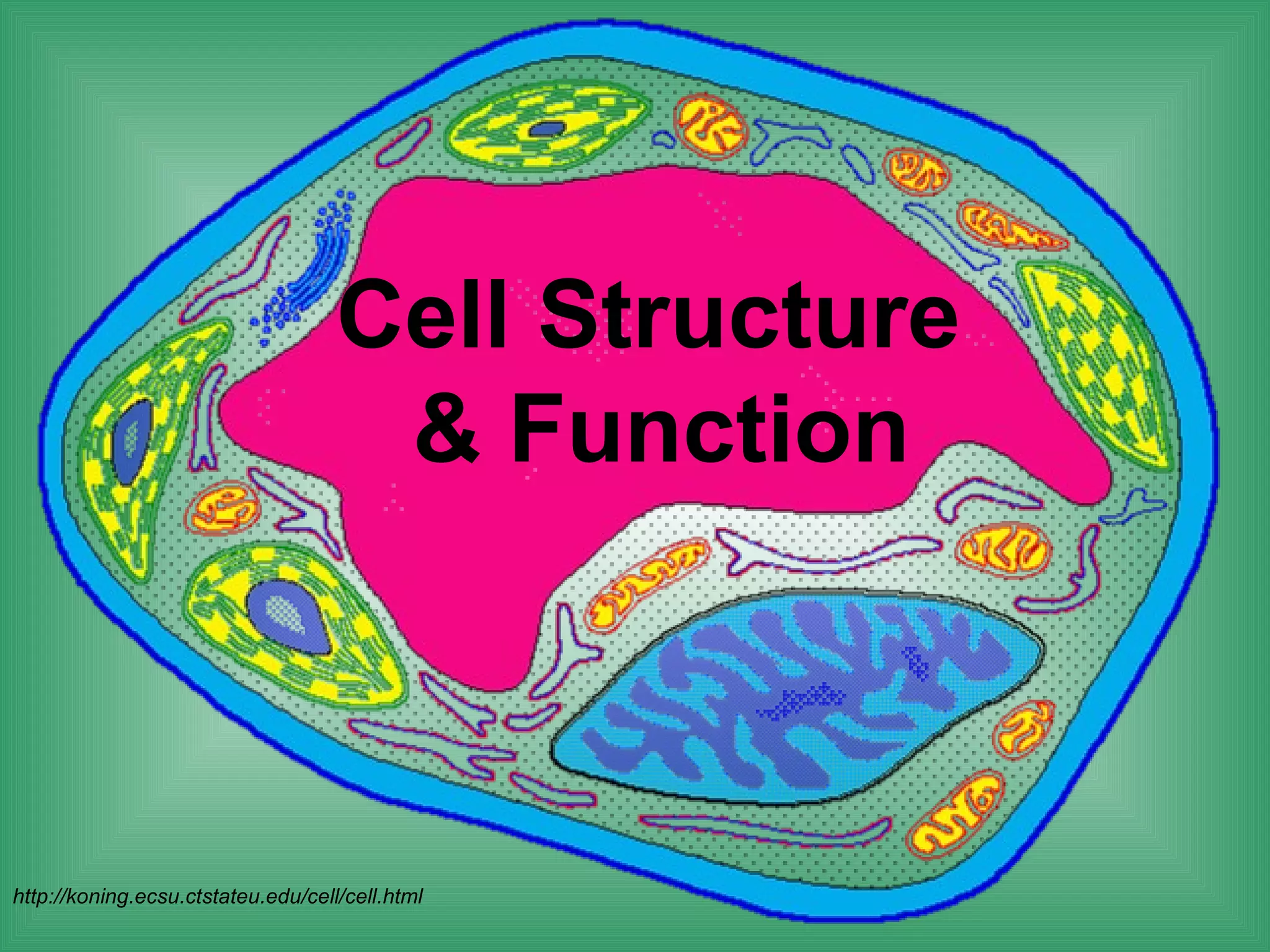
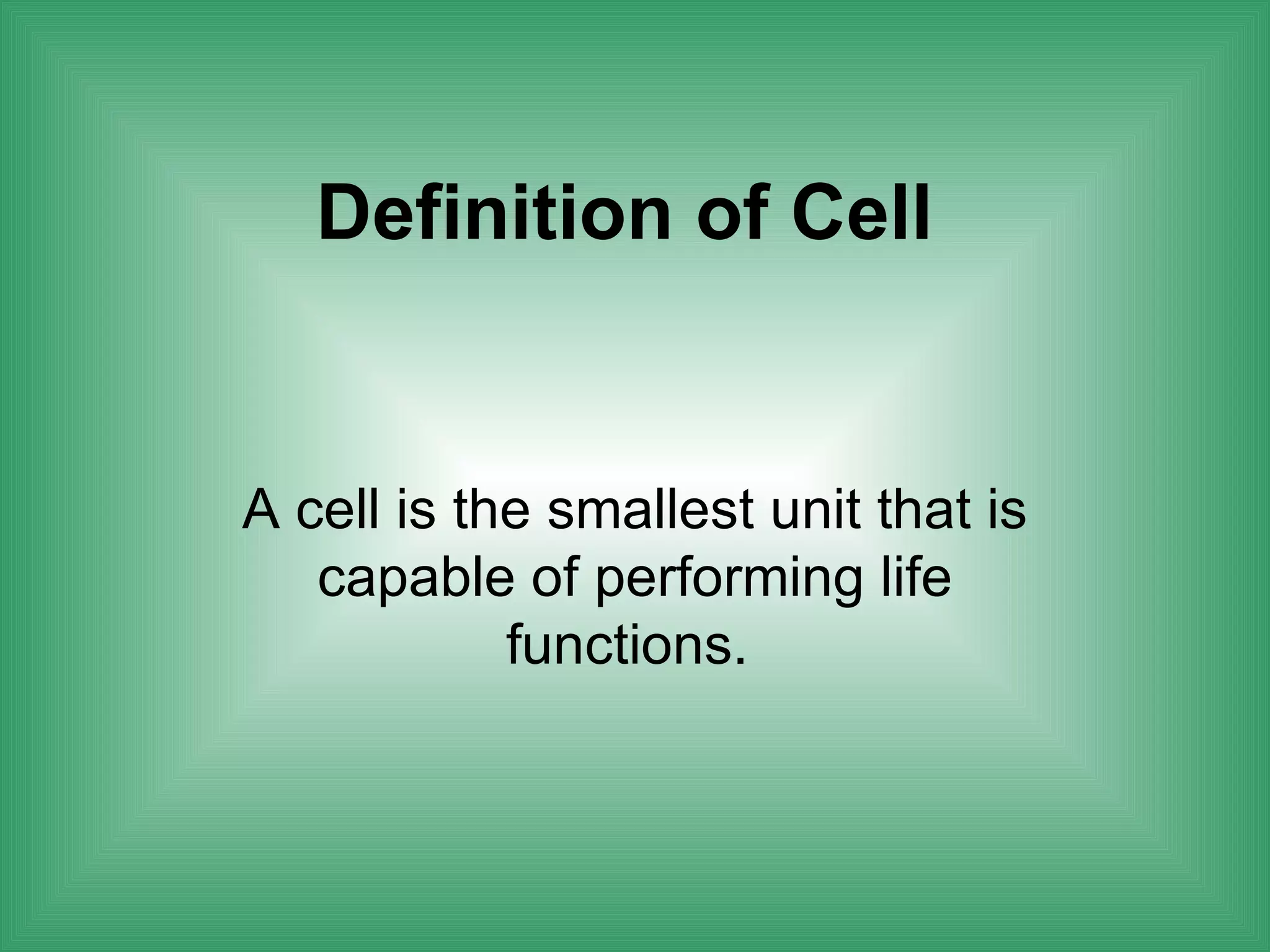
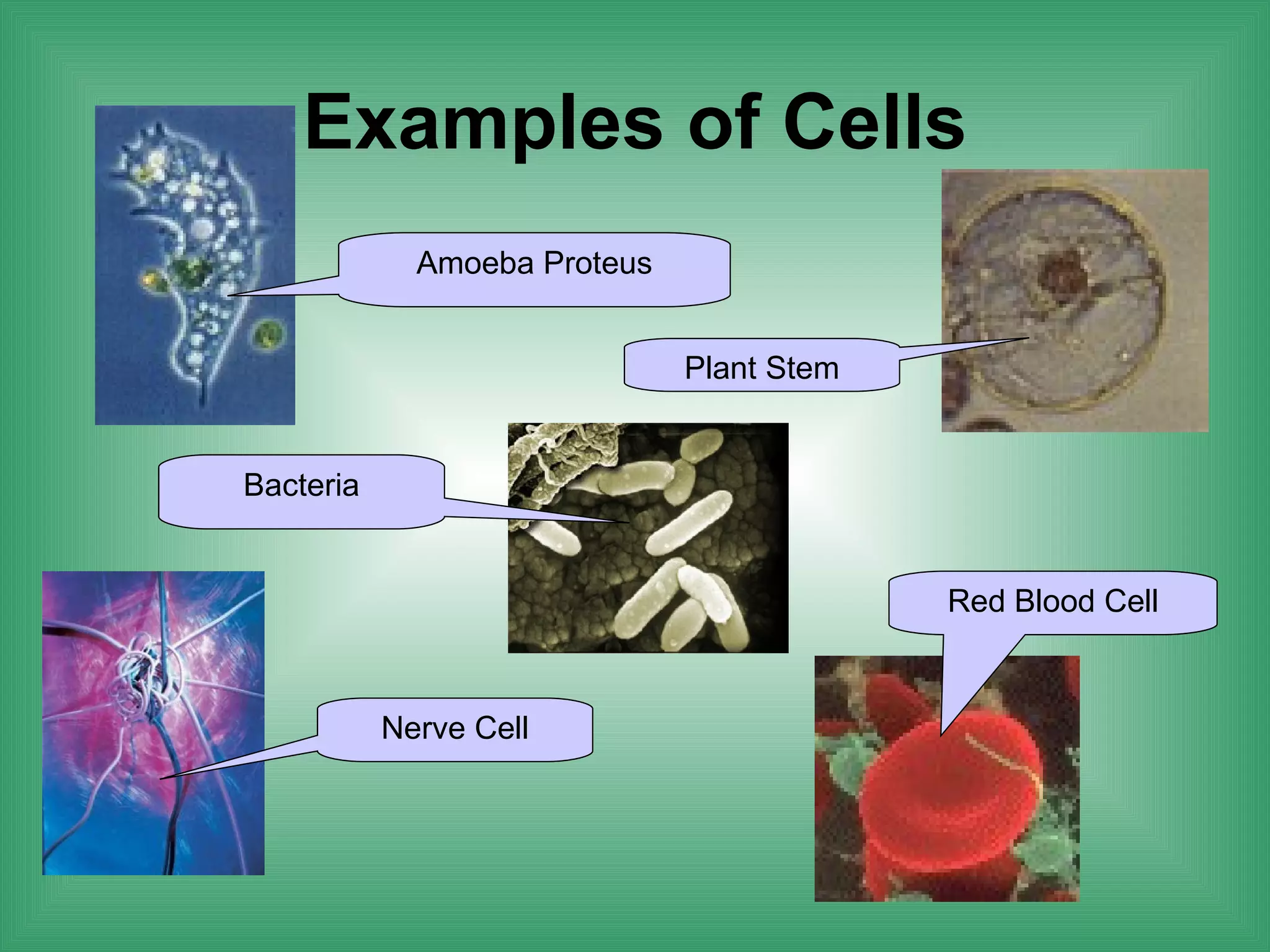
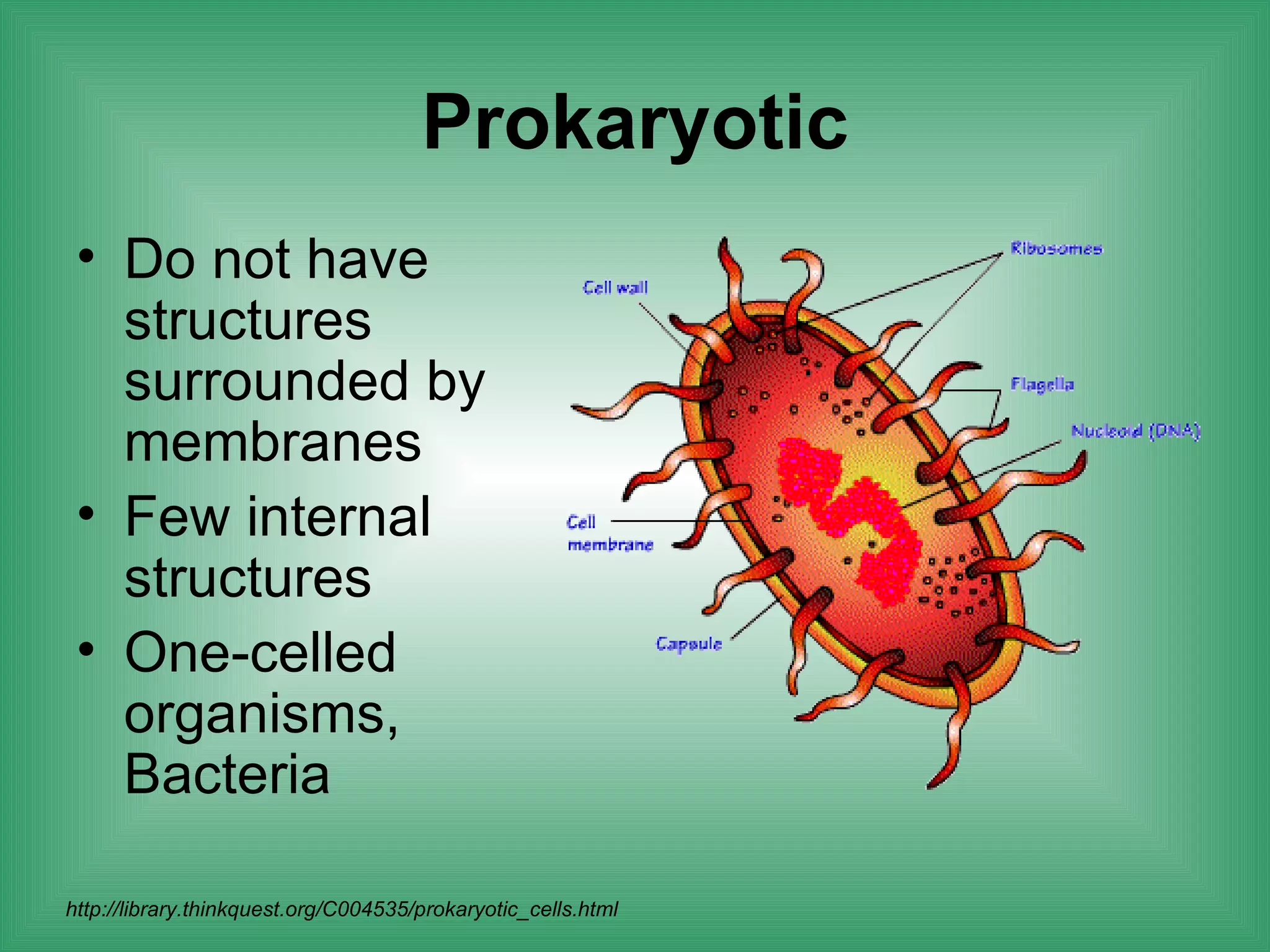
