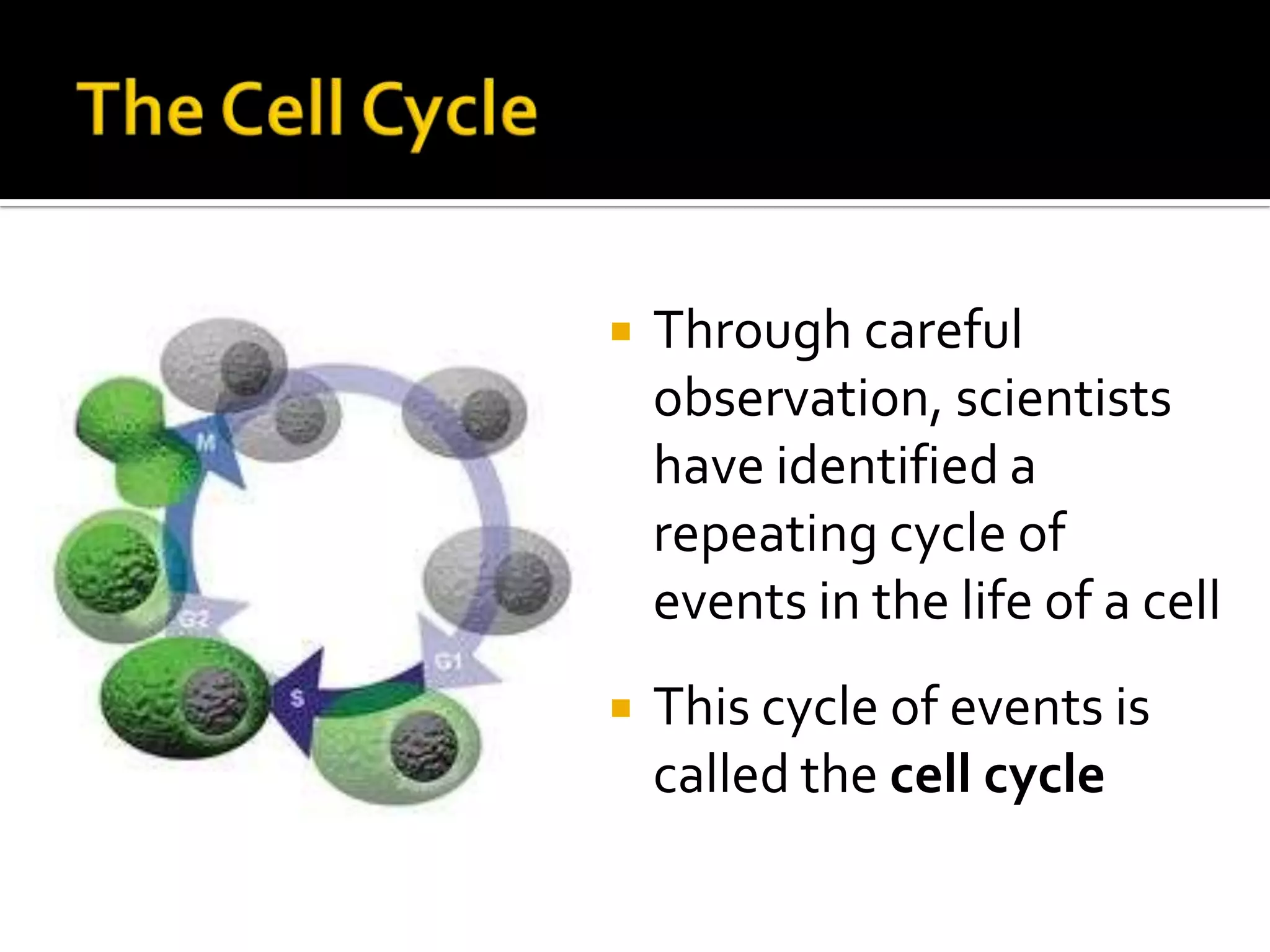
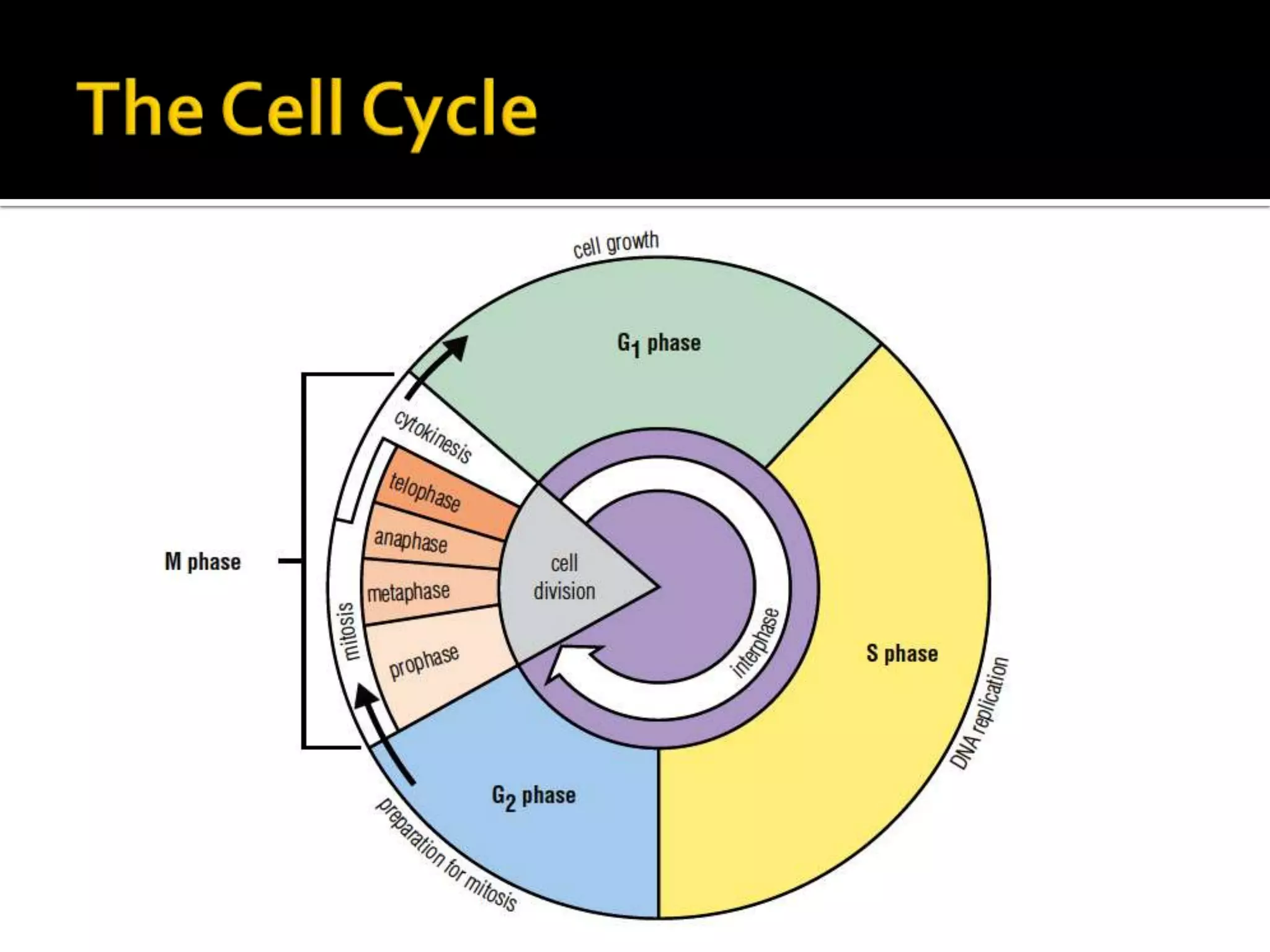
