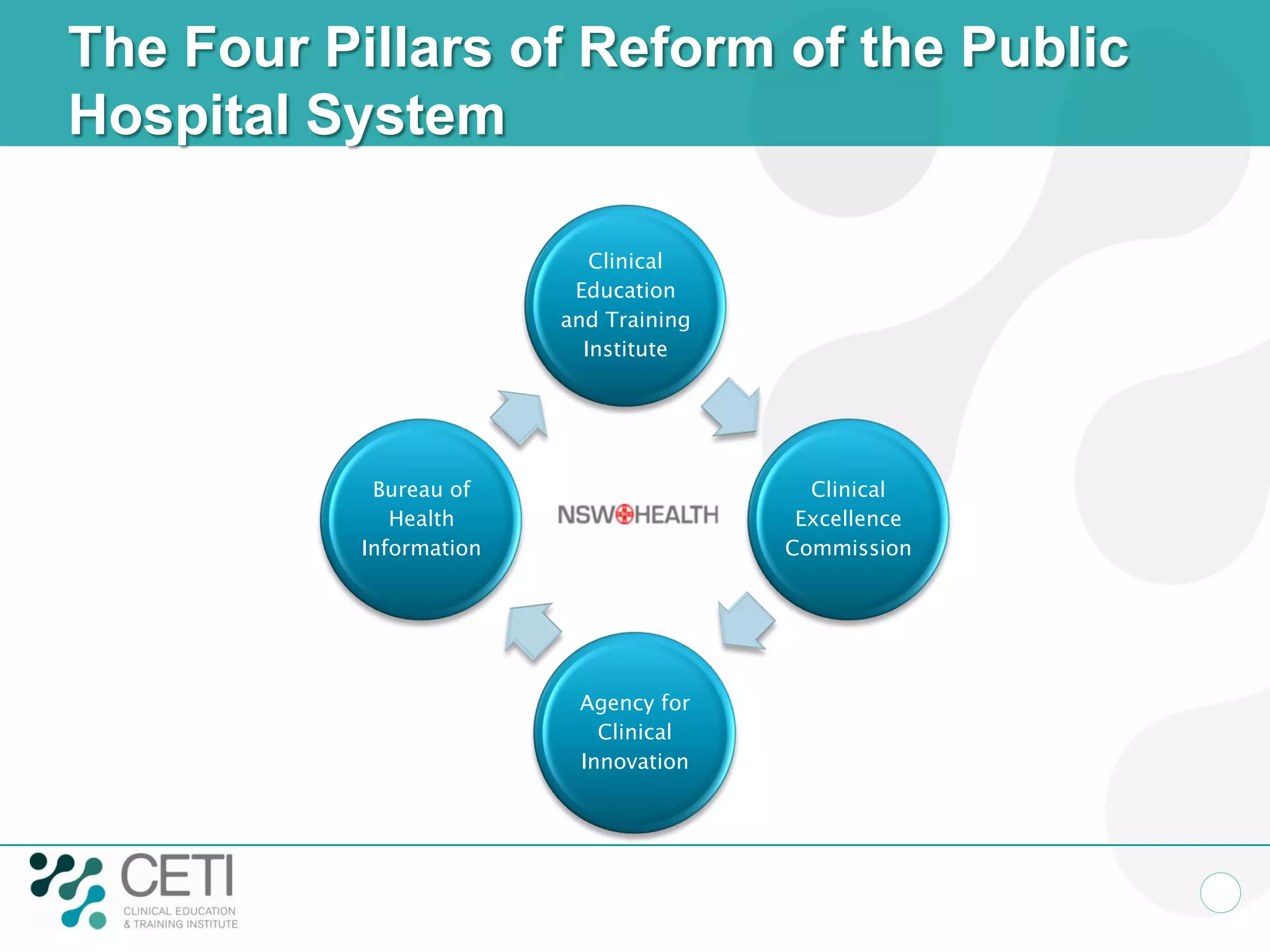
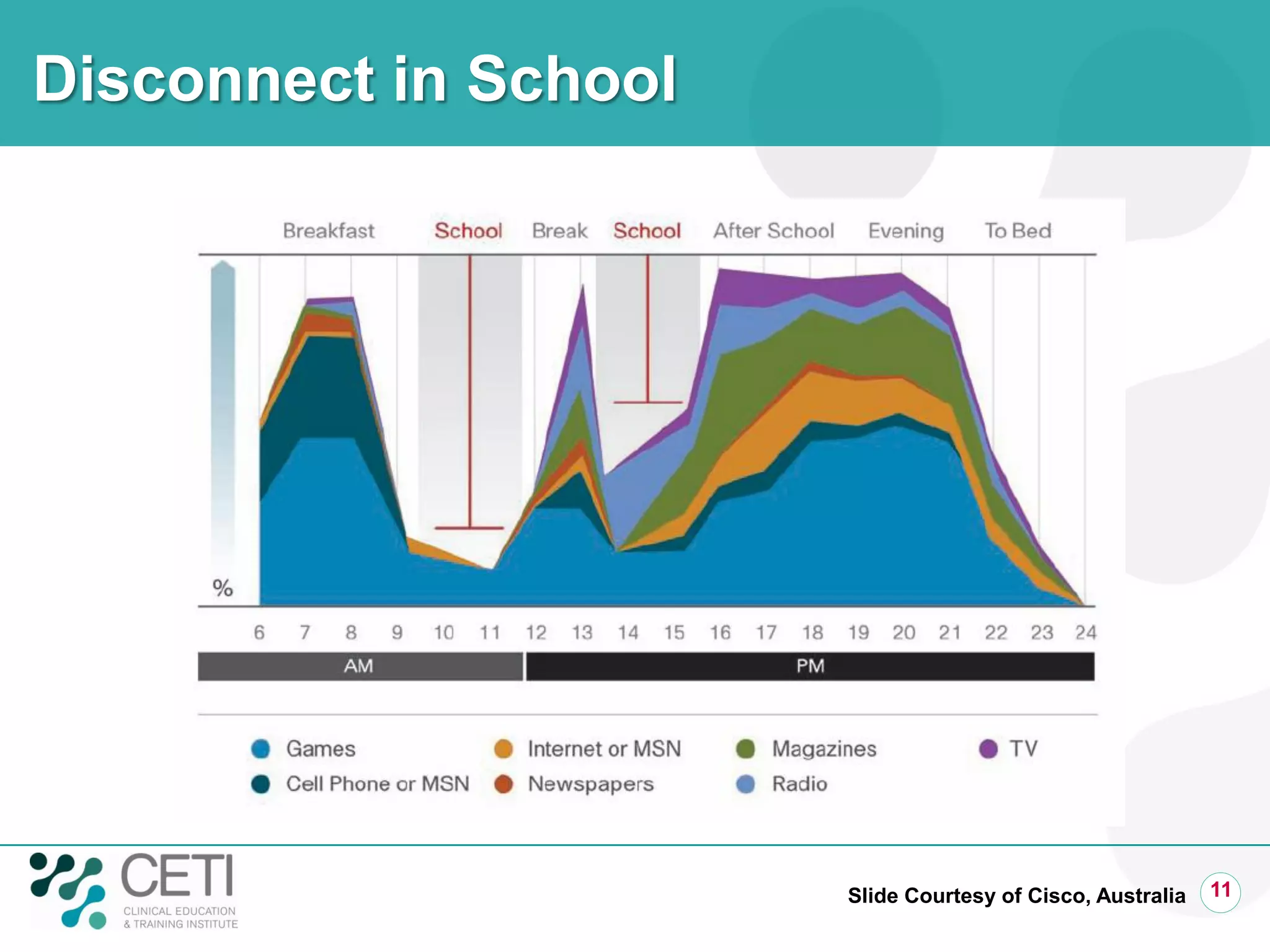
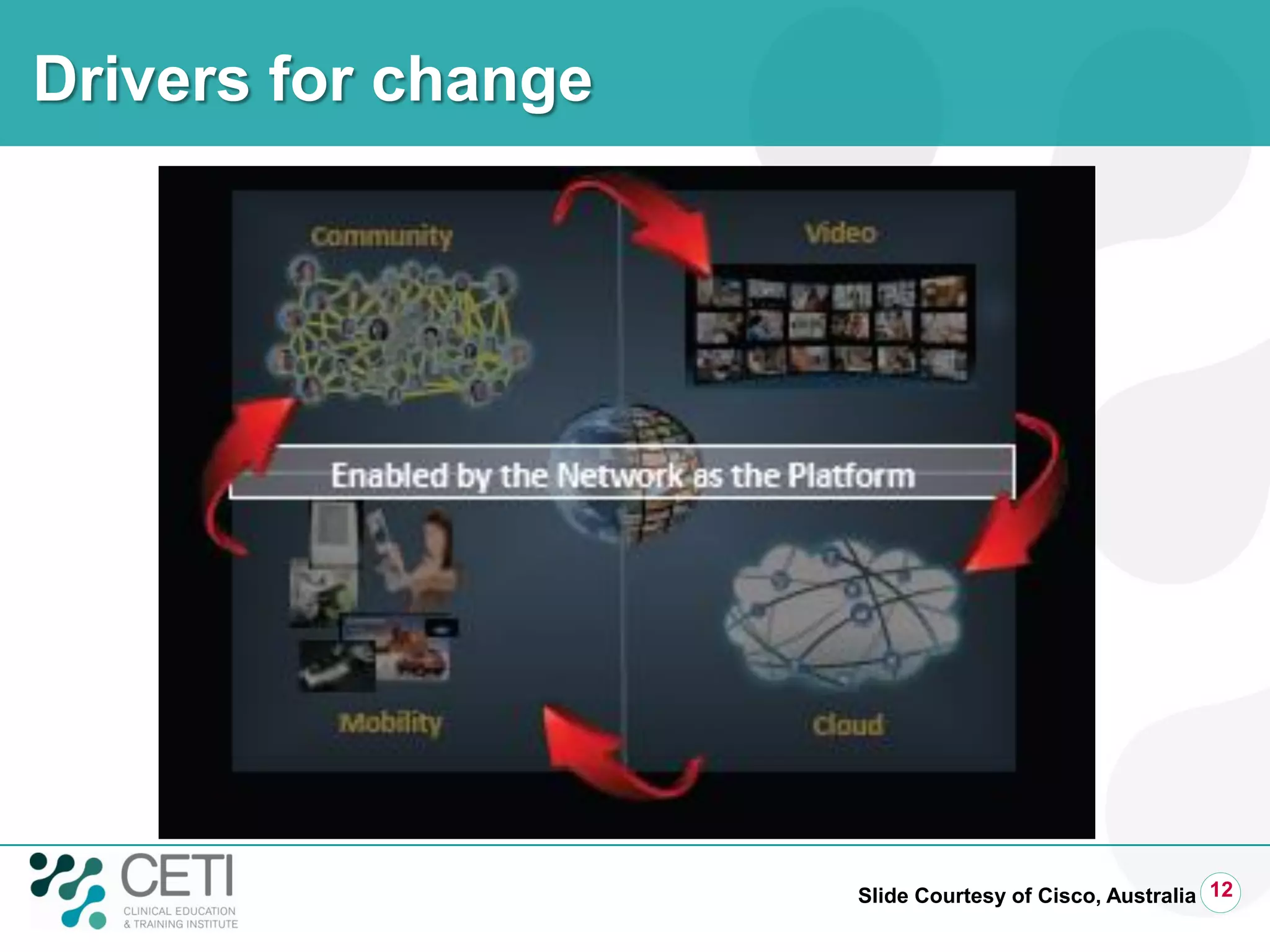