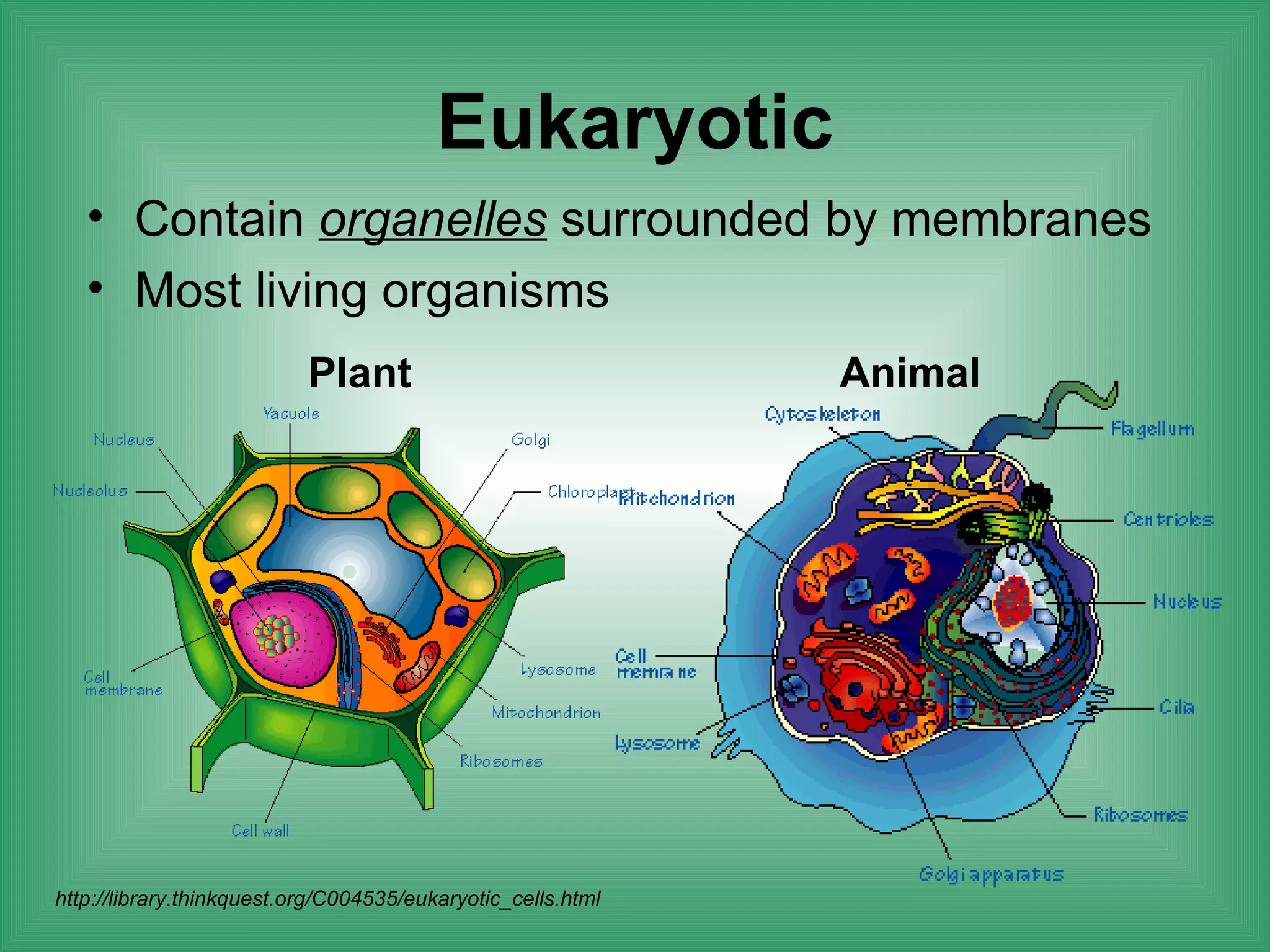
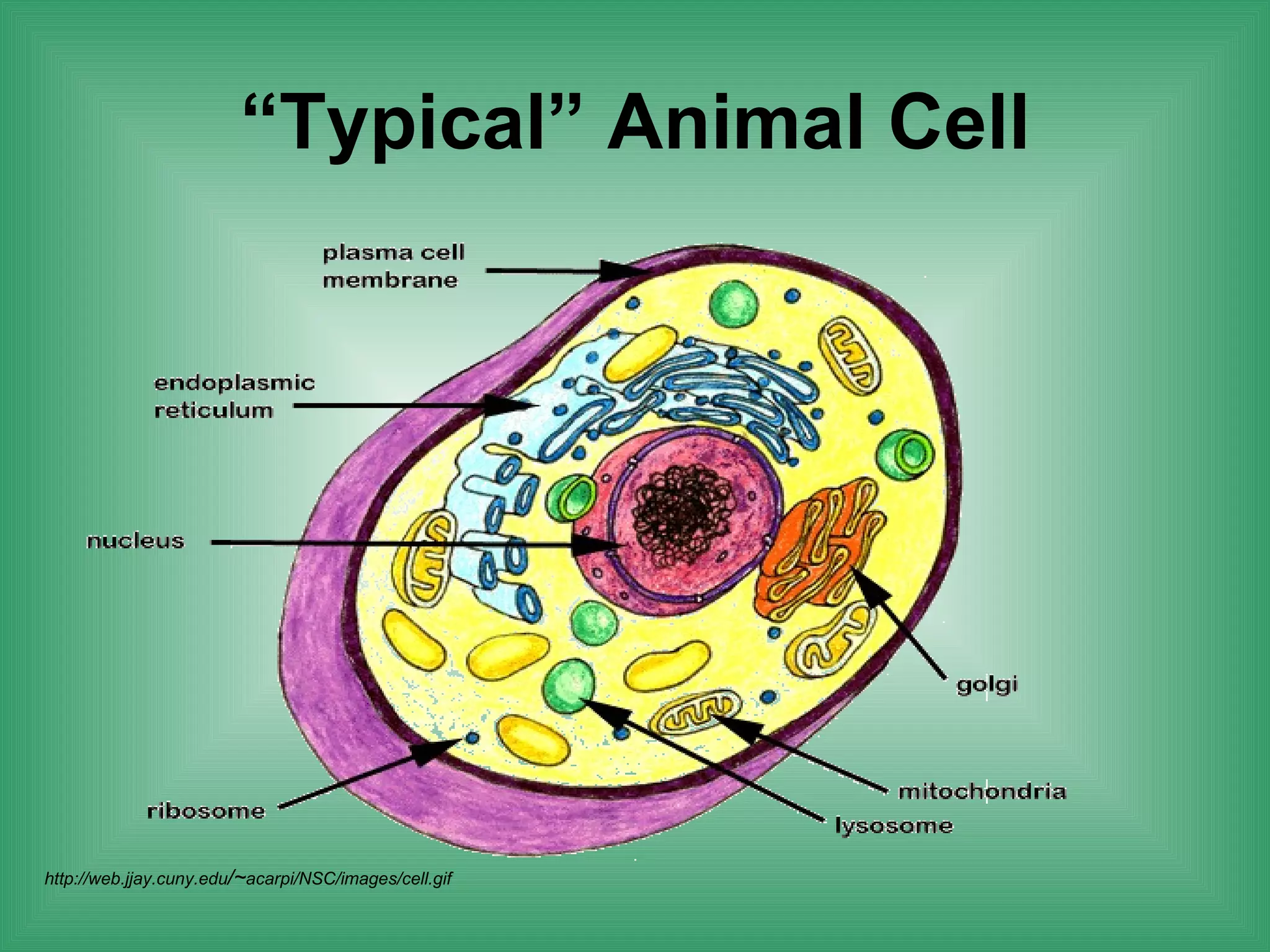
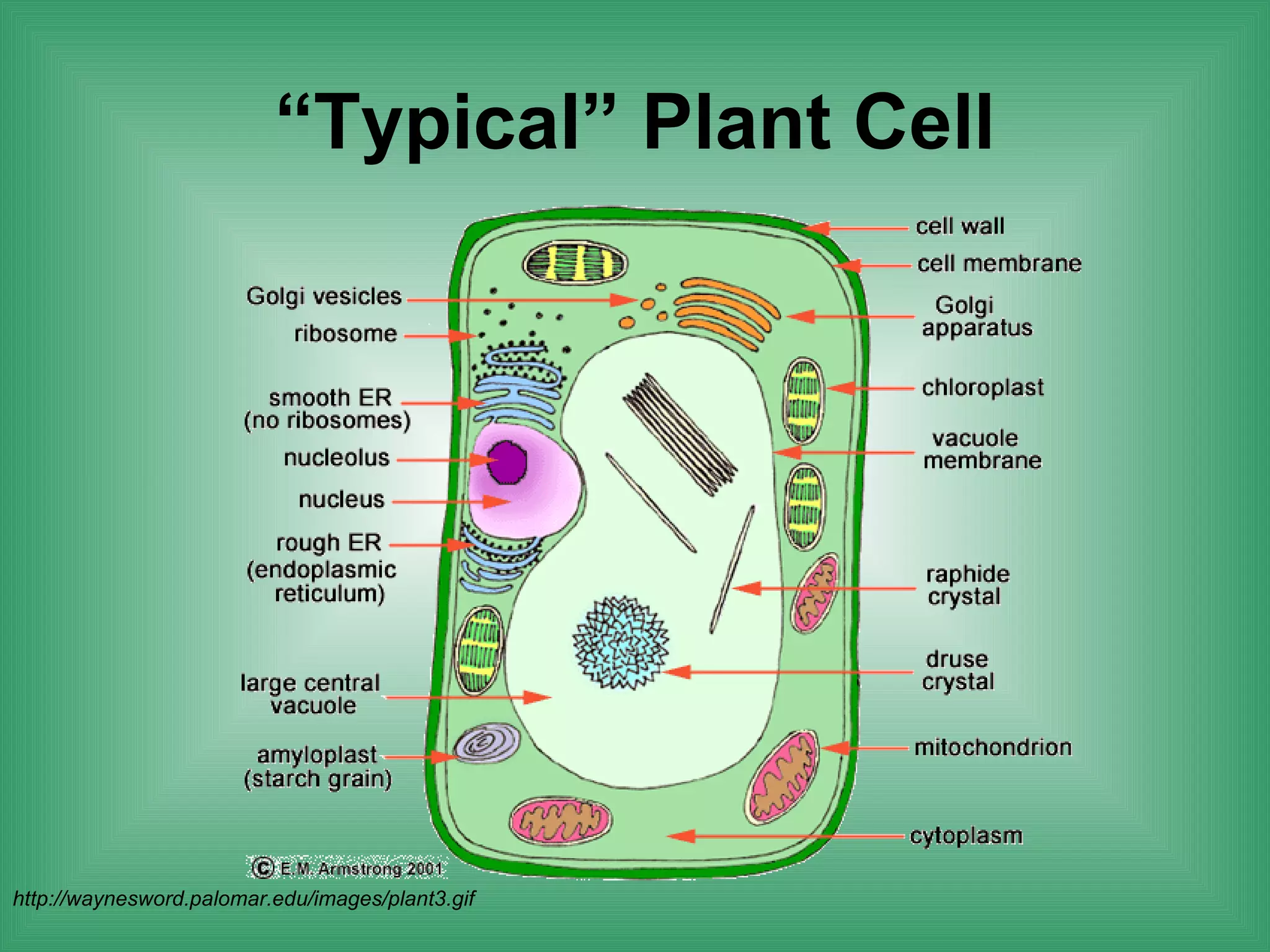
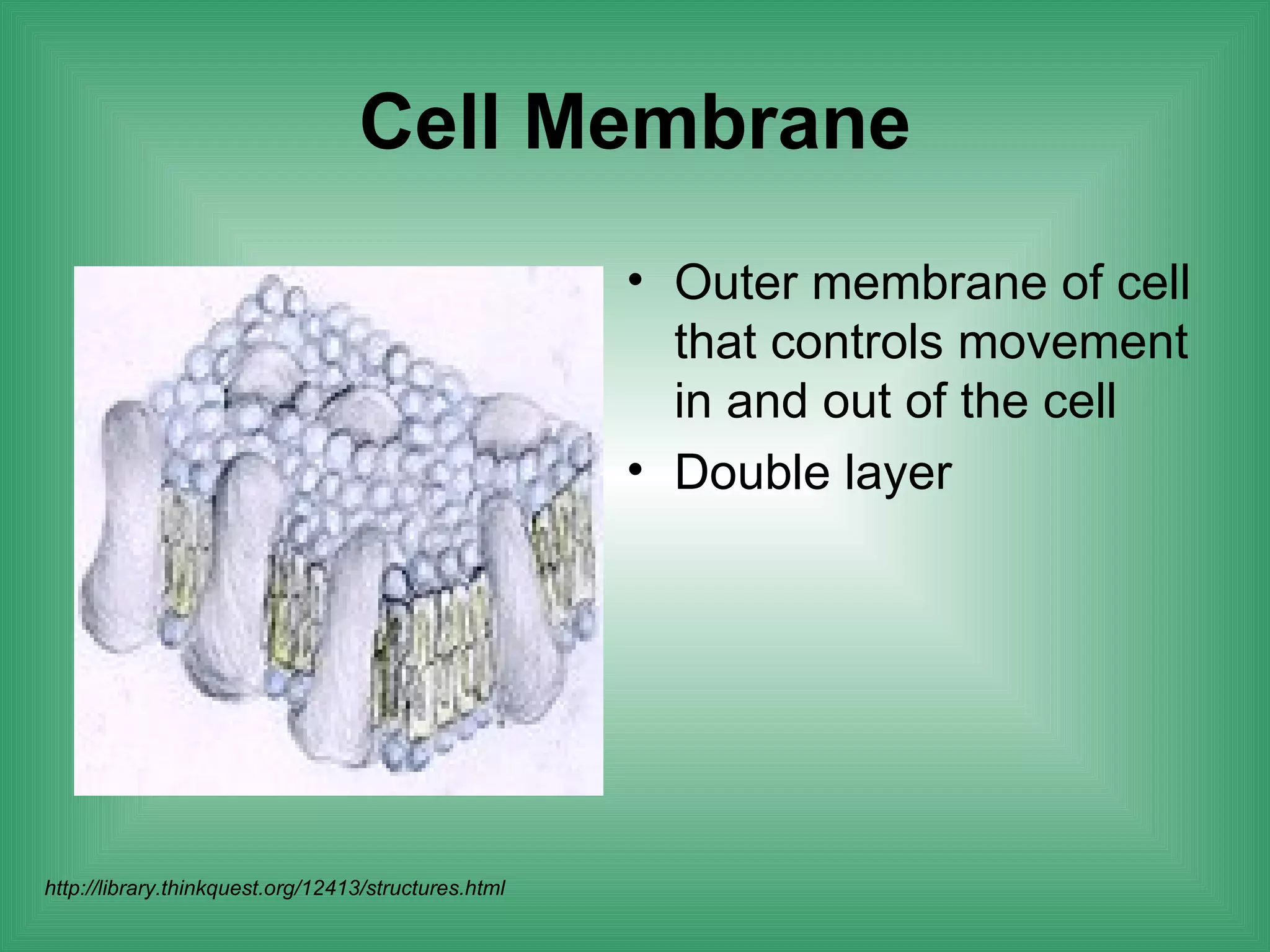
