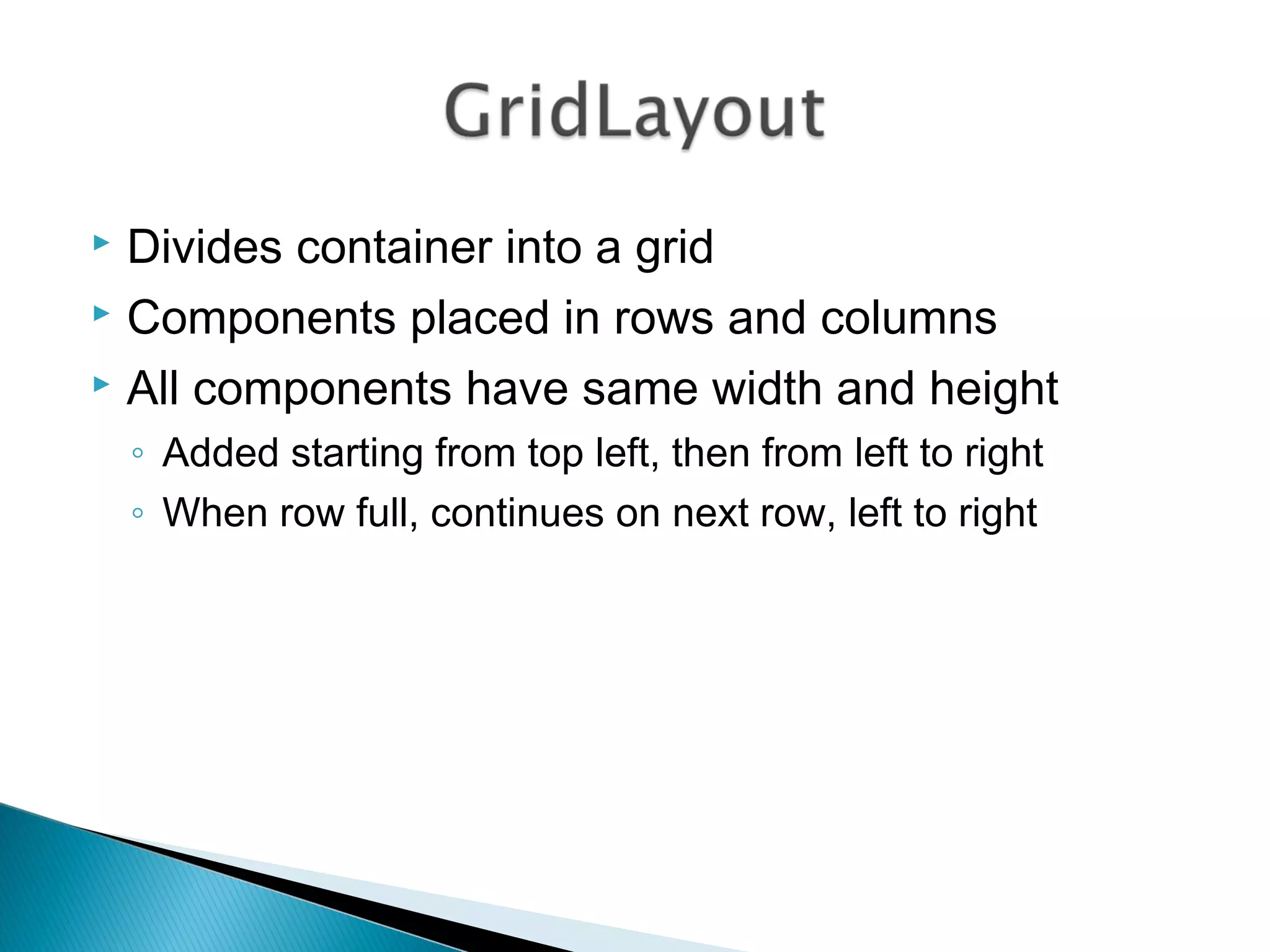
The document discusses 4 common layout managers in AWT: FlowLayout, GridLayout, BorderLayout, and BoxLayout. It provides details on how each layout manager arranges and positions components within a container. Code examples are given to demonstrate implementing each layout manager. The document is intended to help students understand how to define and use layout managers to structure the UI design of an AWT application.