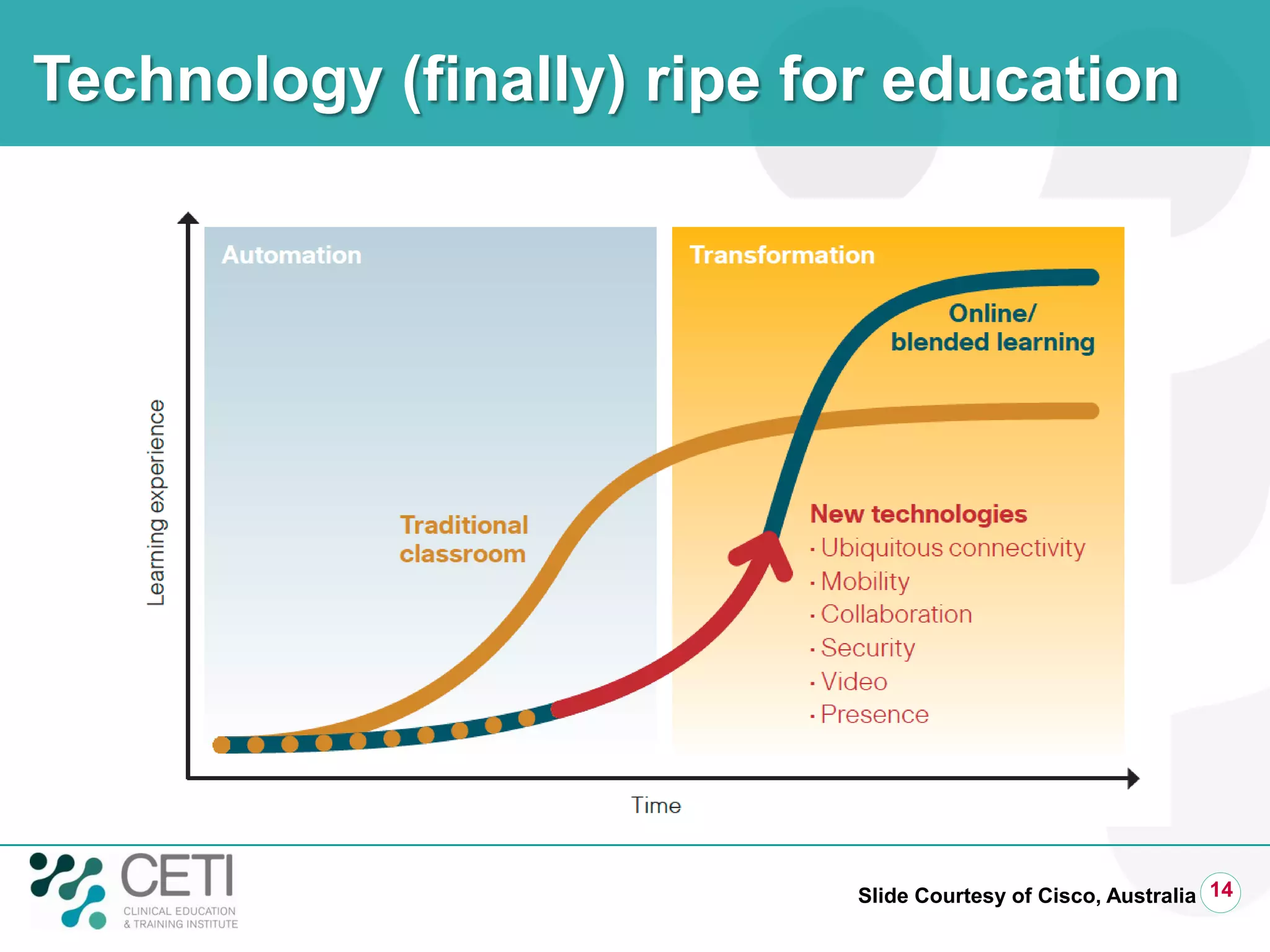
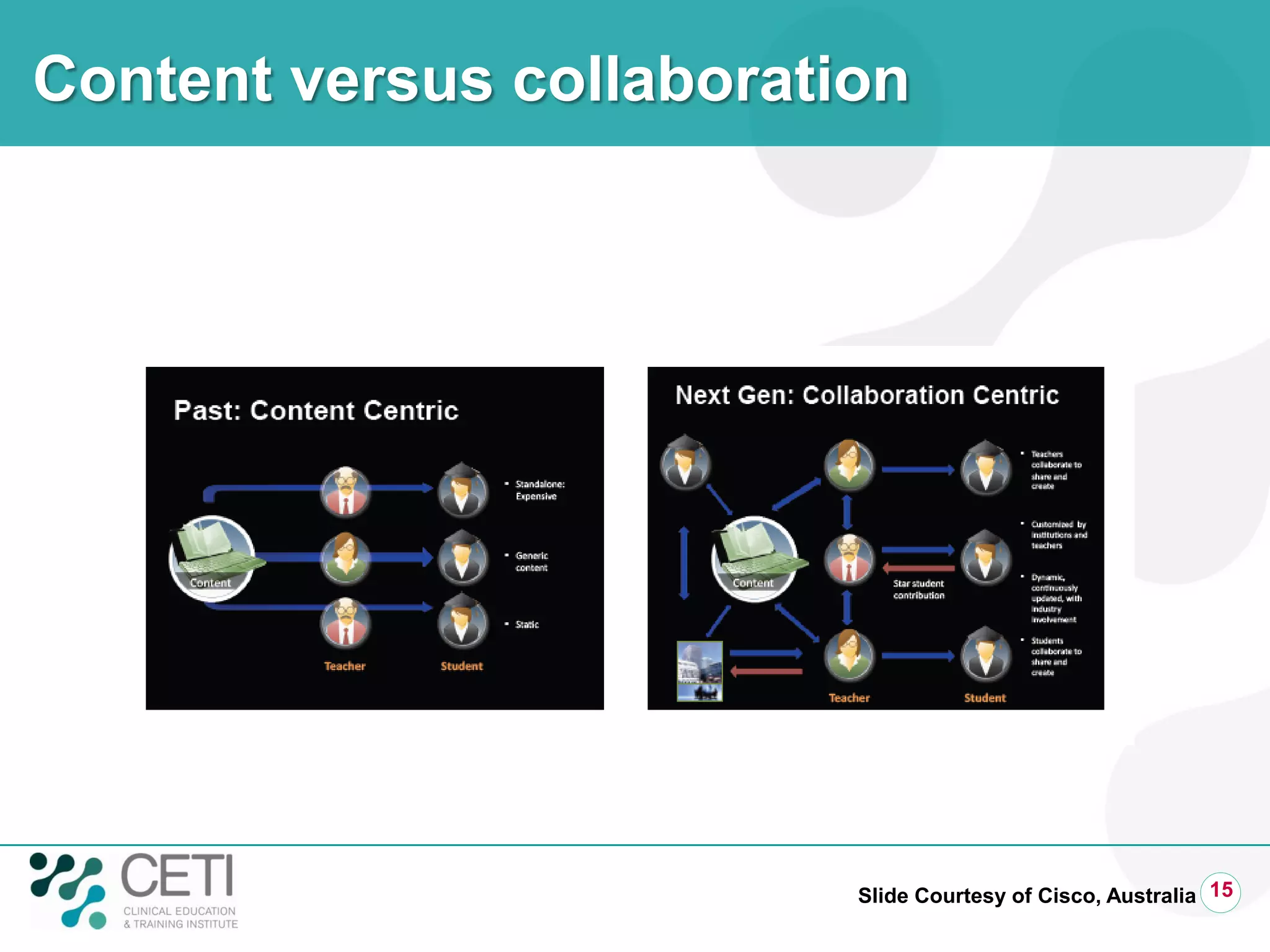
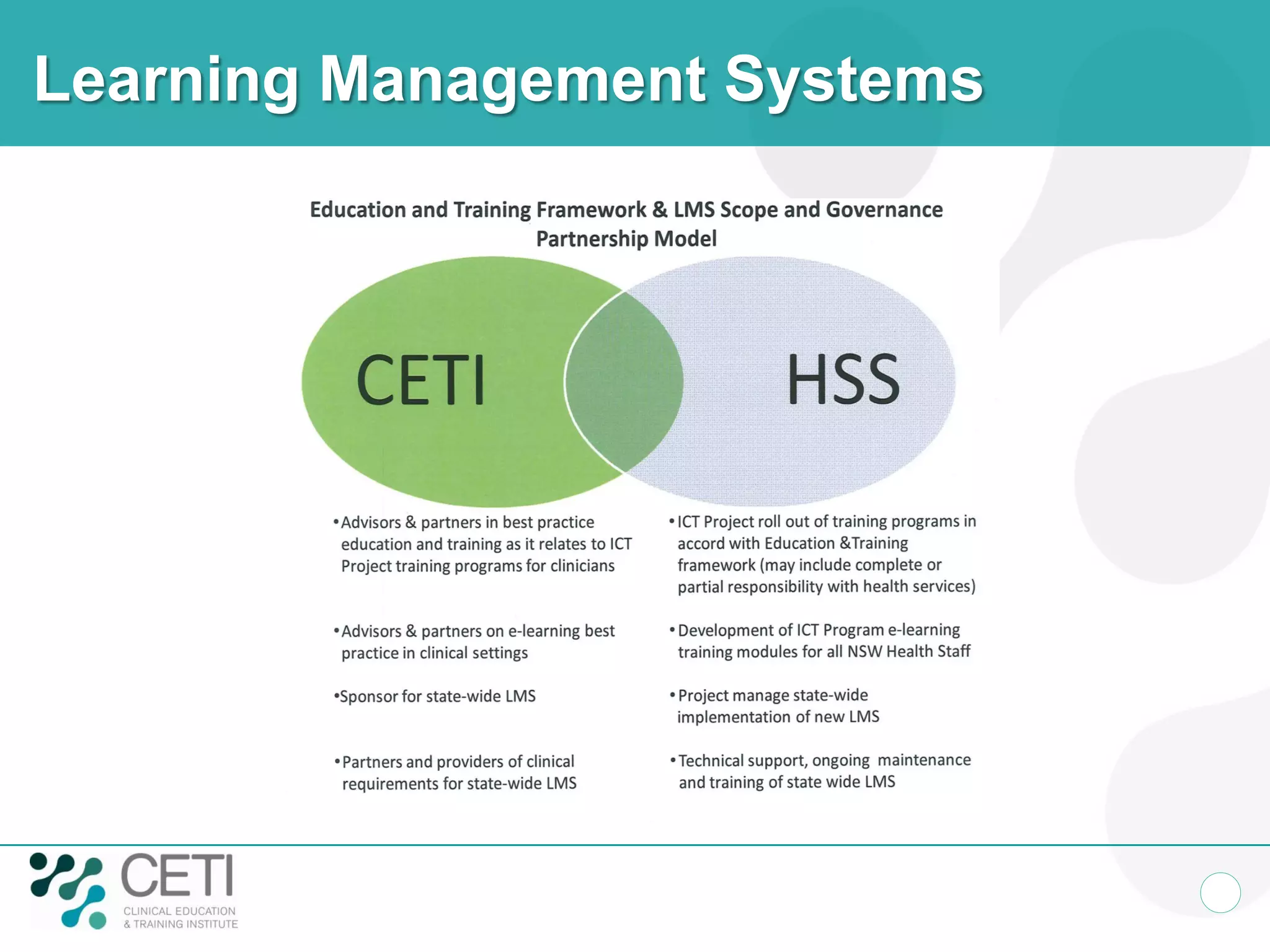