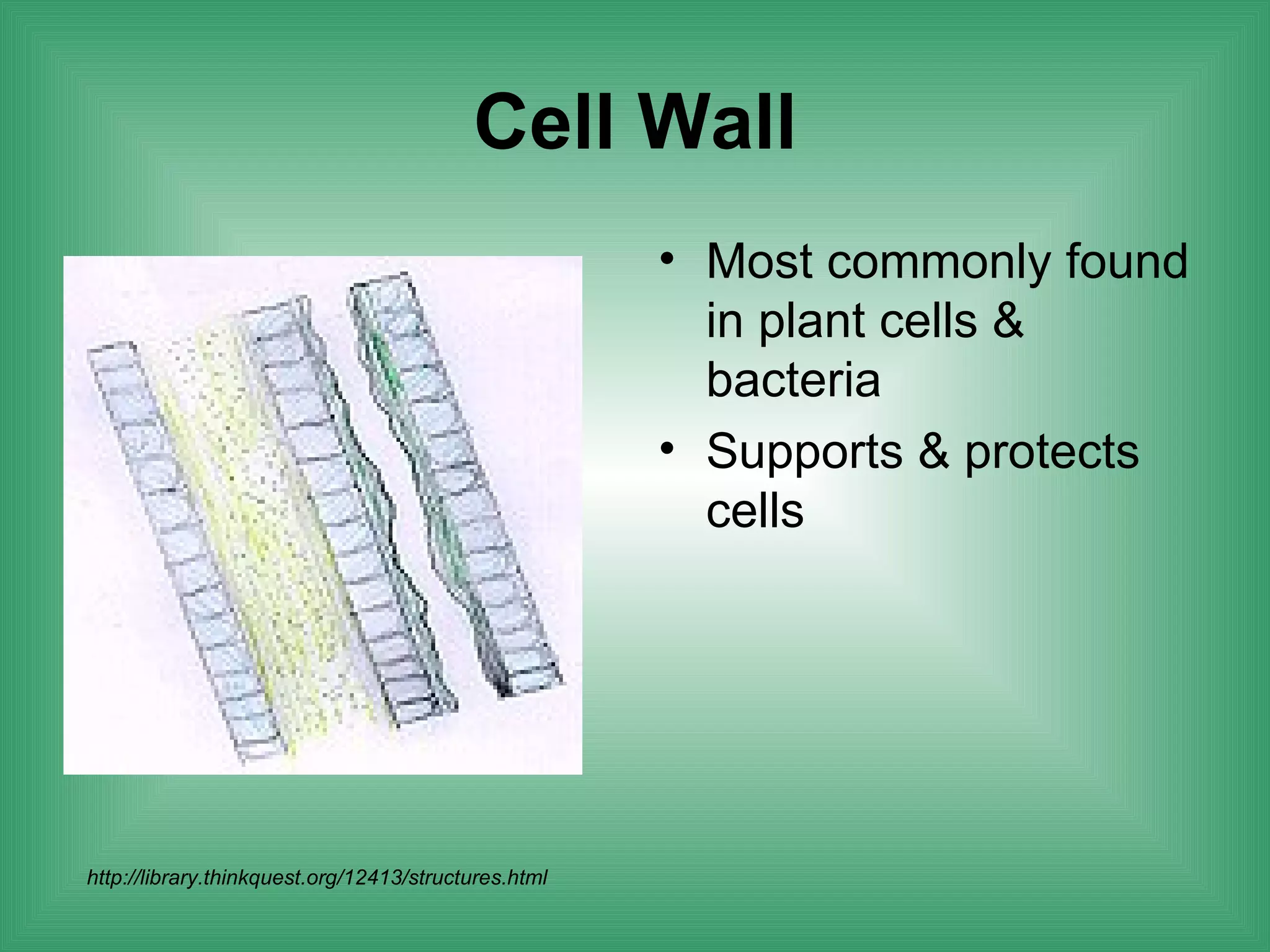
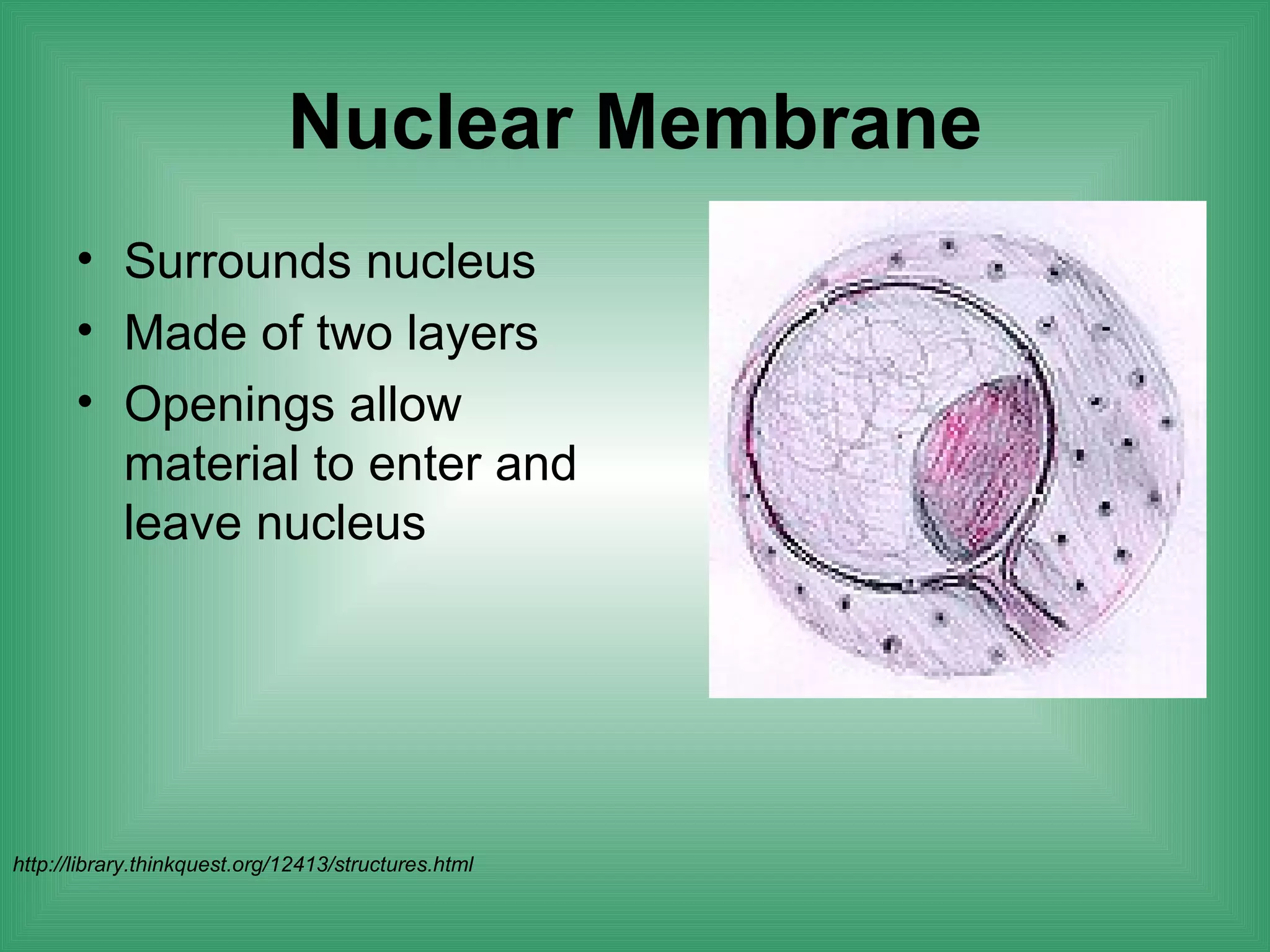
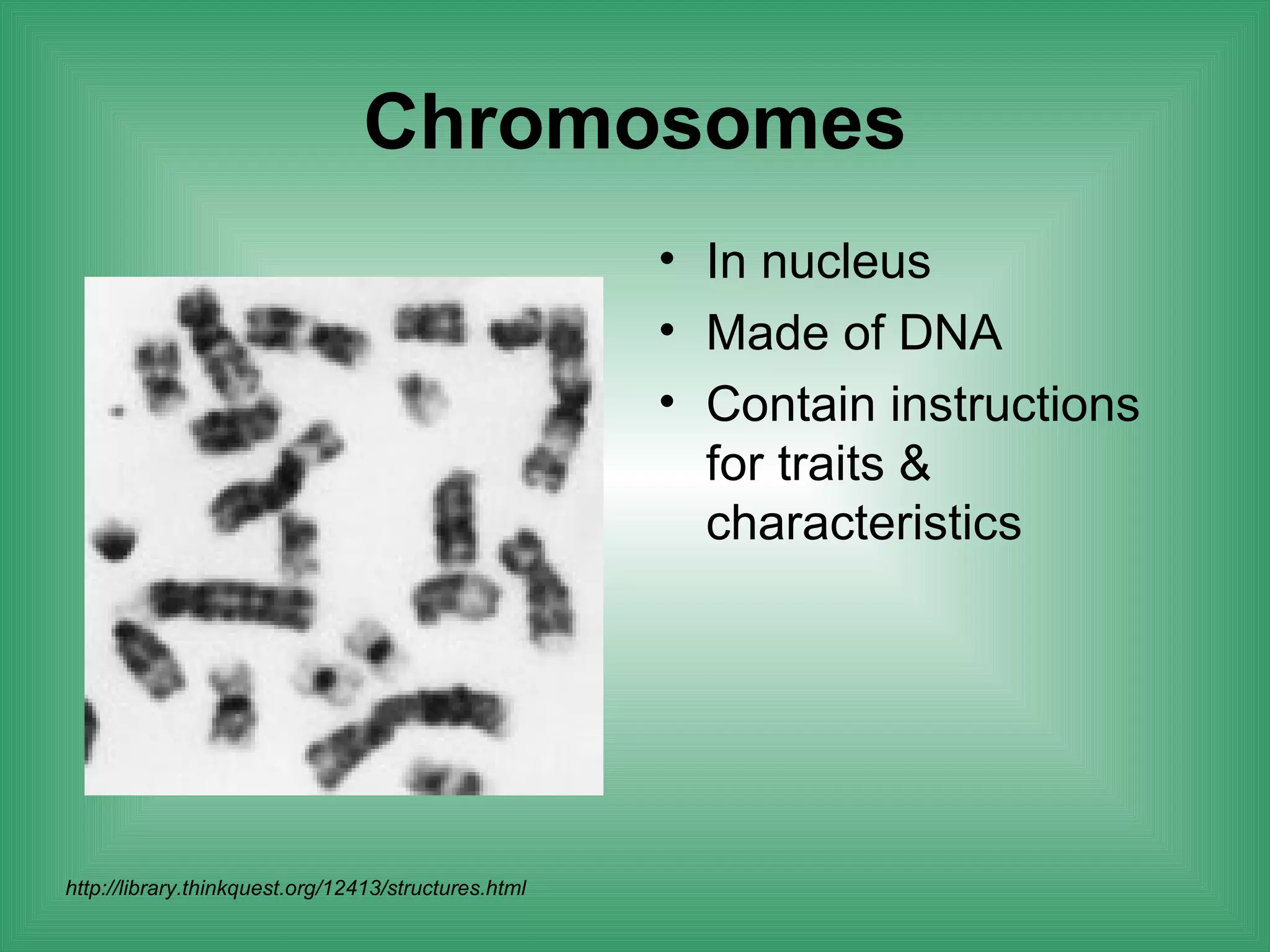