![import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class TestFlowLayout extends JFrame
{
public TestFlowLayout()
{
super(“Create FlowLayout");
Container c = getContentPane();
c.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEFT,20,10));
for (int i=1; i<9;i++)
c.add(new Button("button "+i));
setSize(350,200);
setVisible(true);
}
public static void main(String[] arg)
{
TestFlowLayout s = new TestFlowLayout();
s.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
}
10
20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap11-141222203608-conversion-gate02/75/Chap1-1-4-10-2048.jpg)
![import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
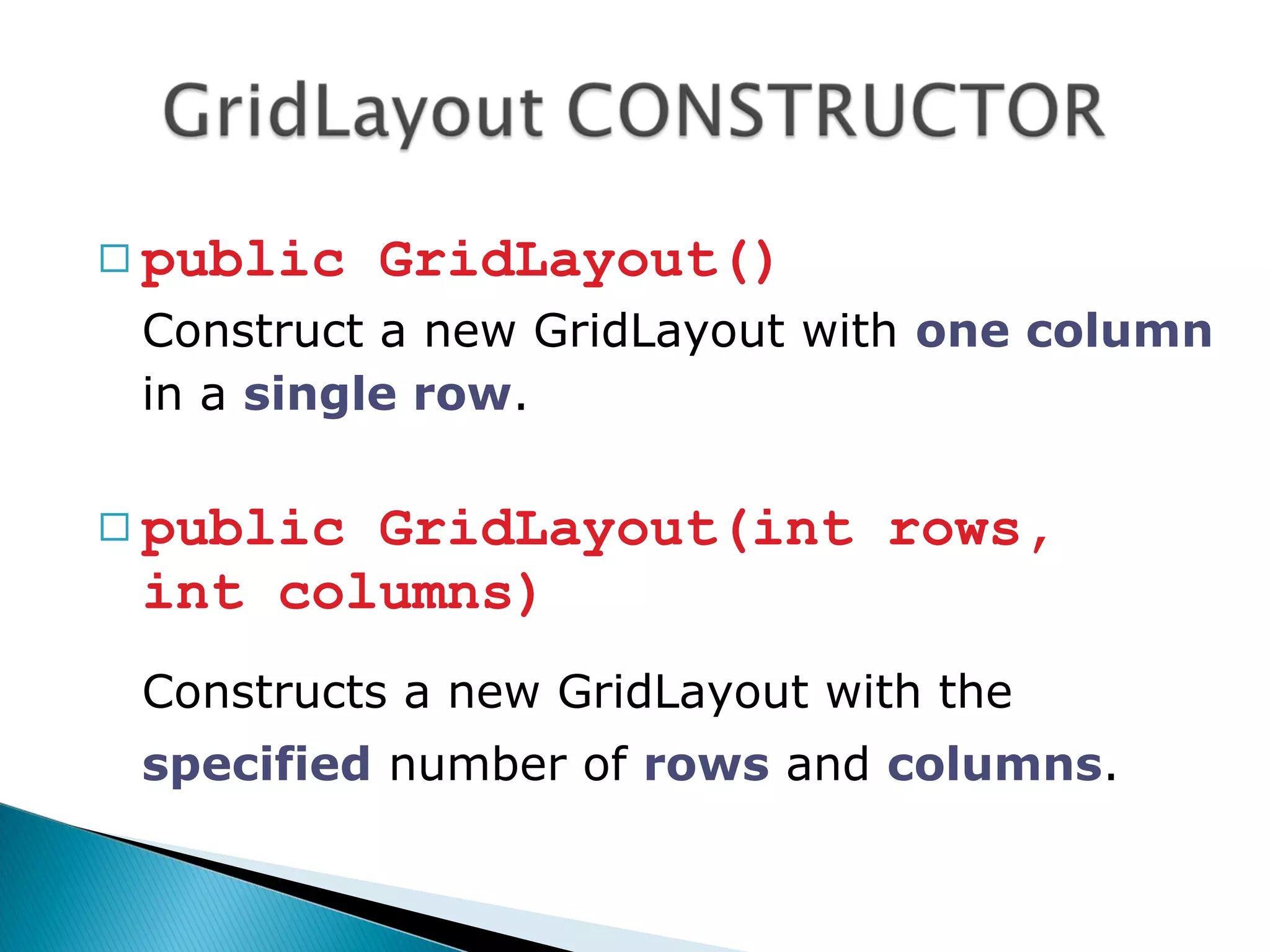
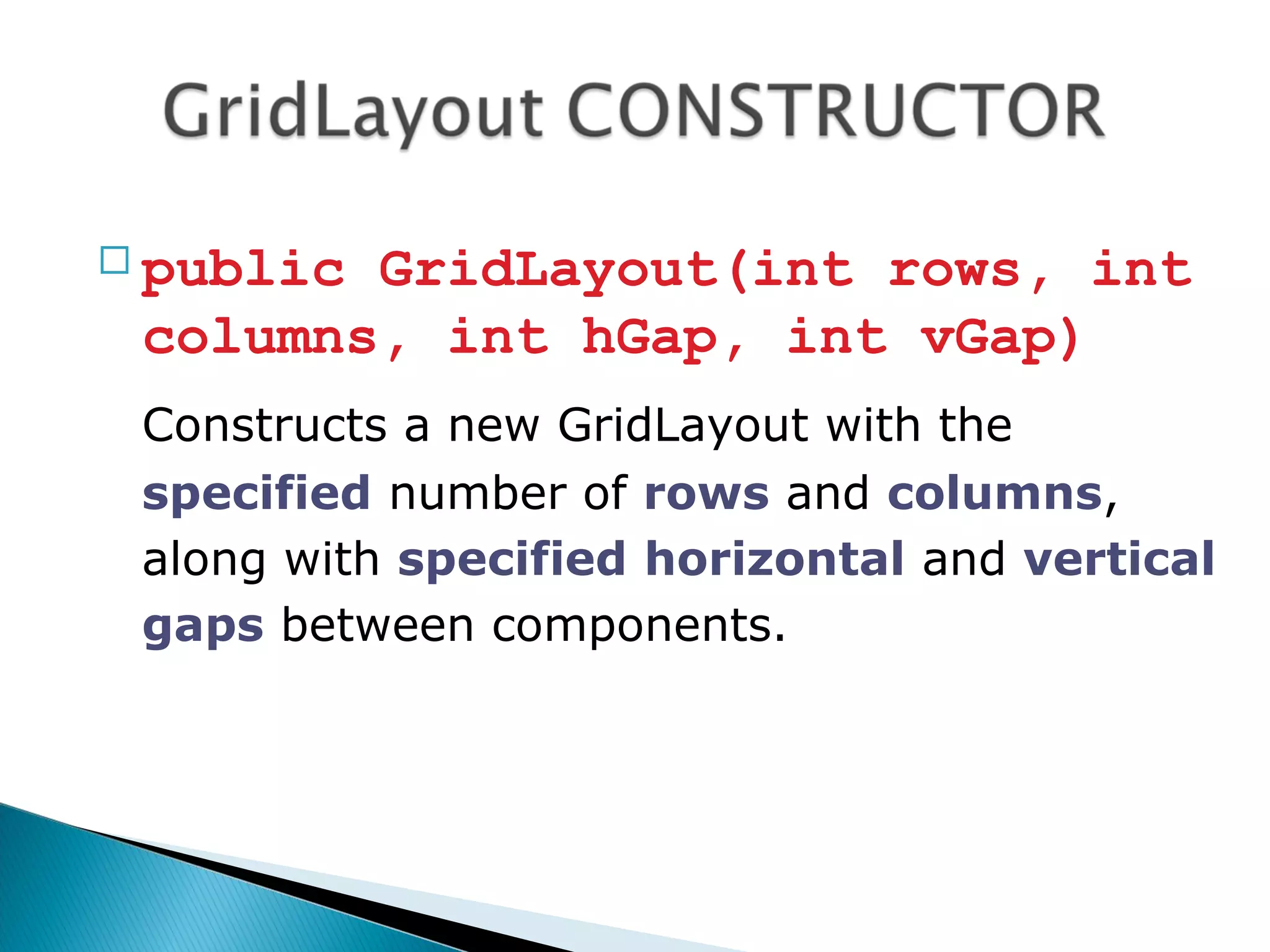
public class TestGridLayout extends JFrame
{
public TestGridLayout()
{
super(“Create GridLayout");
Container s = getContentPane();
s.setLayout(new GridLayout(3,2,20,10));
for (int i=1; i<7;i++)
s.add(new Button("button "+i));
setSize(350,200);
setVisible(true);
}
public static void main(String[] arg)
{
TestGridLayout t = new TestGridLayout();
t.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap11-141222203608-conversion-gate02/75/Chap1-1-4-14-2048.jpg)

![import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
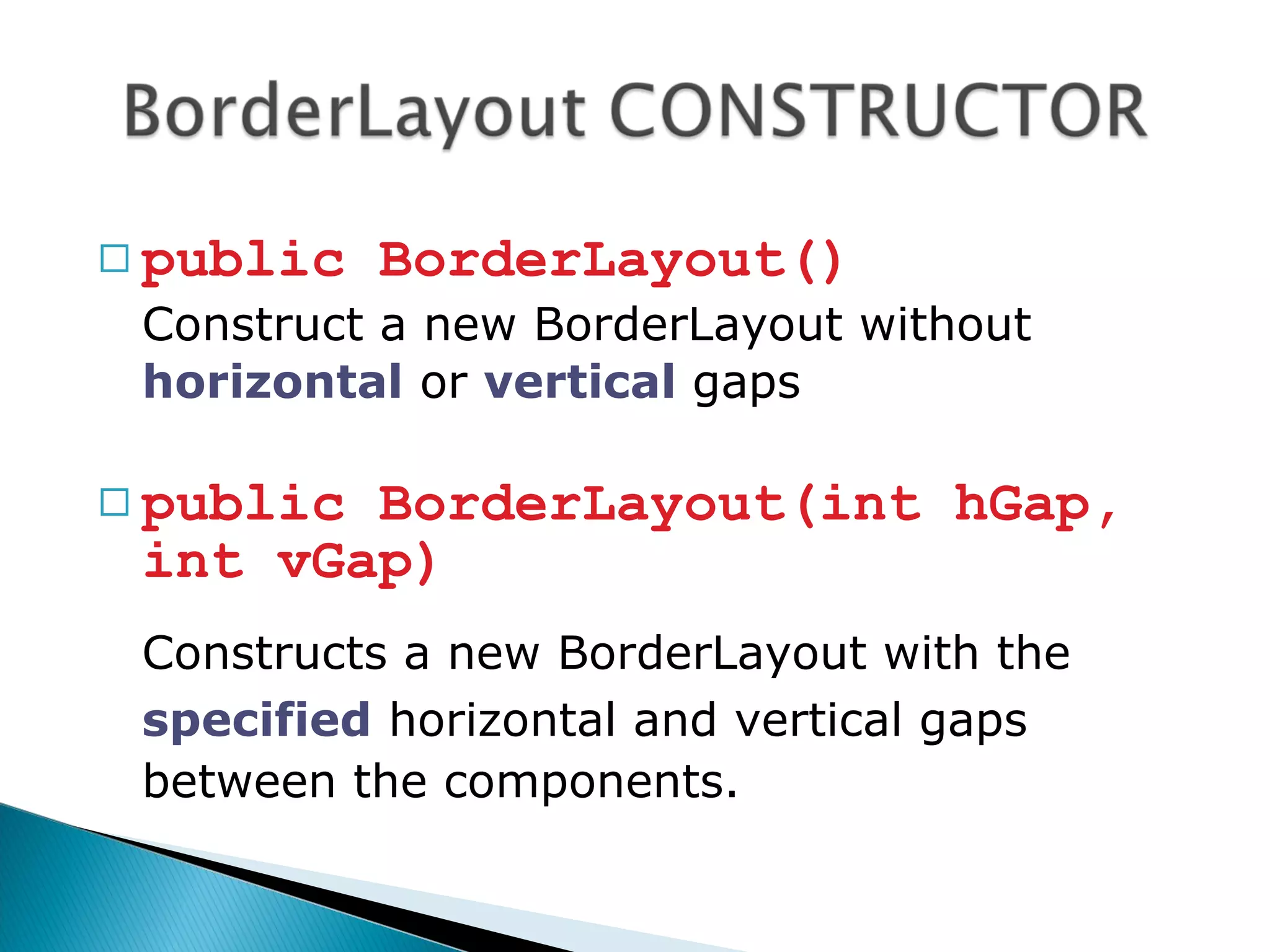
public class TestBorderLayout extends JFrame