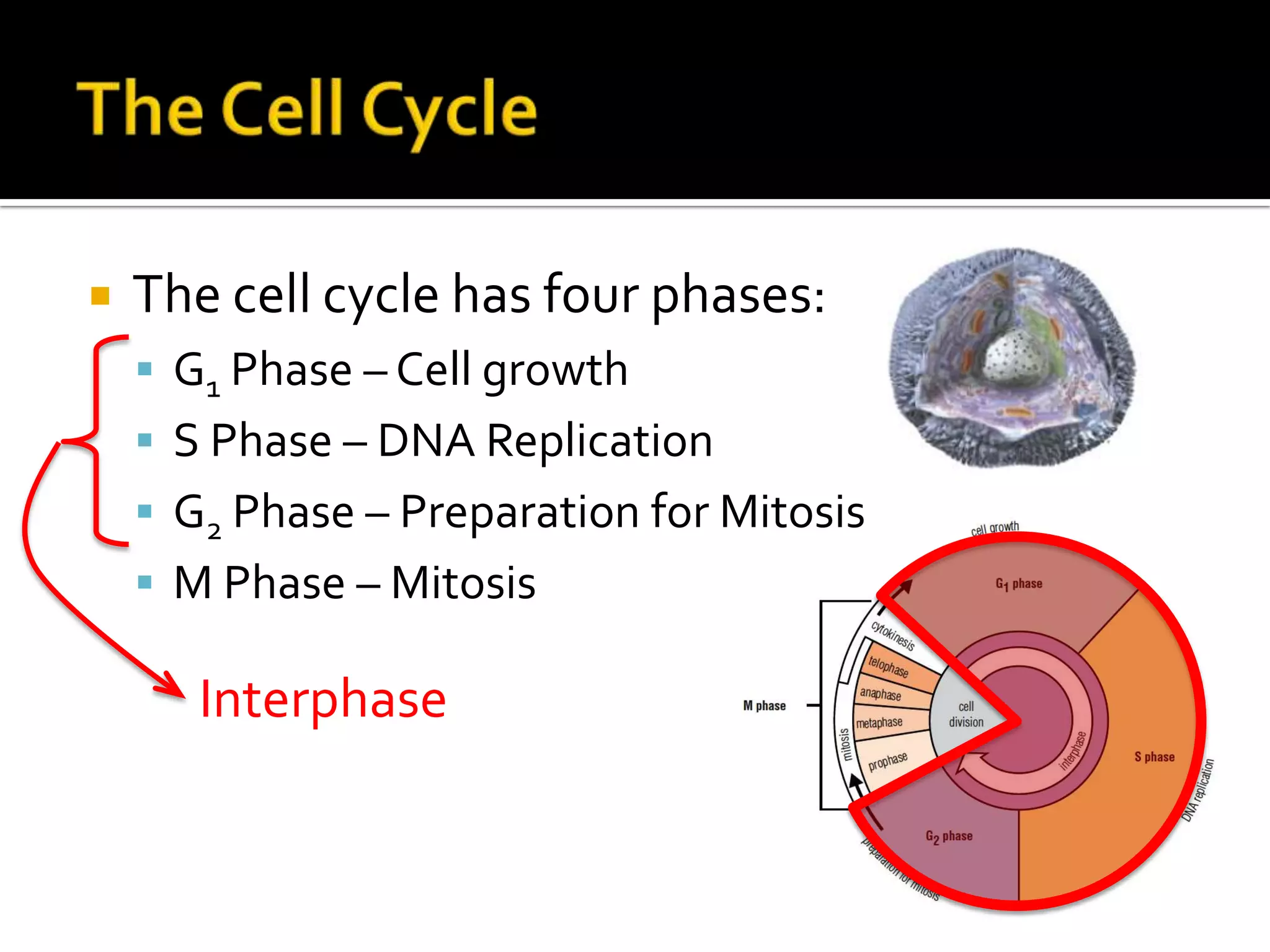
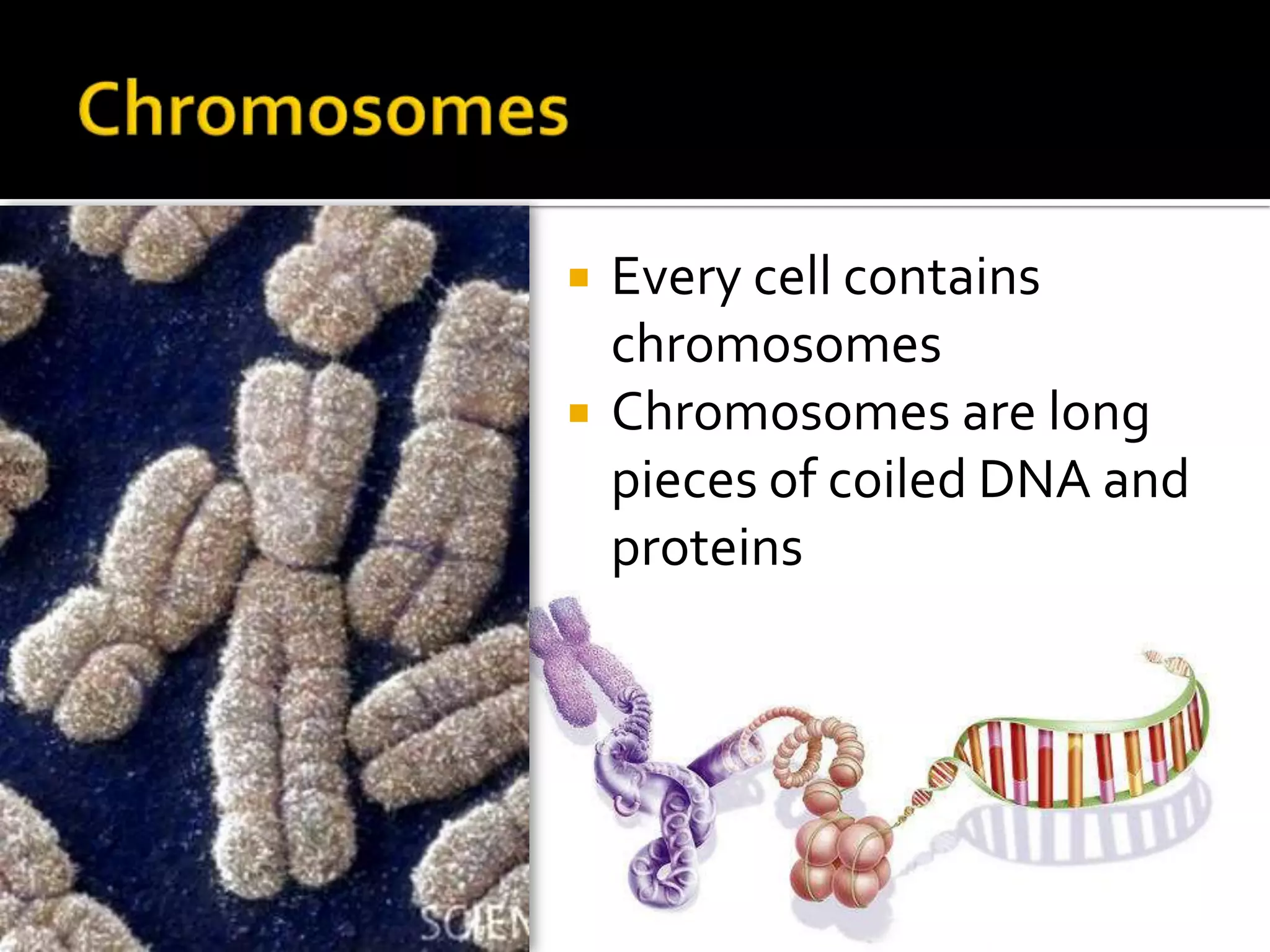