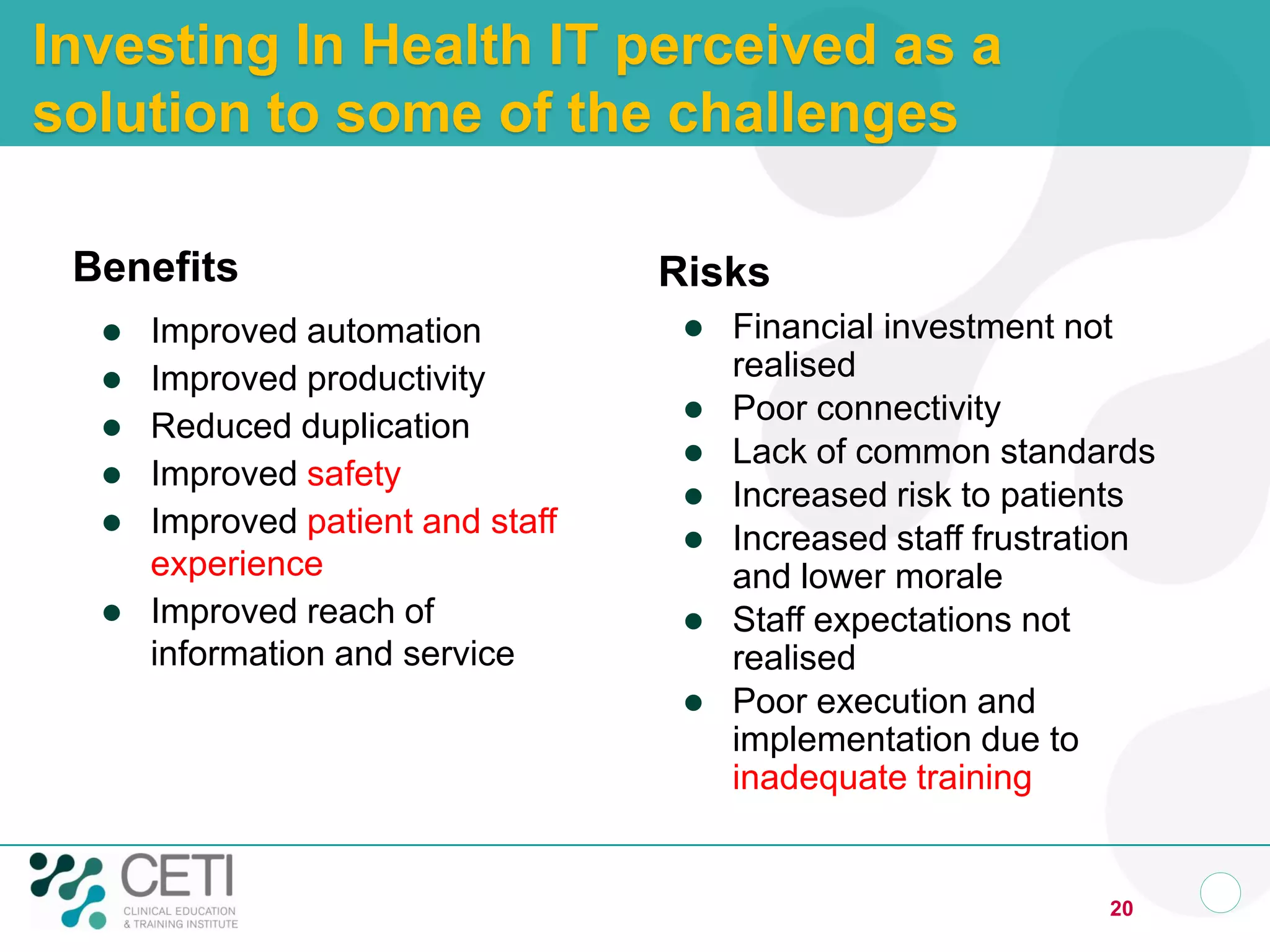
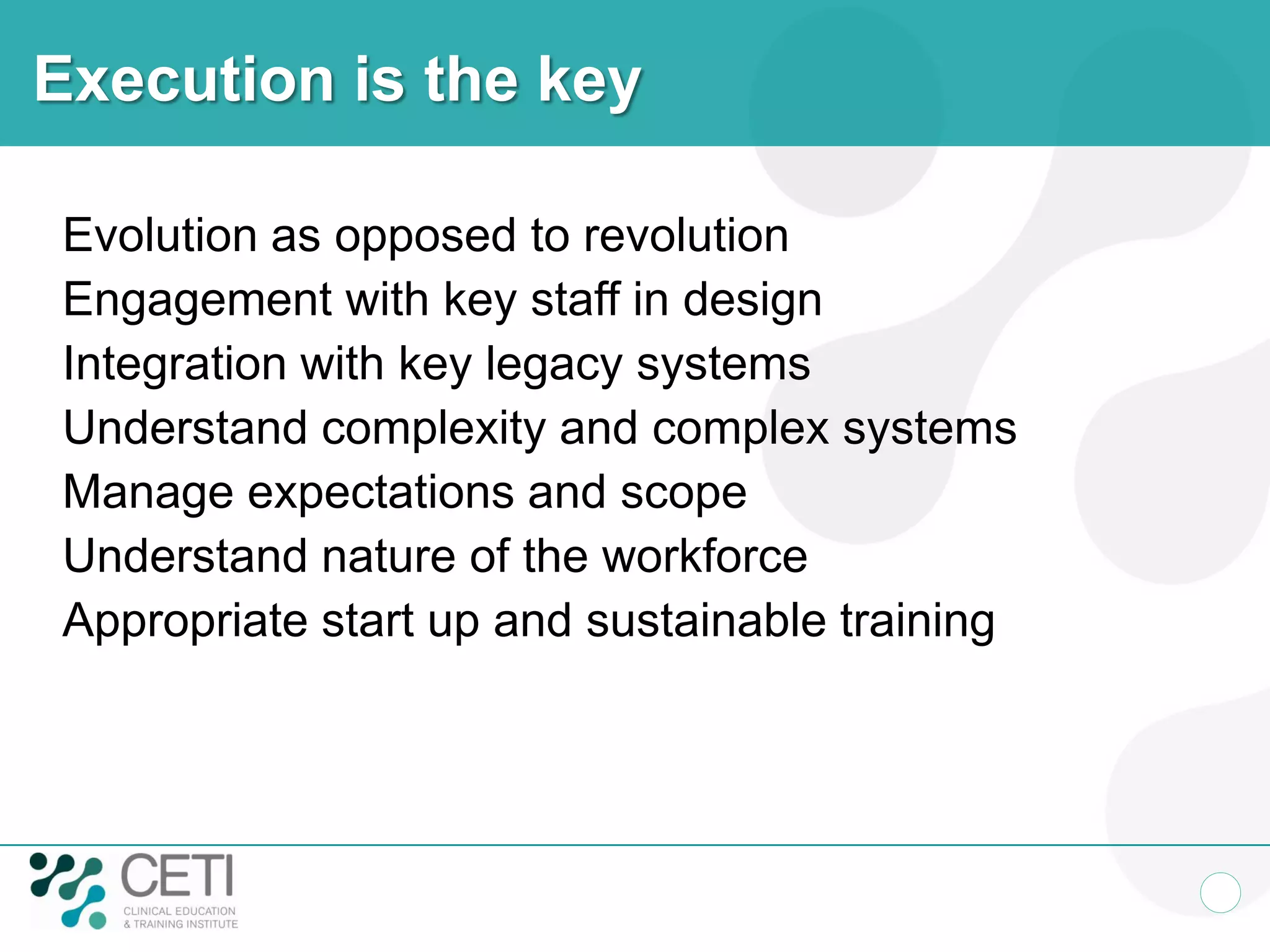
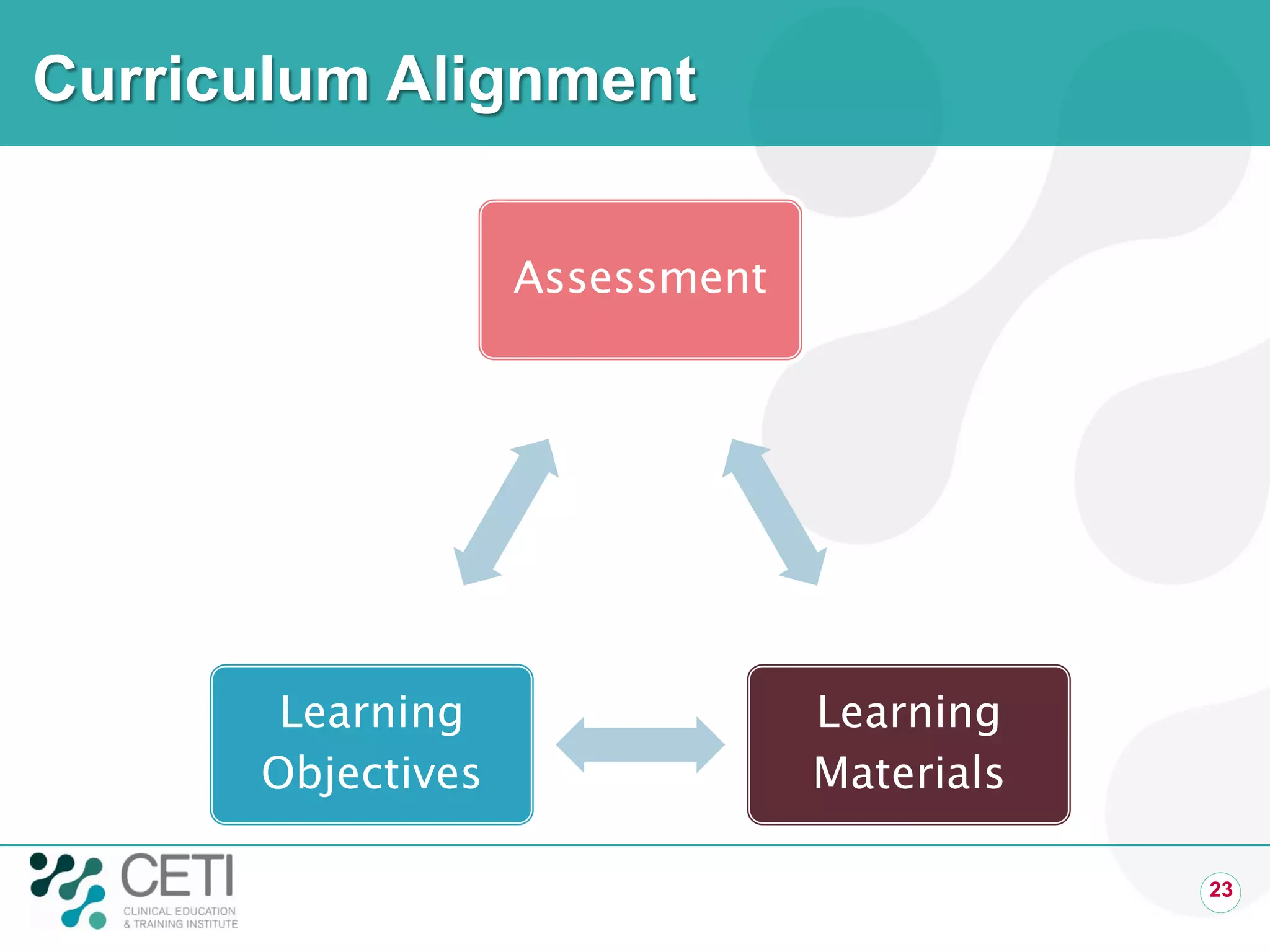
