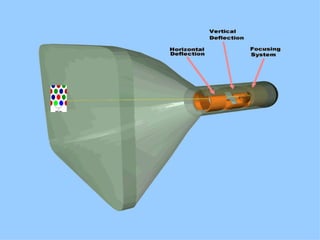
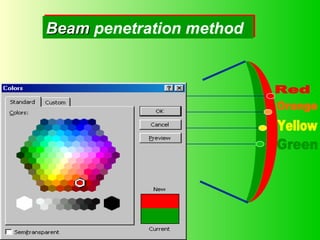
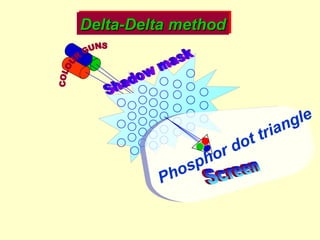
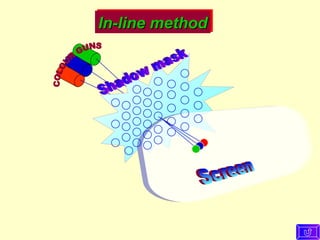
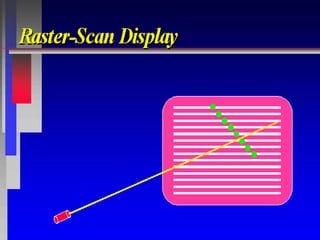
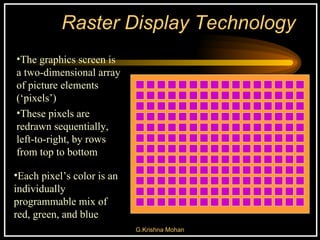
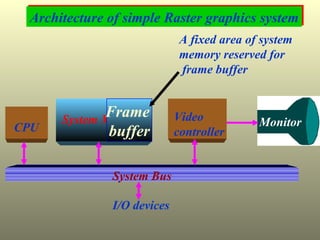
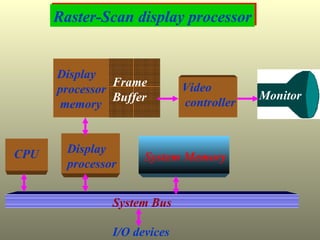
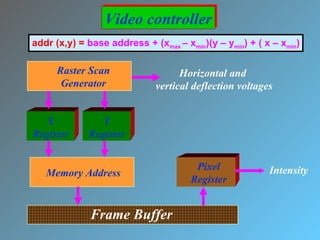
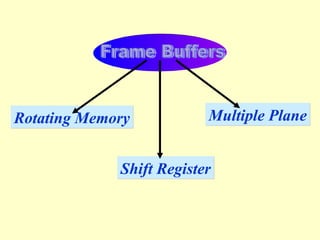
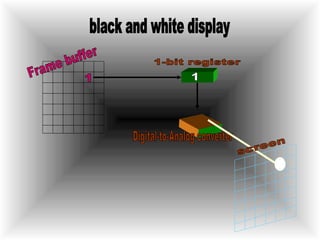
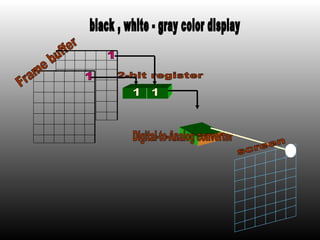
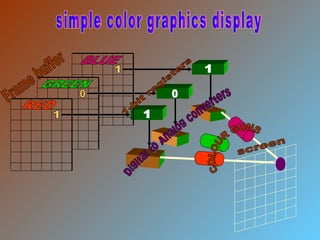
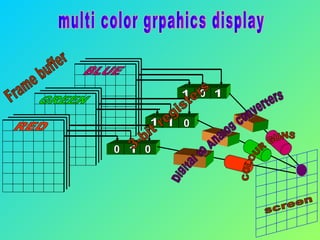
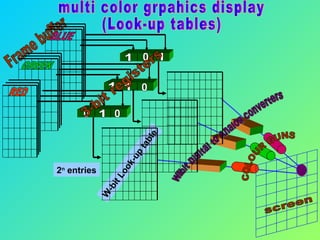
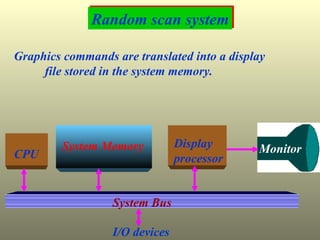
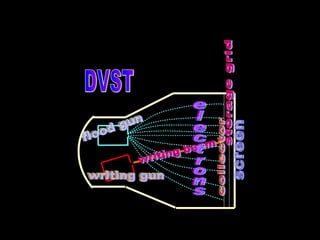
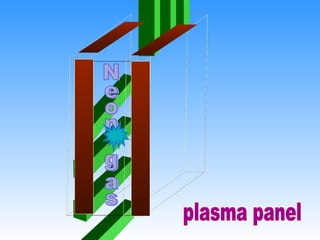
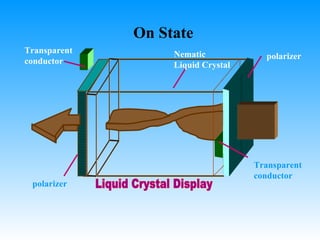
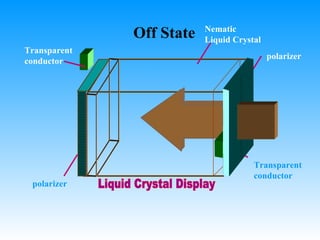
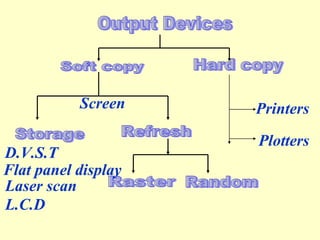
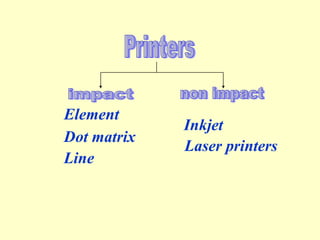
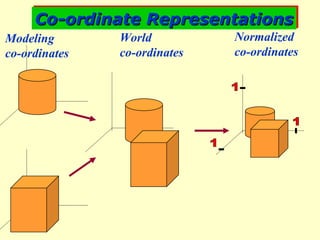
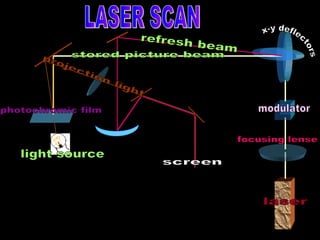
The document discusses different types of graphics display systems including raster scan displays, random scan displays, and flat panel displays. It describes the key components of cathode ray tube (CRT) displays such as the electron gun and phosphor screen and how they generate images. It also covers color reproduction methods for CRTs like beam penetration and three color guns.