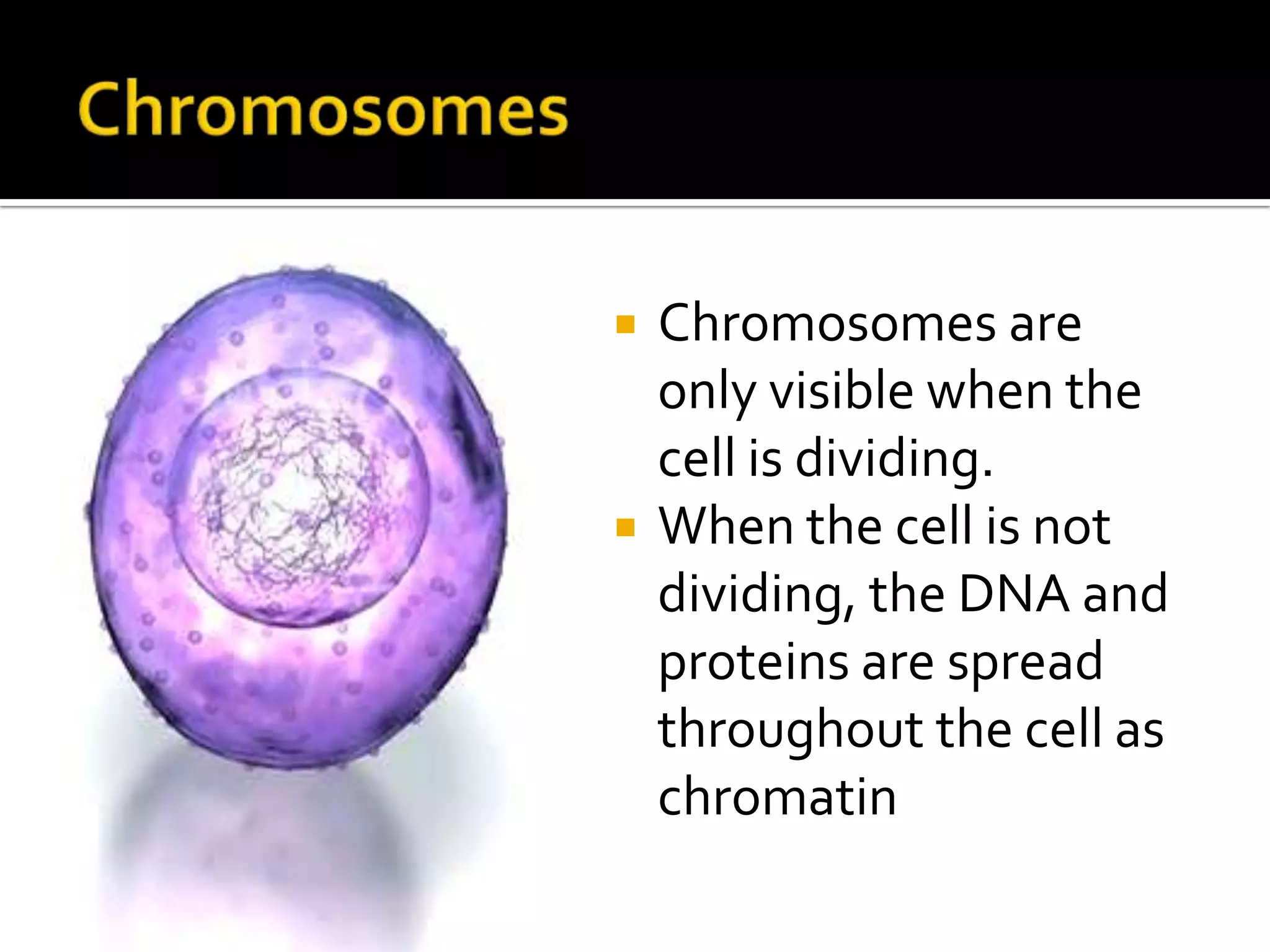
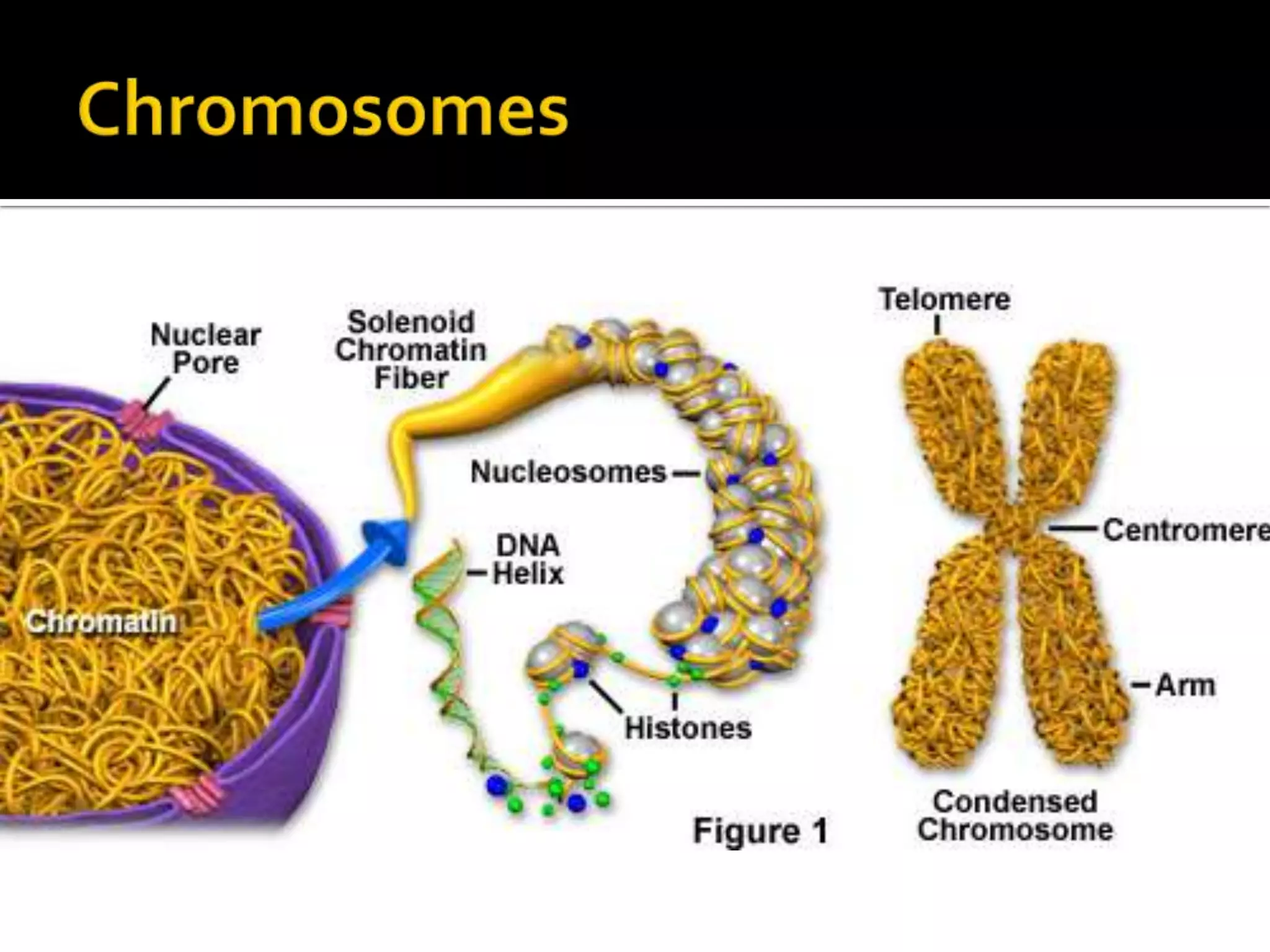