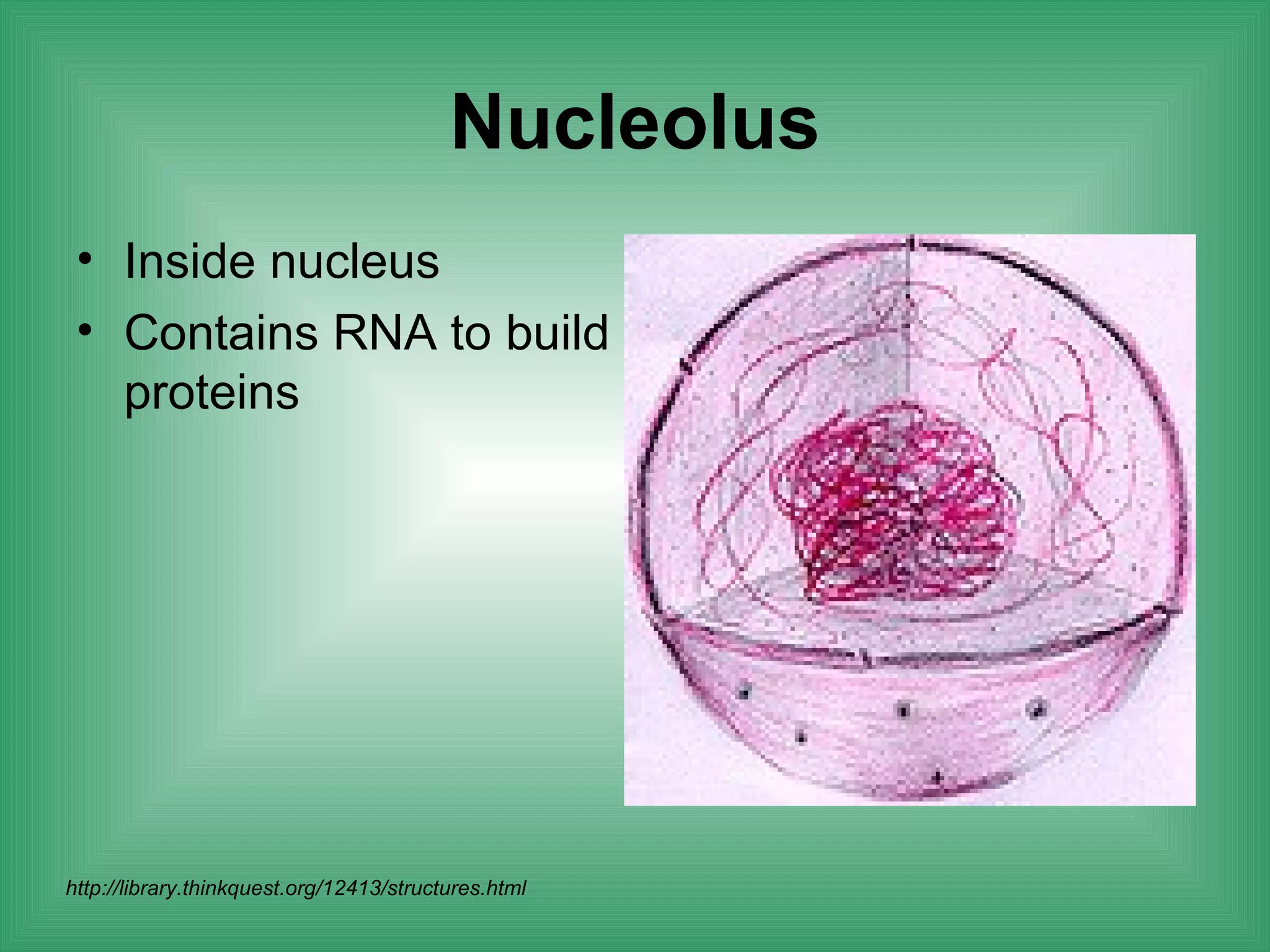
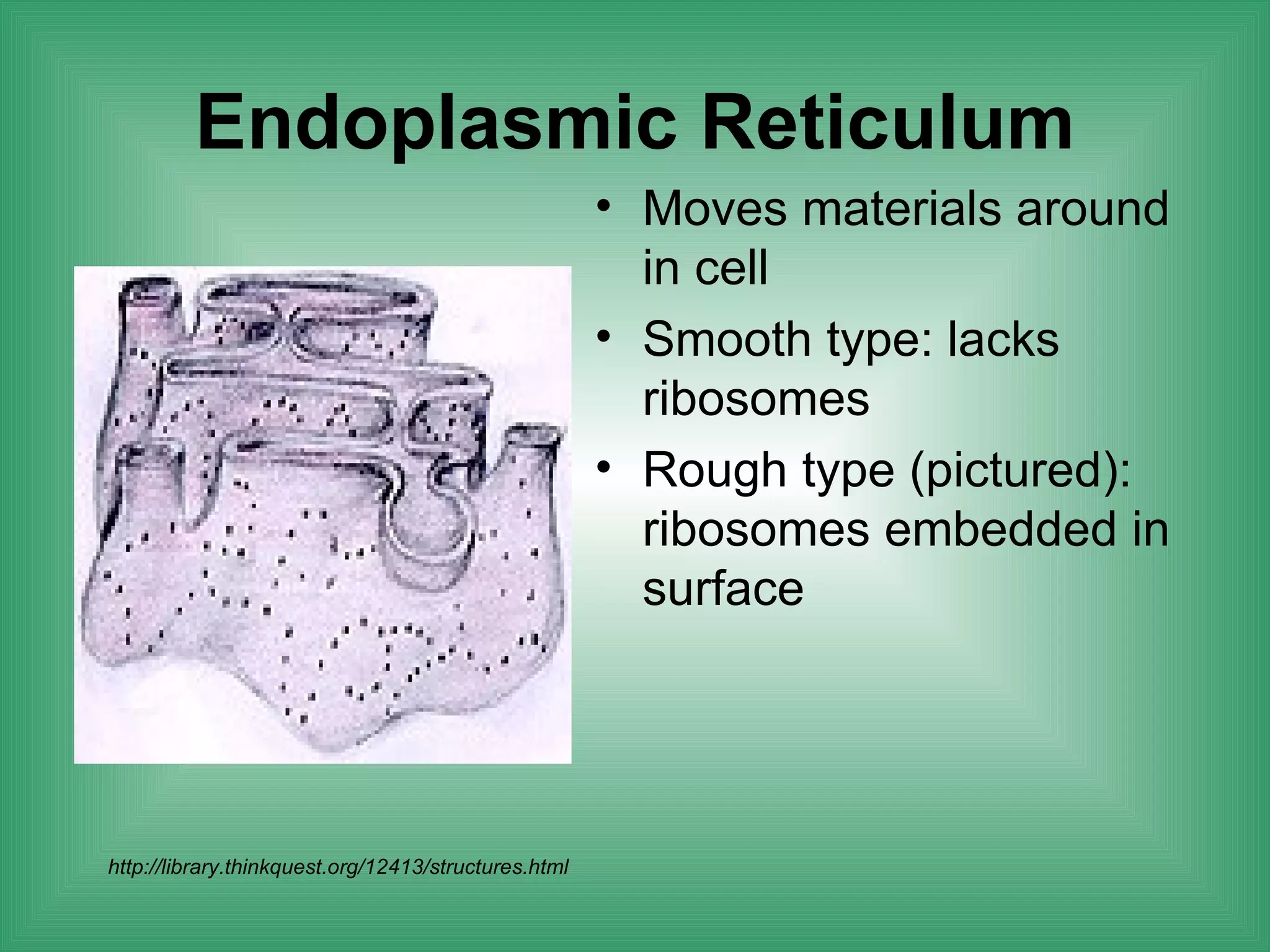
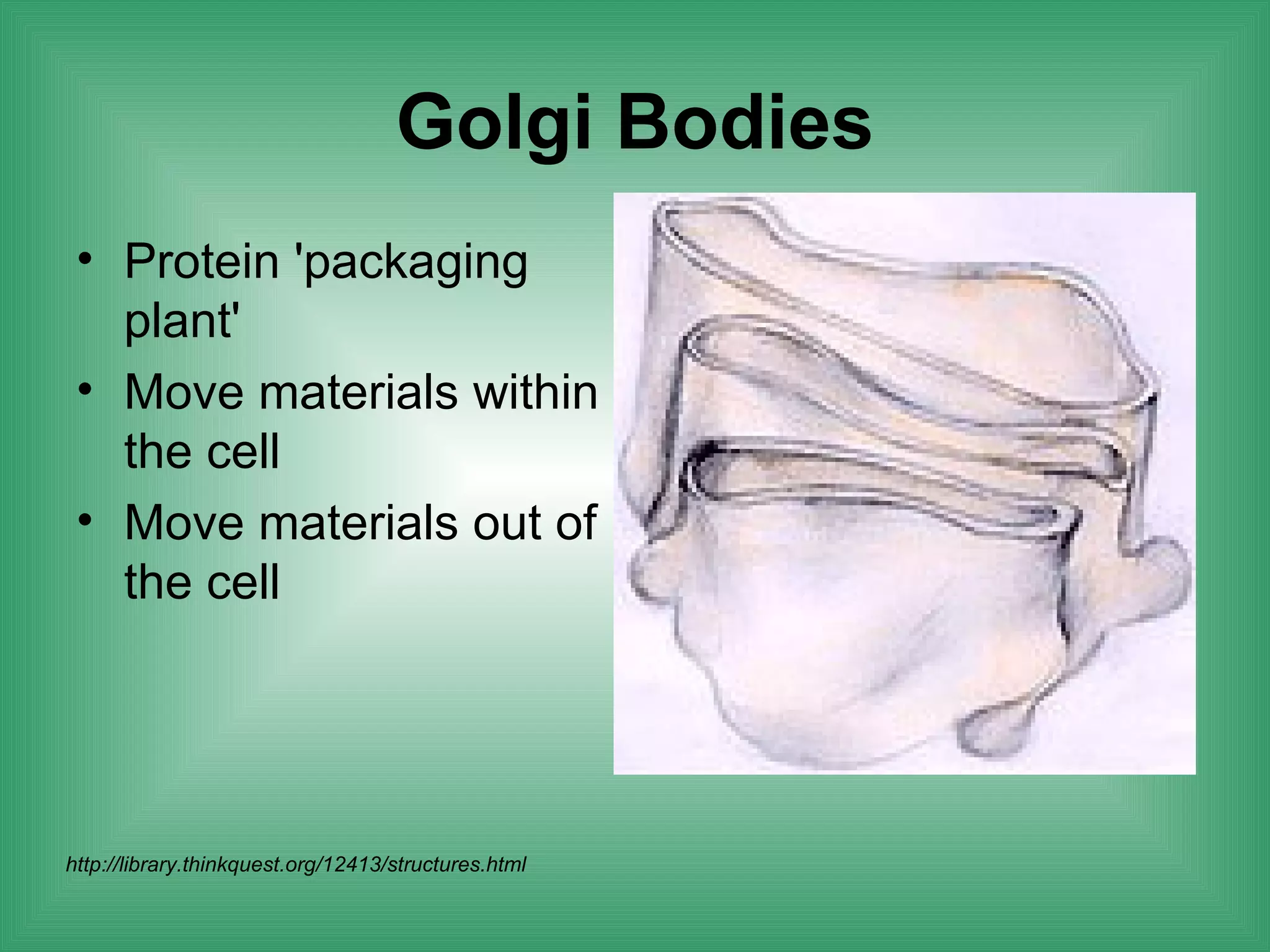
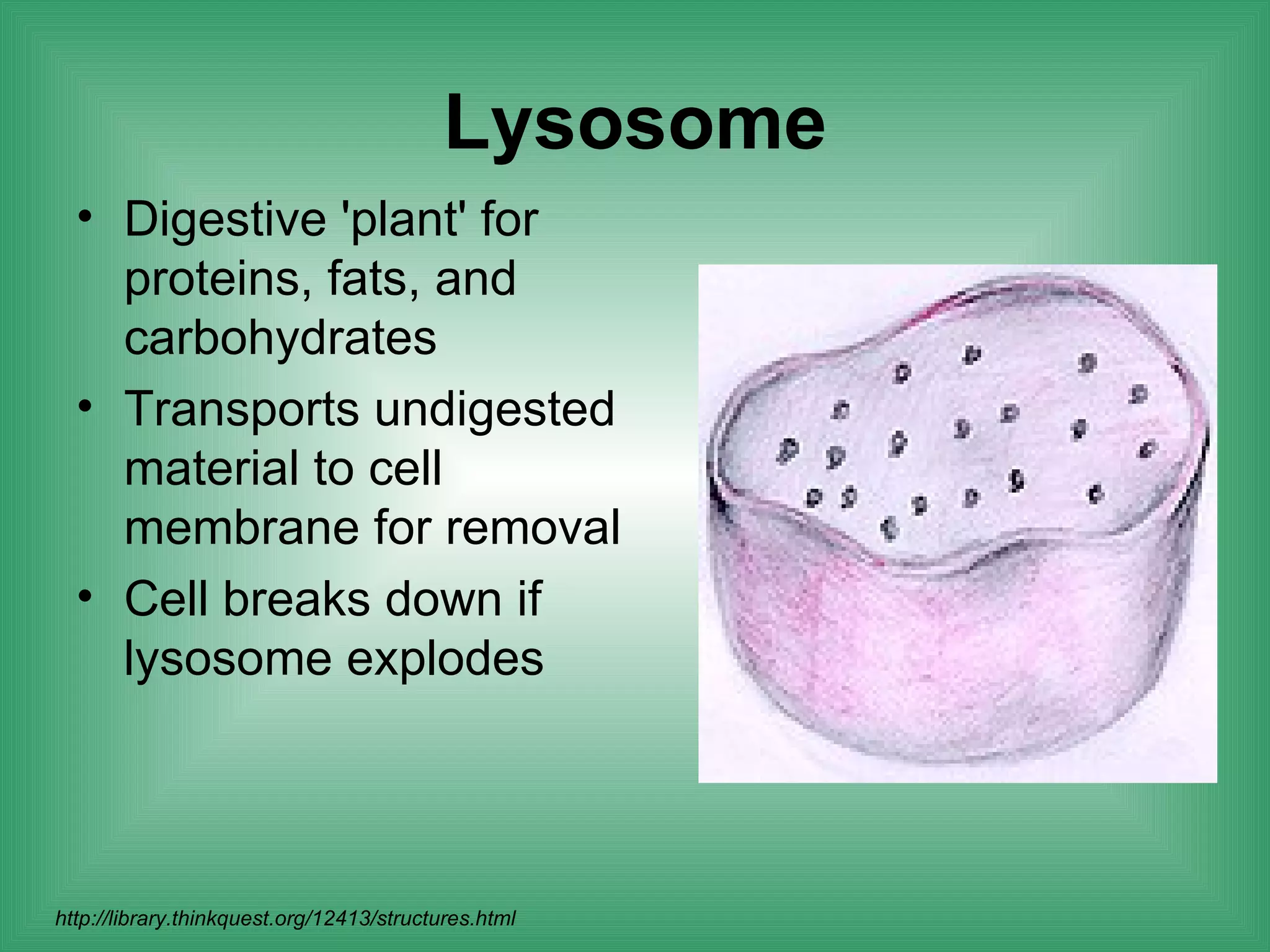