{
public TestBorderLayout()
{
super(“Create BorderLayout");
Container s = getContentPane();
s.setLayout(new BorderLayout(20,10));
Button bNorth = new Button(“North");
Button bSouth = new Button(“South");
Button bEast = new Button(“East");
Button bWest = new Button(“West");
Button bCenter = new Button(“Center");
s.add(bNorth,BorderLayout.NORTH);
s.add(bSouth,BorderLayout.SOUTH);
s.add(bEast,BorderLayout.EAST);
s.add(bWest,BorderLayout.WEST);
s.add(bCenter,BorderLayout.CENTER);
setSize(350,200);
setVisible(true);
}
public static void main(String[] arg)
{
TestBorderLayout t = new TestBorderLayout();
t.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap11-141222203608-conversion-gate02/75/Chap1-1-4-17-2048.jpg)
![import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class TestBorderLayout extends JFrame
{
public TestBorderLayout()
{
super(“Create BorderLayout");
Container s = getContentPane();
s.setLayout(new BorderLayout(20,10));
Button bNorth = new Button(“North");
Button bSouth = new Button(“South");
Button bEast = new Button(“East");
Button bWest = new Button(“West");
Button bCenter = new Button(“Center");
//s.add(bNorth,BorderLayout.NORTH);
s.add(bSouth,BorderLayout.SOUTH);
s.add(bEast,BorderLayout.EAST);
s.add(bWest,BorderLayout.WEST);
s.add(bCenter,BorderLayout.CENTER);
setSize(350,200);