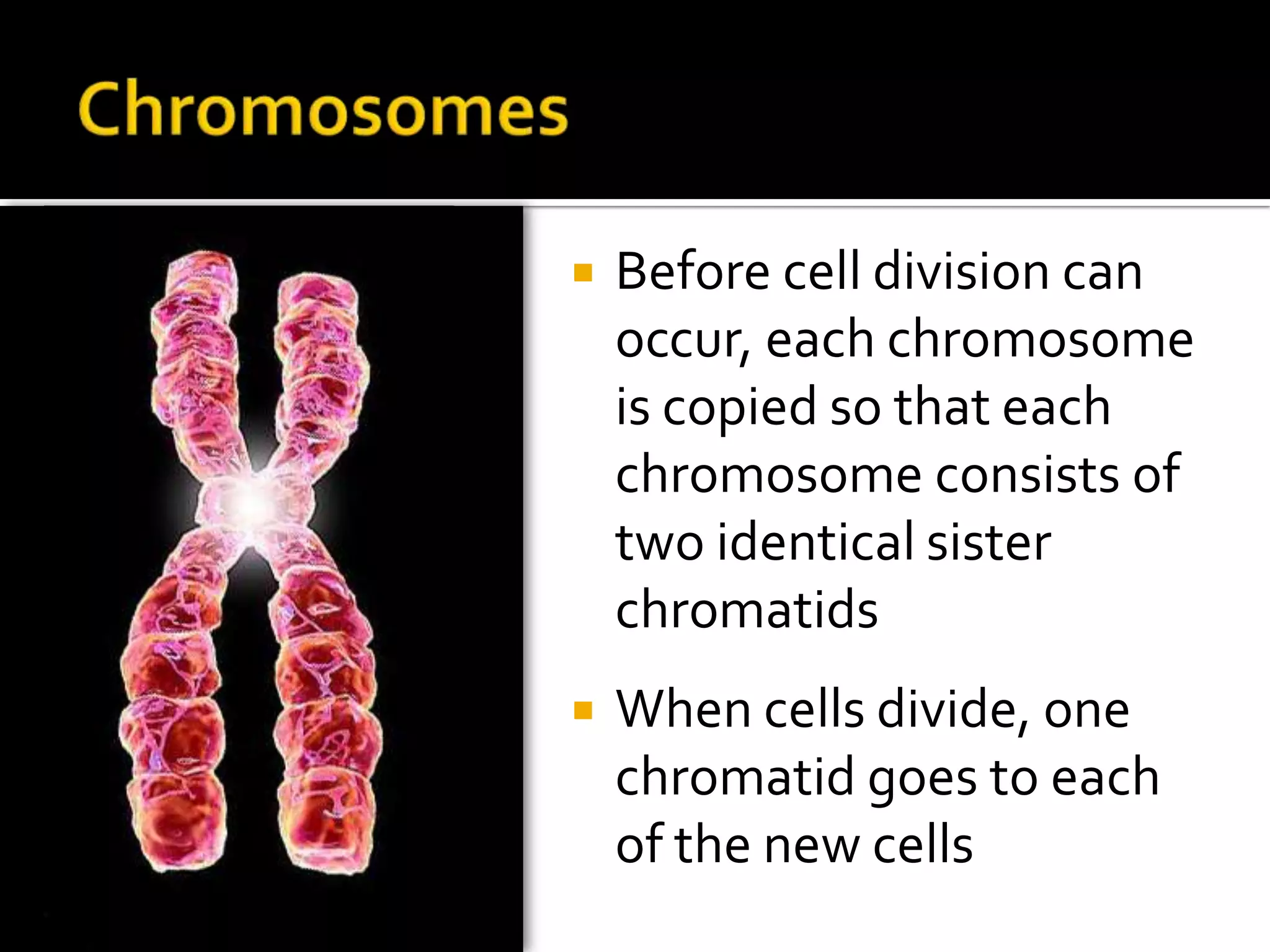
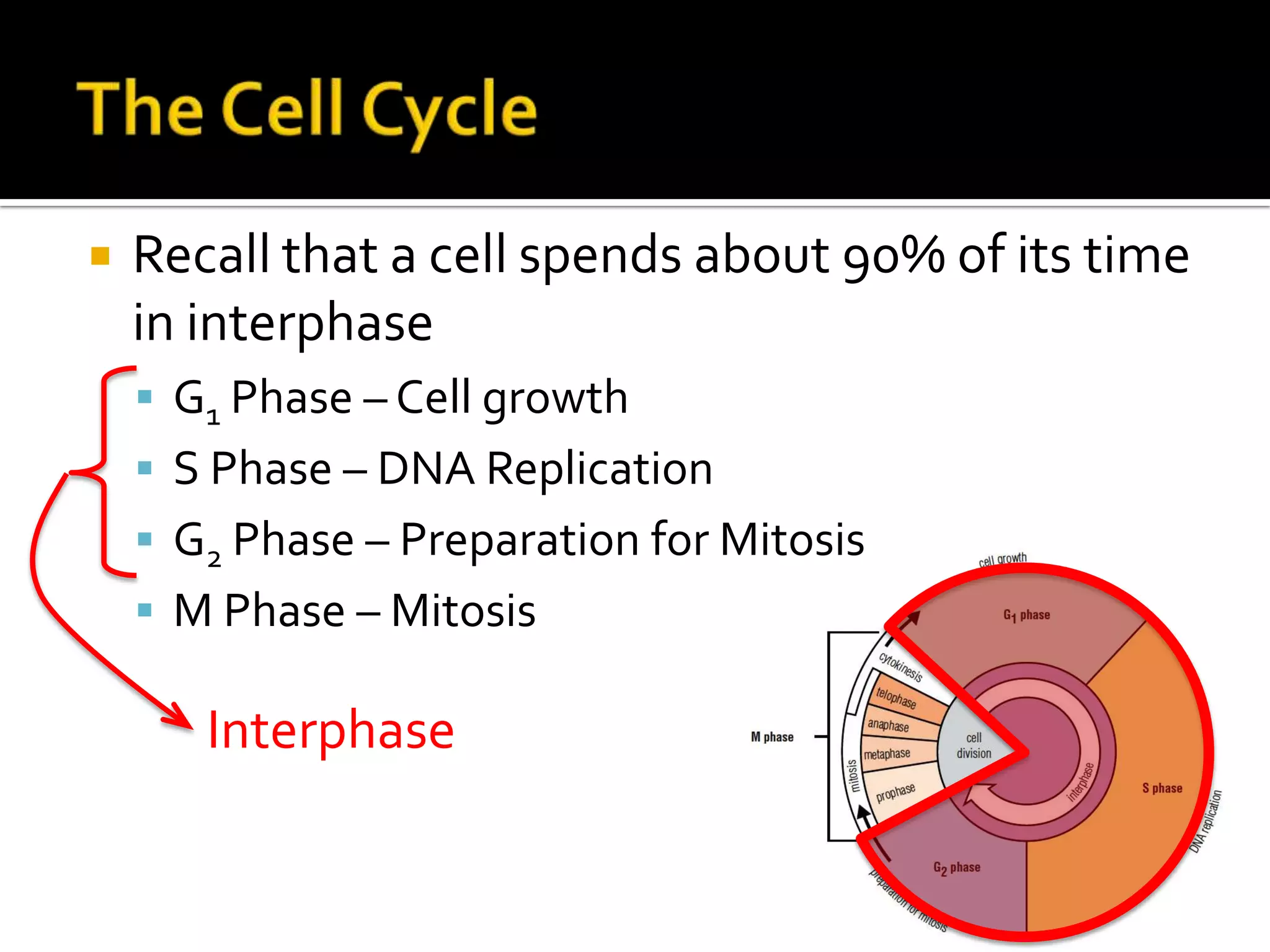