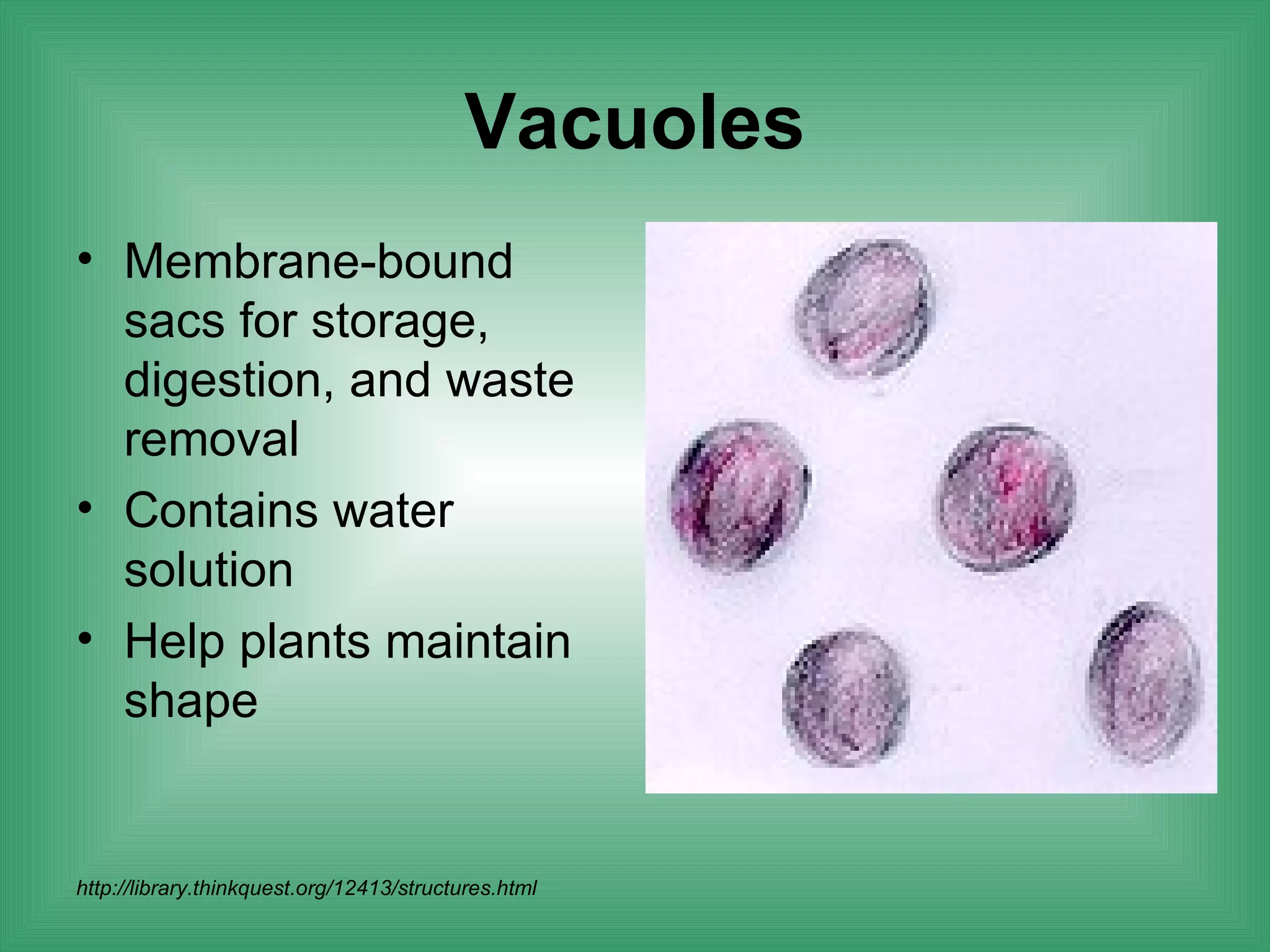
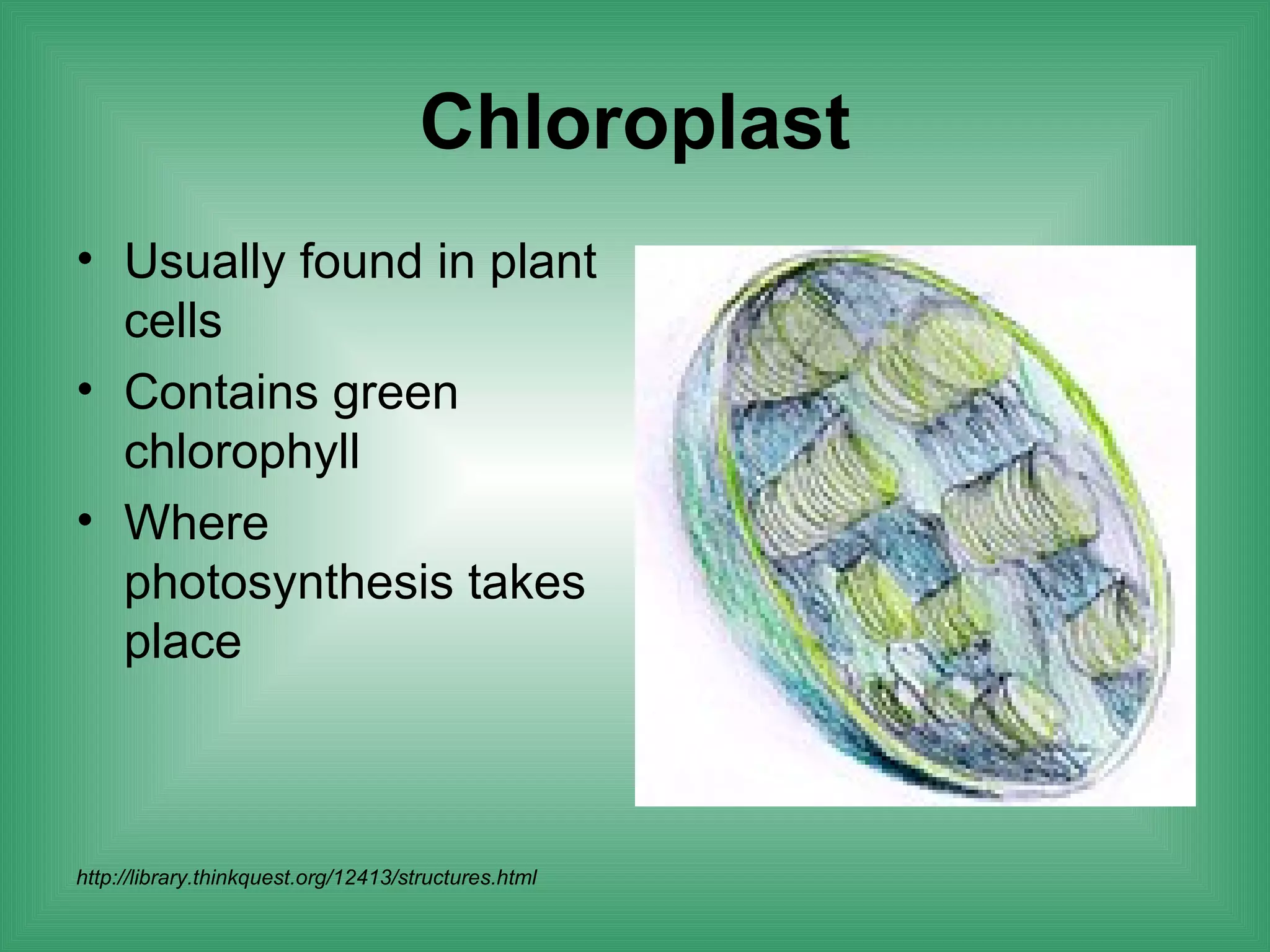
The document discusses the basic structure and function of cells. It outlines cell theory, which states that all living things are made of cells, cells are the basic functional units of life, and new cells are produced from existing cells. The document then describes the key components of cells, including the cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, organelles like mitochondria and chloroplasts, and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Examples of plant, animal, and bacterial cells are provided with labeled diagrams.