setVisible(true);
}
public static void main(String[] arg)
{
TestBorderLayout t = new TestBorderLayout();
t.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap11-141222203608-conversion-gate02/75/Chap1-1-4-18-2048.jpg)
![import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class TestBorderLayout extends JFrame
{
public TestBorderLayout()
{
super(“Create BorderLayout");
Container s = getContentPane();
s.setLayout(new BorderLayout(20,10));
Button bNorth = new Button(“North");
Button bSouth = new Button(“South");
Button bEast = new Button(“East");
Button bWest = new Button(“West");
Button bCenter = new Button(“Center");
s.add(bNorth,BorderLayout.NORTH);
s.add(bSouth,BorderLayout.SOUTH);
//s.add(bEast,BorderLayout.EAST);
s.add(bWest,BorderLayout.WEST);
s.add(bCenter,BorderLayout.CENTER);
setSize(350,200);
setVisible(true);
}
public static void main(String[] arg)
{
TestBorderLayout t = new TestBorderLayout();
t.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap11-141222203608-conversion-gate02/75/Chap1-1-4-19-2048.jpg)
![import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class TestBorderLayout extends JFrame
{
public TestBorderLayout()
{
super(“Create BorderLayout");
Container s = getContentPane();
s.setLayout(new BorderLayout(20,10));
Button bNorth = new Button(“North");
Button bSouth = new Button(“South");