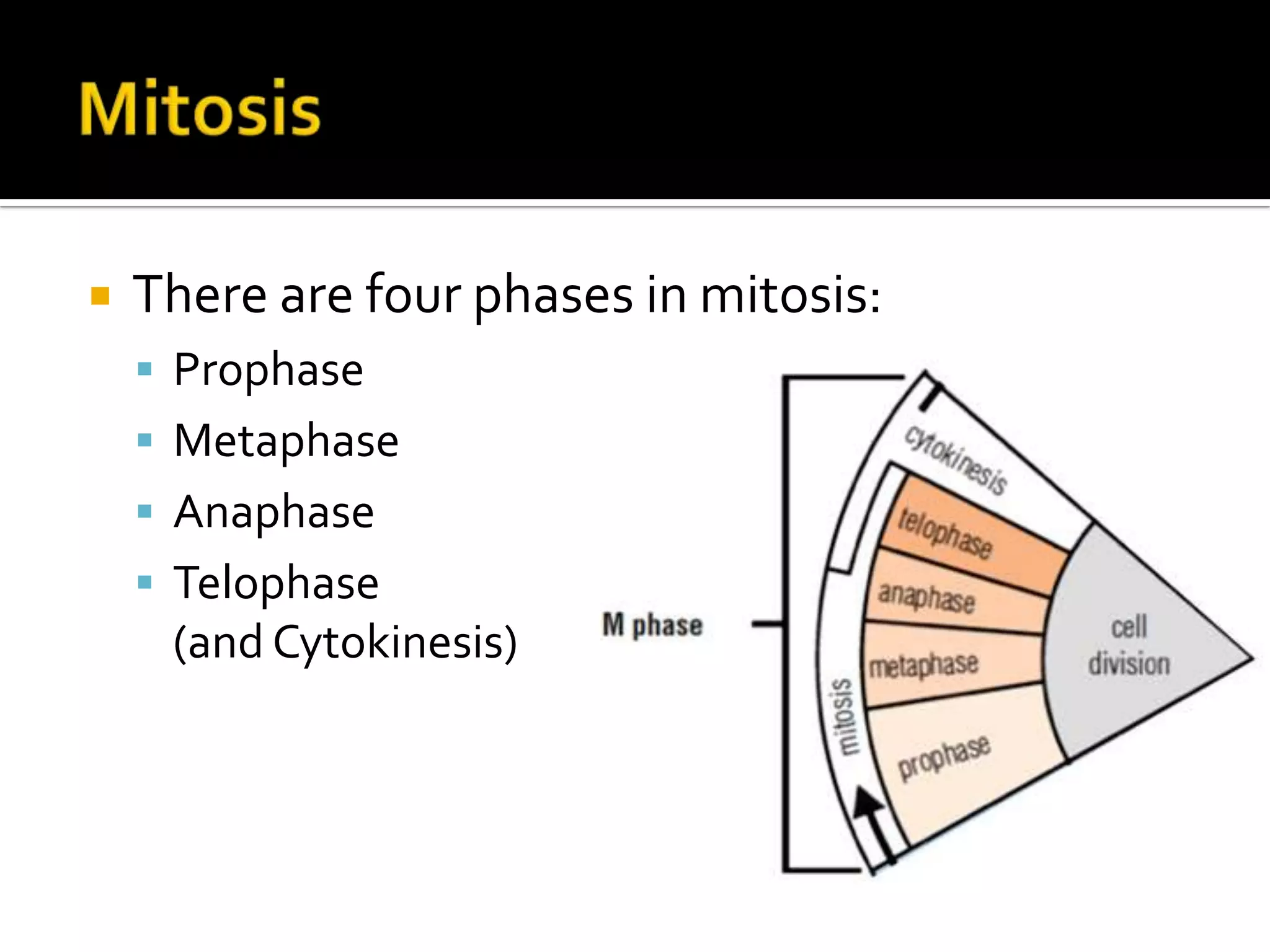
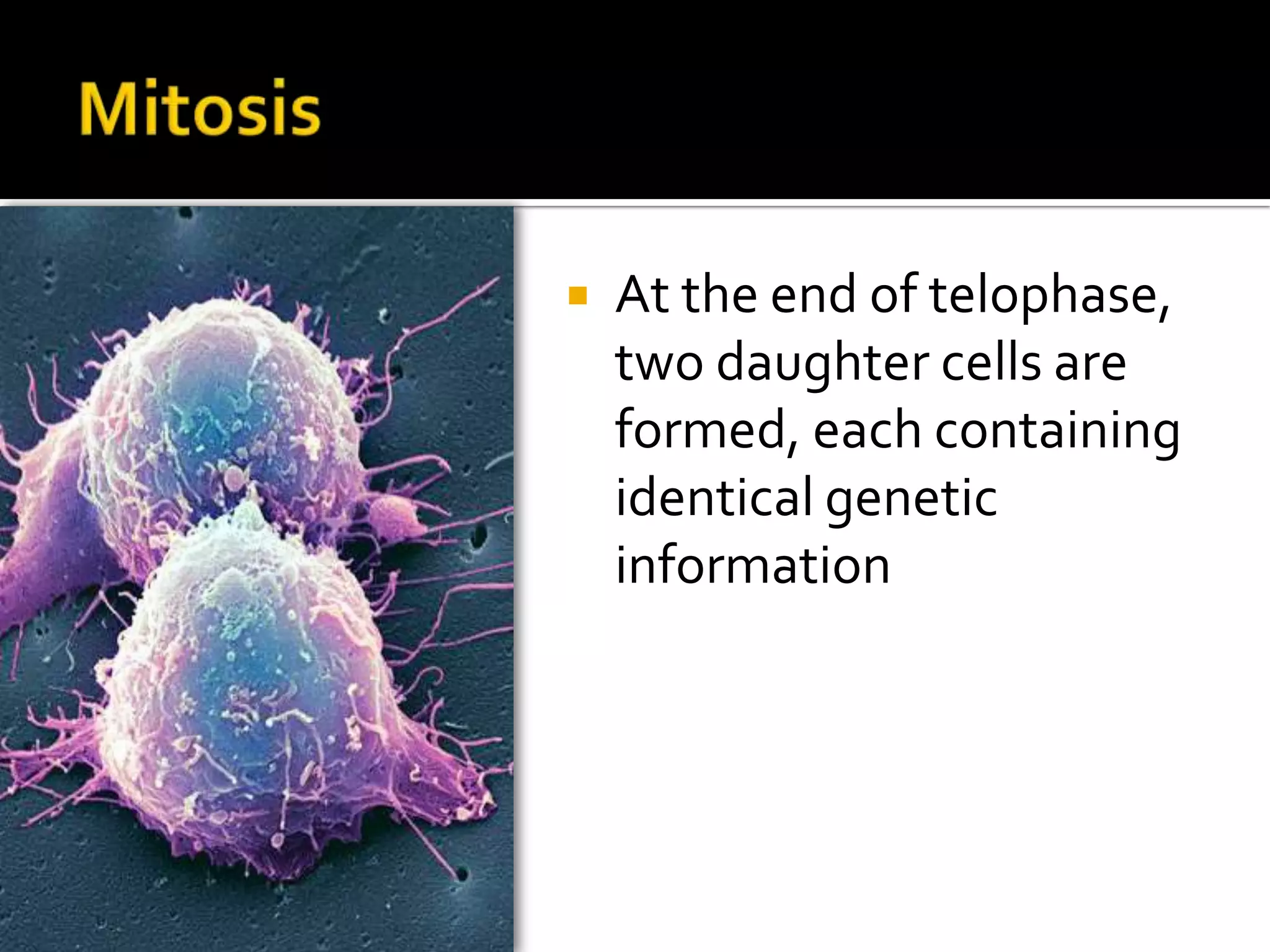
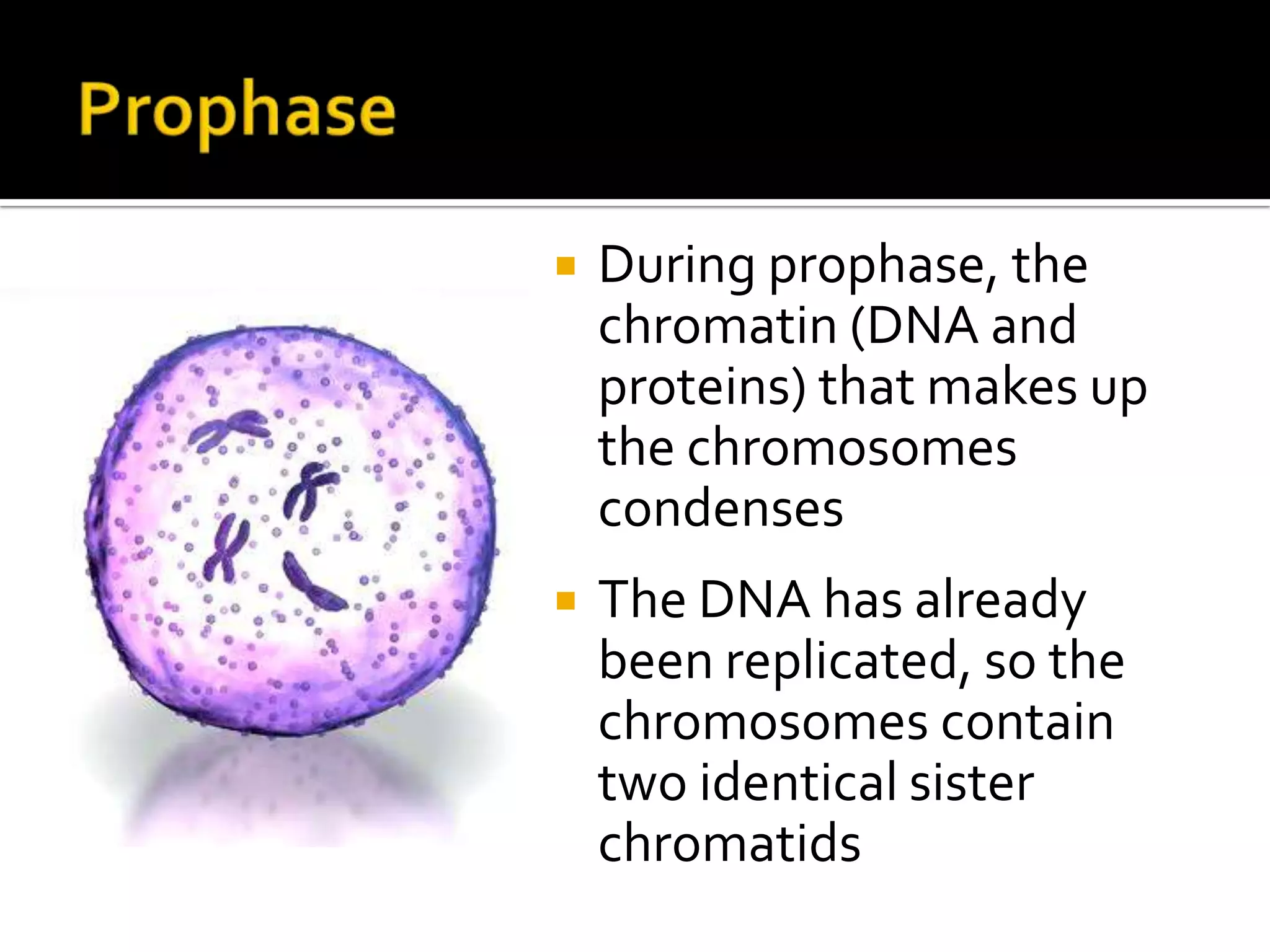
