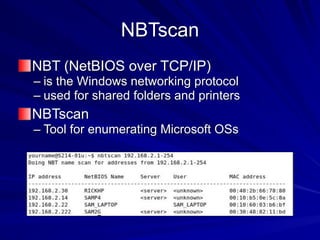
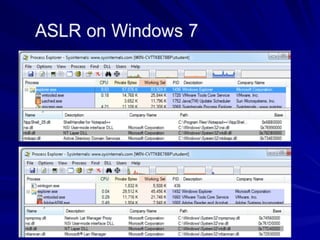
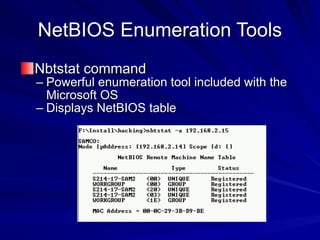
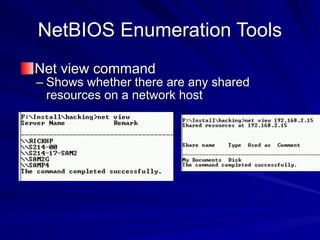
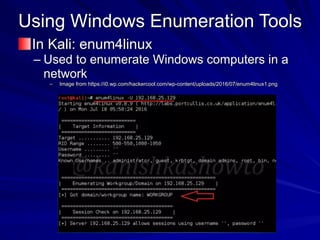
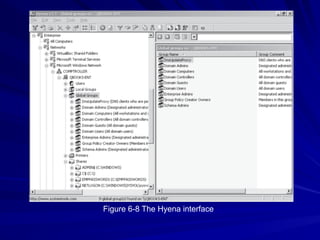
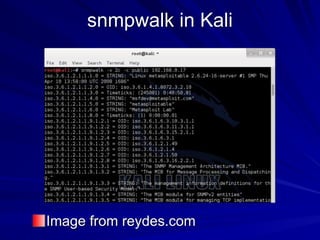
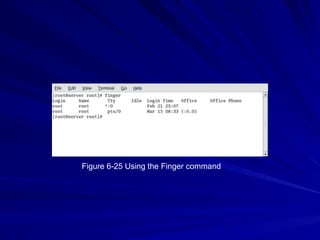
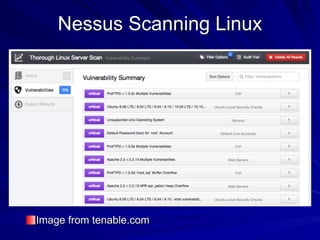
The document is focused on enumeration within the context of ethical hacking and network defense, detailing methods for extracting information about network resources, users, and operating system specifications. It discusses various tools and techniques for enumerating both Microsoft and Unix-based operating systems, highlighting specific features and security upgrades across different Windows versions. Additionally, it covers enumeration tools such as nbtscan, dumpsec, and nessus, which assist in identifying network vulnerabilities and user information.