Button bEast = new Button(“East");
Button bWest = new Button(“West");
Button bCenter = new Button(“Center");
//s.add(bNorth,BorderLayout.NORTH);
s.add(bSouth,BorderLayout.SOUTH);
//s.add(bEast,BorderLayout.EAST);
//s.add(bWest,BorderLayout.WEST);
s.add(bCenter,BorderLayout.CENTER);
setSize(350,200);
setVisible(true);
}
public static void main(String[] arg)
{
TestBorderLayout t = new TestBorderLayout();
t.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap11-141222203608-conversion-gate02/75/Chap1-1-4-20-2048.jpg)
![import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class TestBorderLayout extends JFrame
{
public TestBorderLayout()
{
super(“Create BorderLayout");
Container s = getContentPane();
s.setLayout(new BorderLayout(20,10));
Button bNorth = new Button(“North");
Button bSouth = new Button(“South");
Button bEast = new Button(“East");
Button bWest = new Button(“West");
Button bCenter = new Button(“Center");
s.add(bNorth,BorderLayout.NORTH);
s.add(bSouth,BorderLayout.SOUTH);
s.add(bEast,BorderLayout.EAST);
s.add(bWest,BorderLayout.WEST);
//s.add(bCenter,BorderLayout.CENTER);
setSize(350,200);
setVisible(true);
}
public static void main(String[] arg)
{
TestBorderLayout t = new TestBorderLayout();
t.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap11-141222203608-conversion-gate02/75/Chap1-1-4-21-2048.jpg)