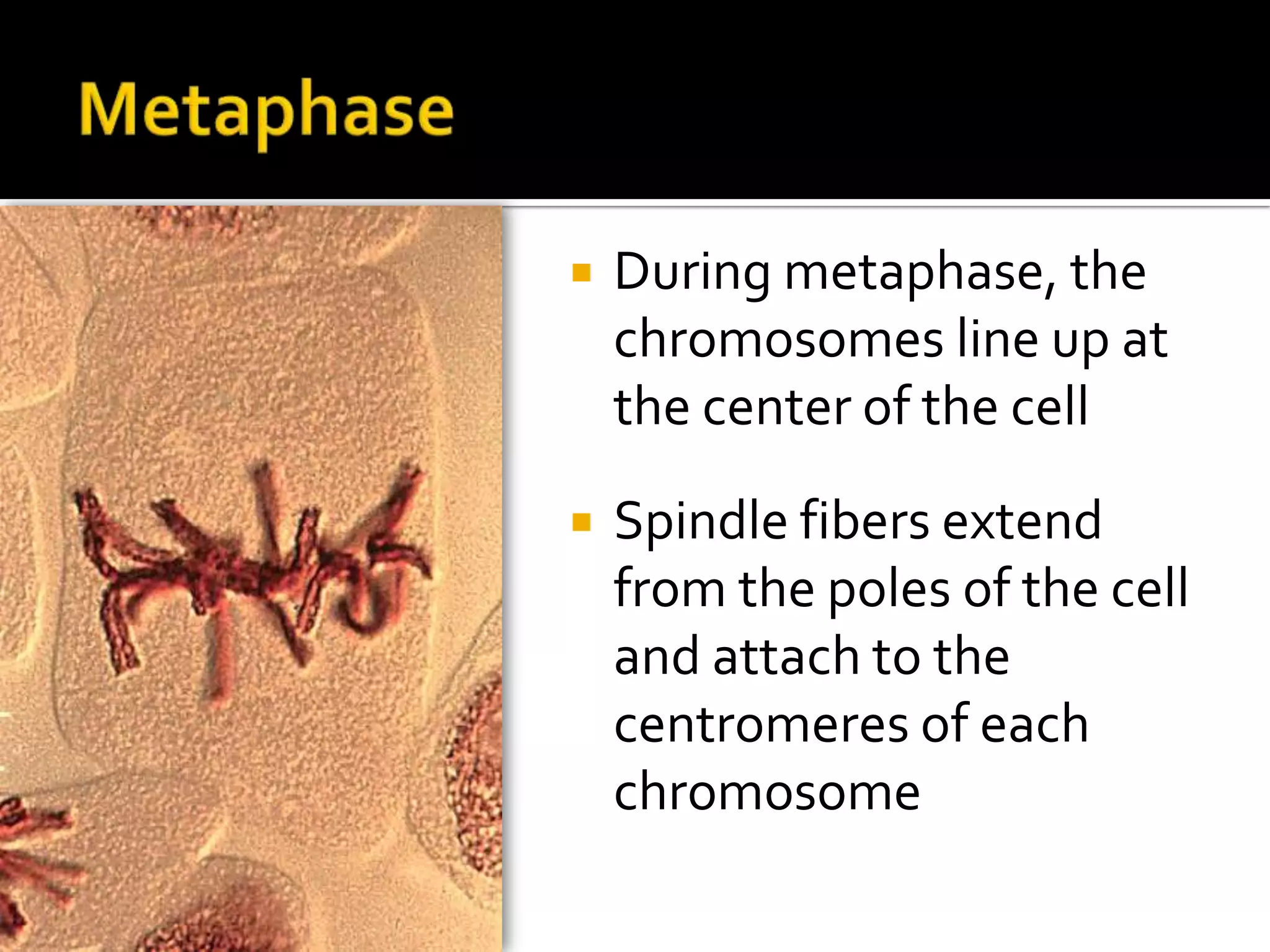
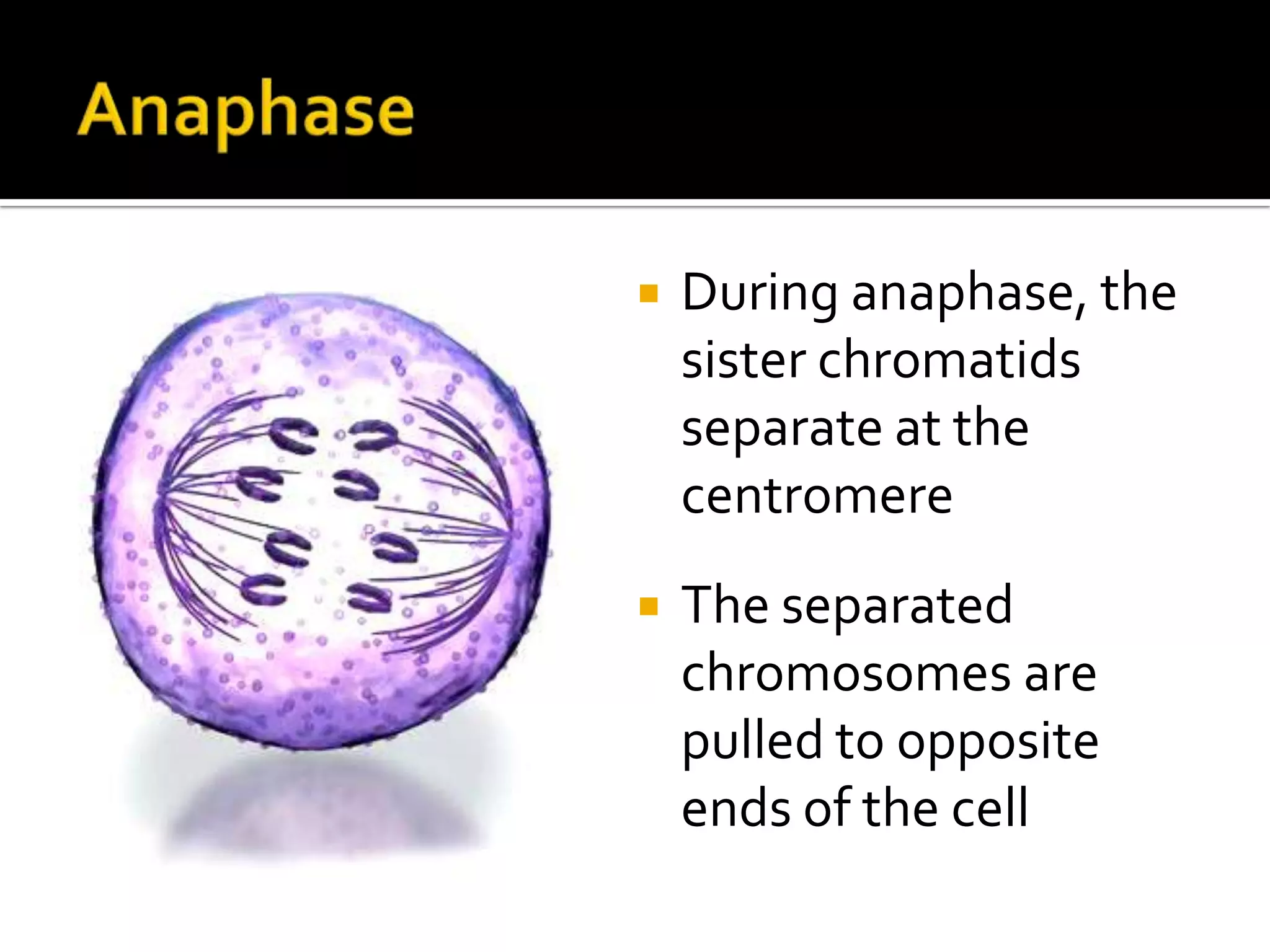