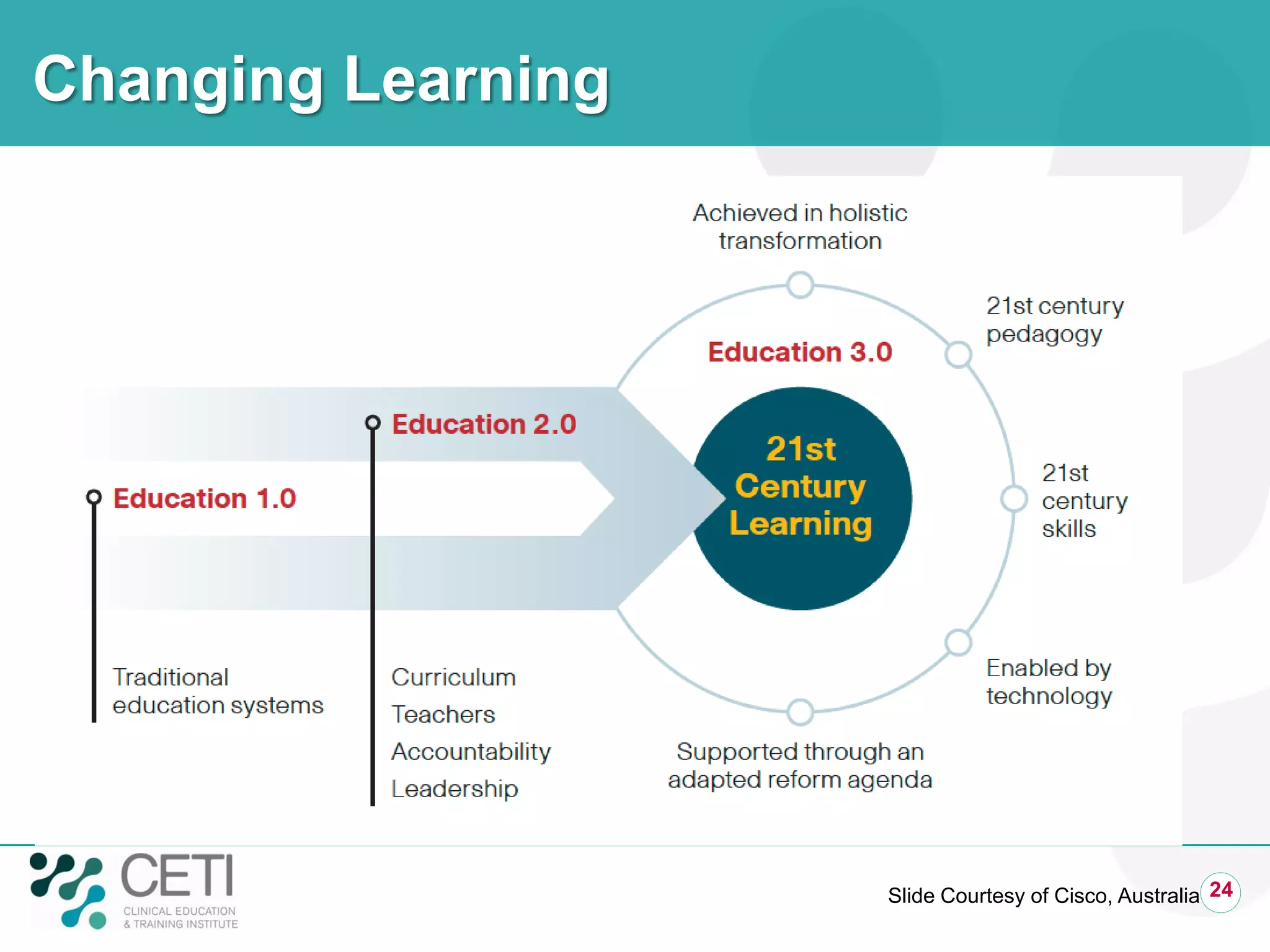
The document discusses challenges facing the health system including rising demand and constrained capacity. It introduces the Clinical Education and Training Institute which aims to improve clinical workforce development through education and training. Key goals include achieving competency standards for graduates and building better clinical supervision systems. Success requires a focus on factors like competency, context, coordination, culture, communication, capacity and collaboration. Technology is seen as enabling new learning models if implemented appropriately through engagement and integration.