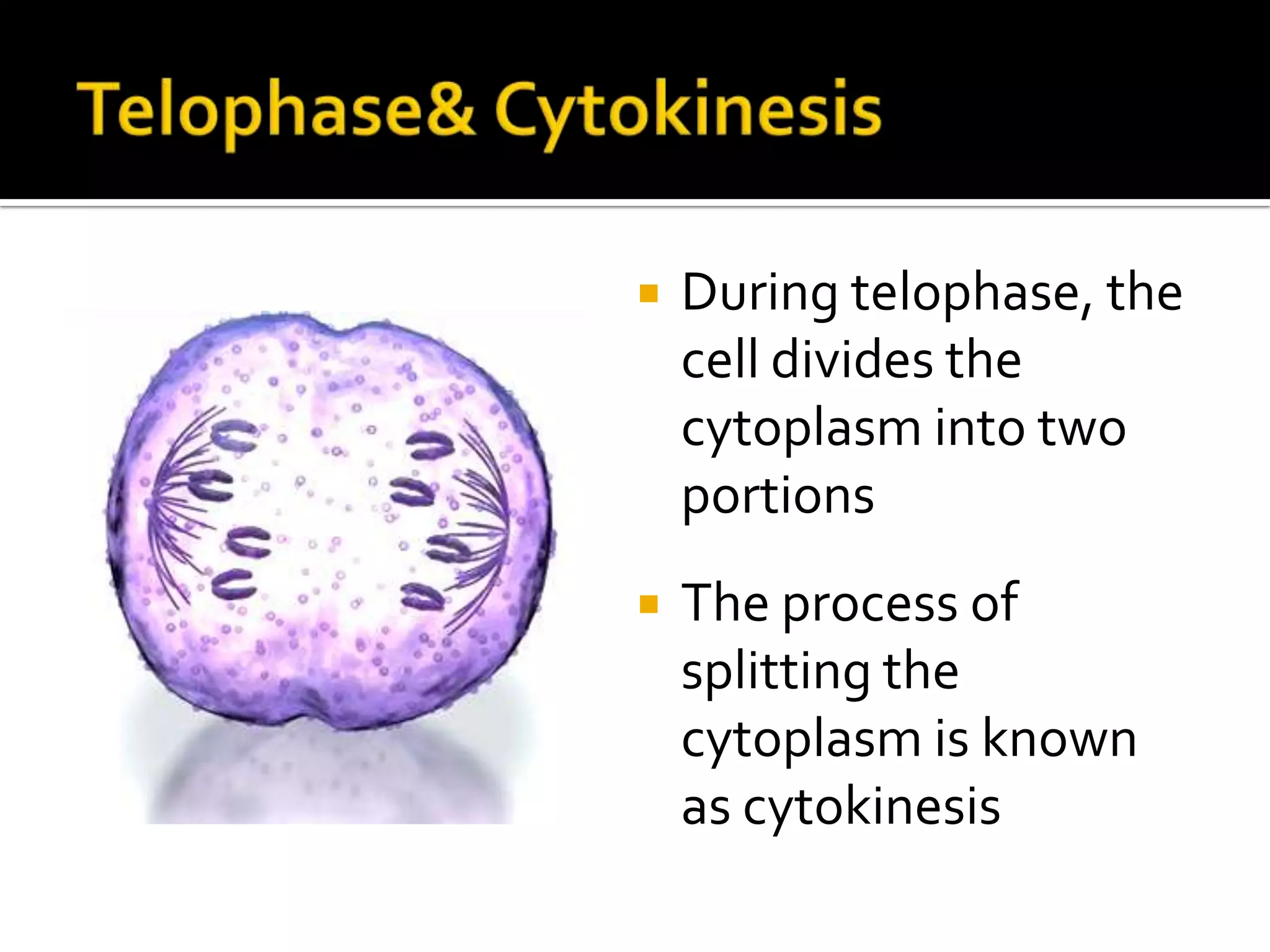
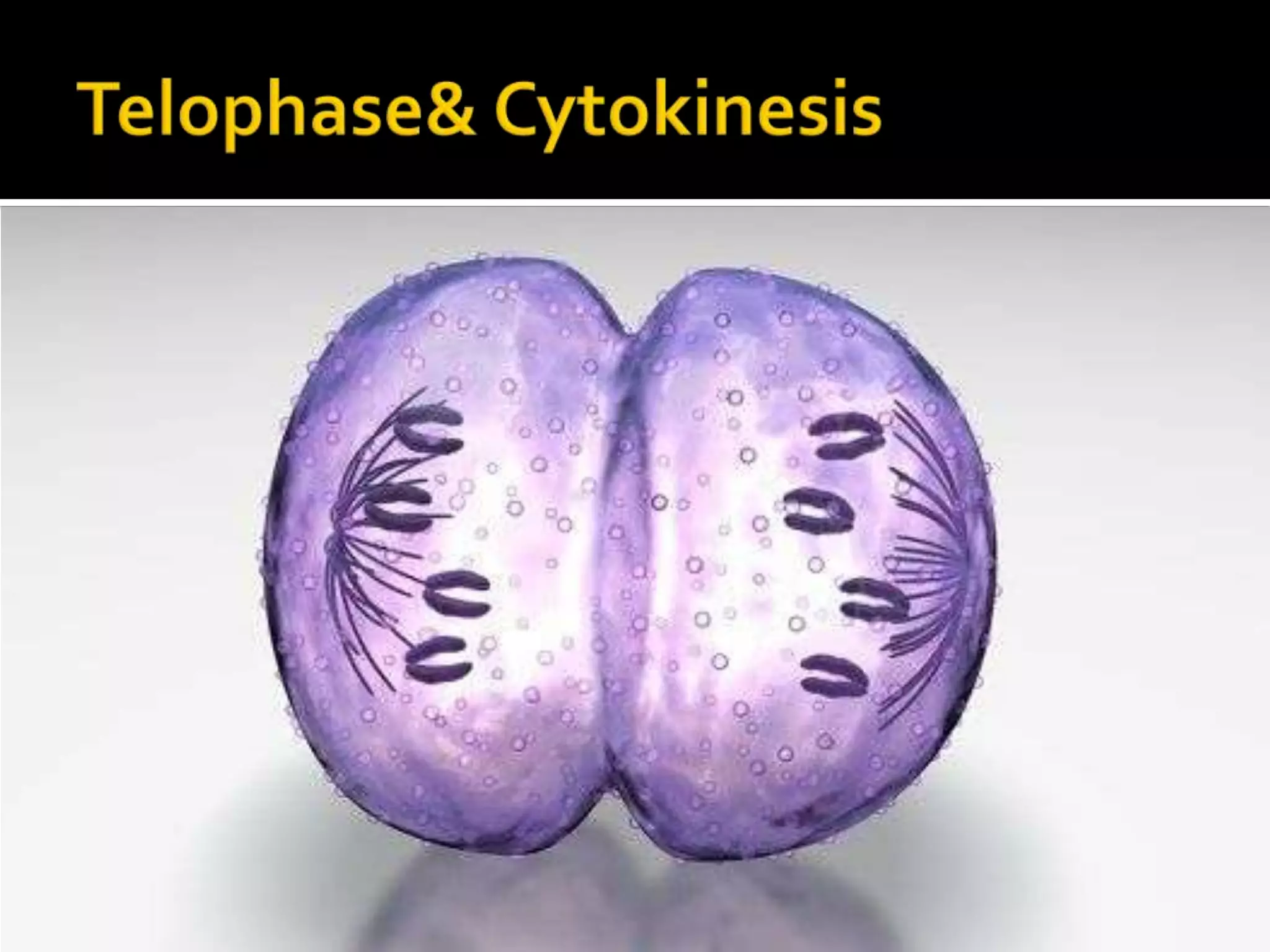
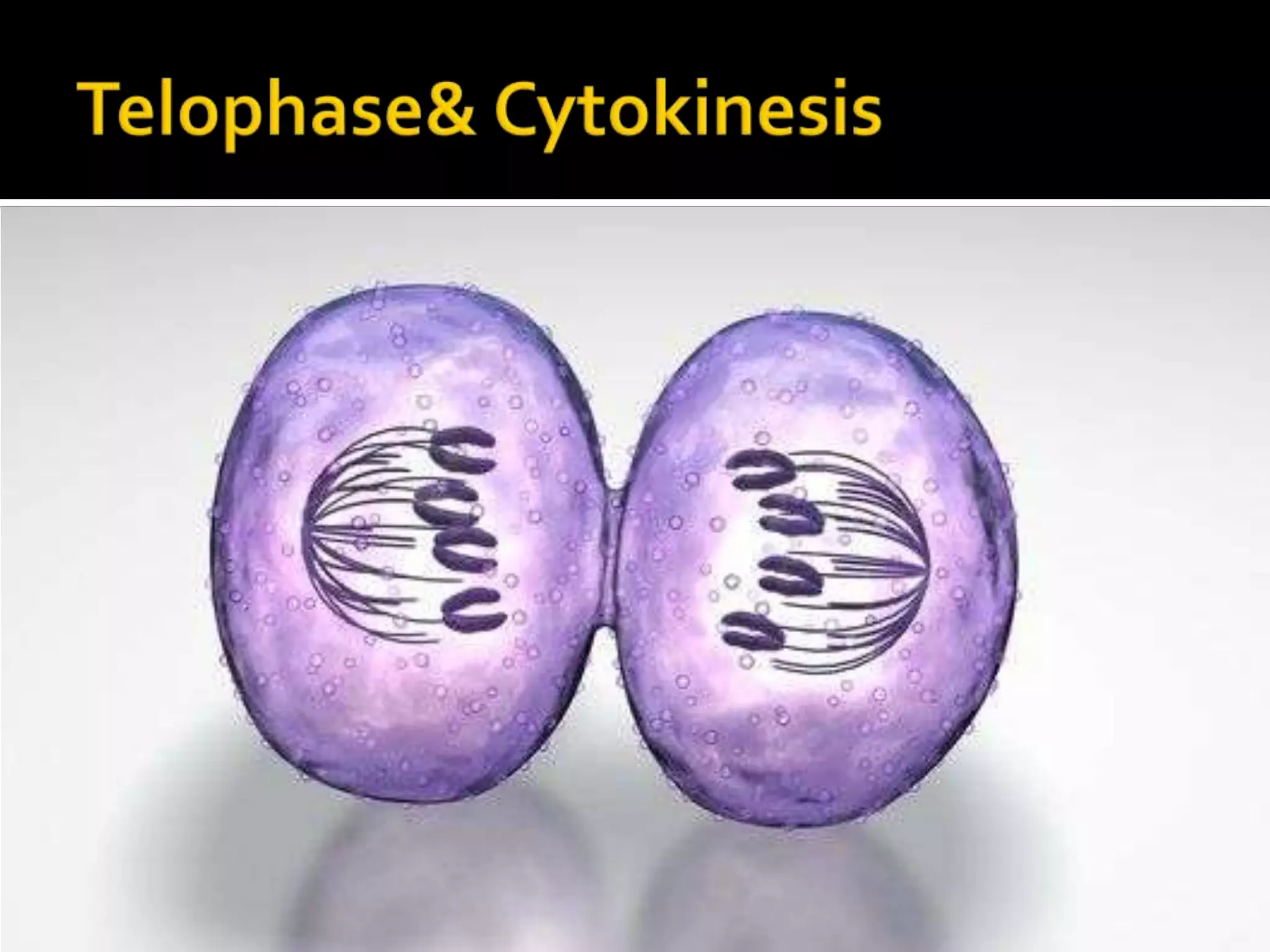
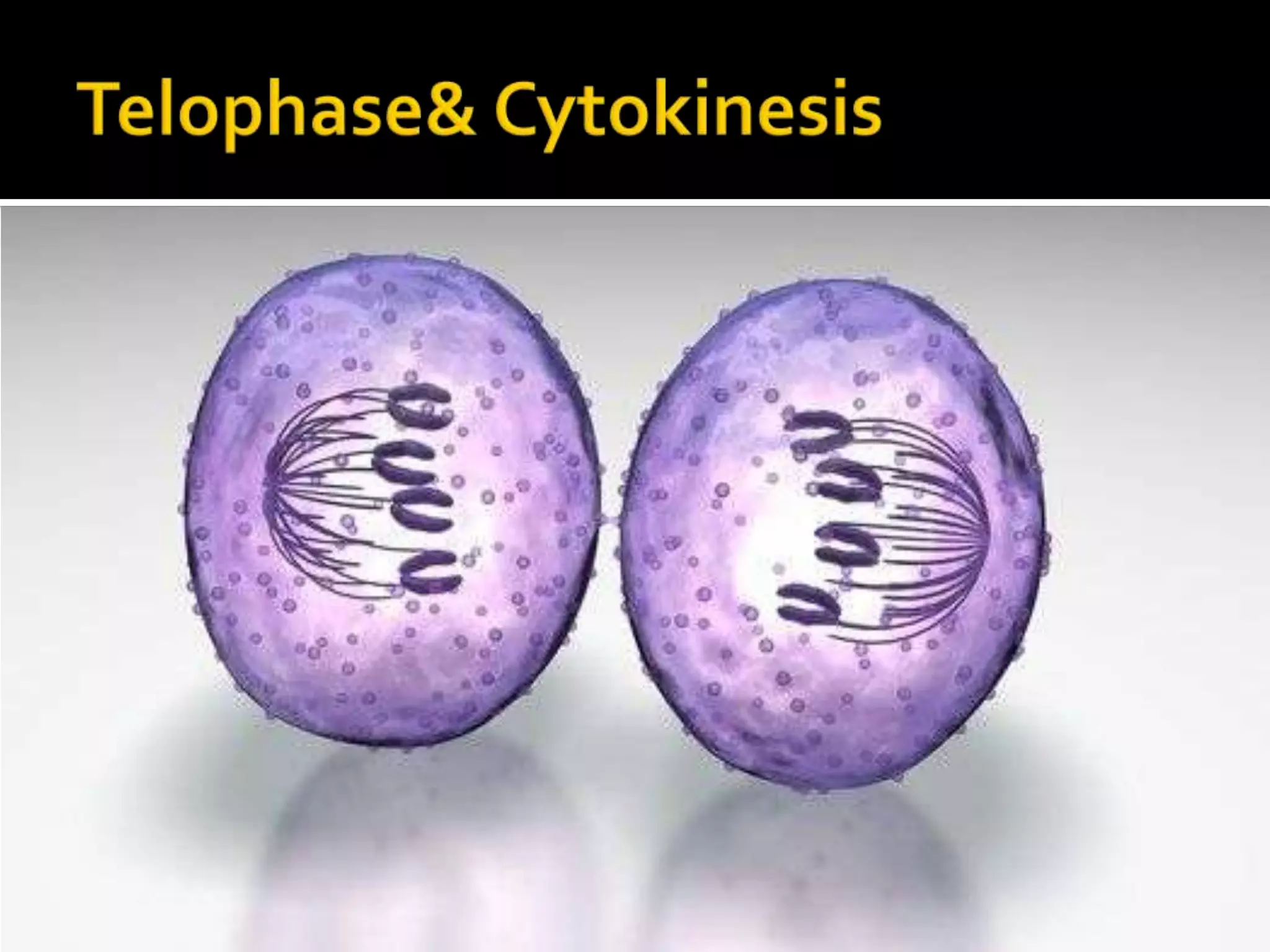
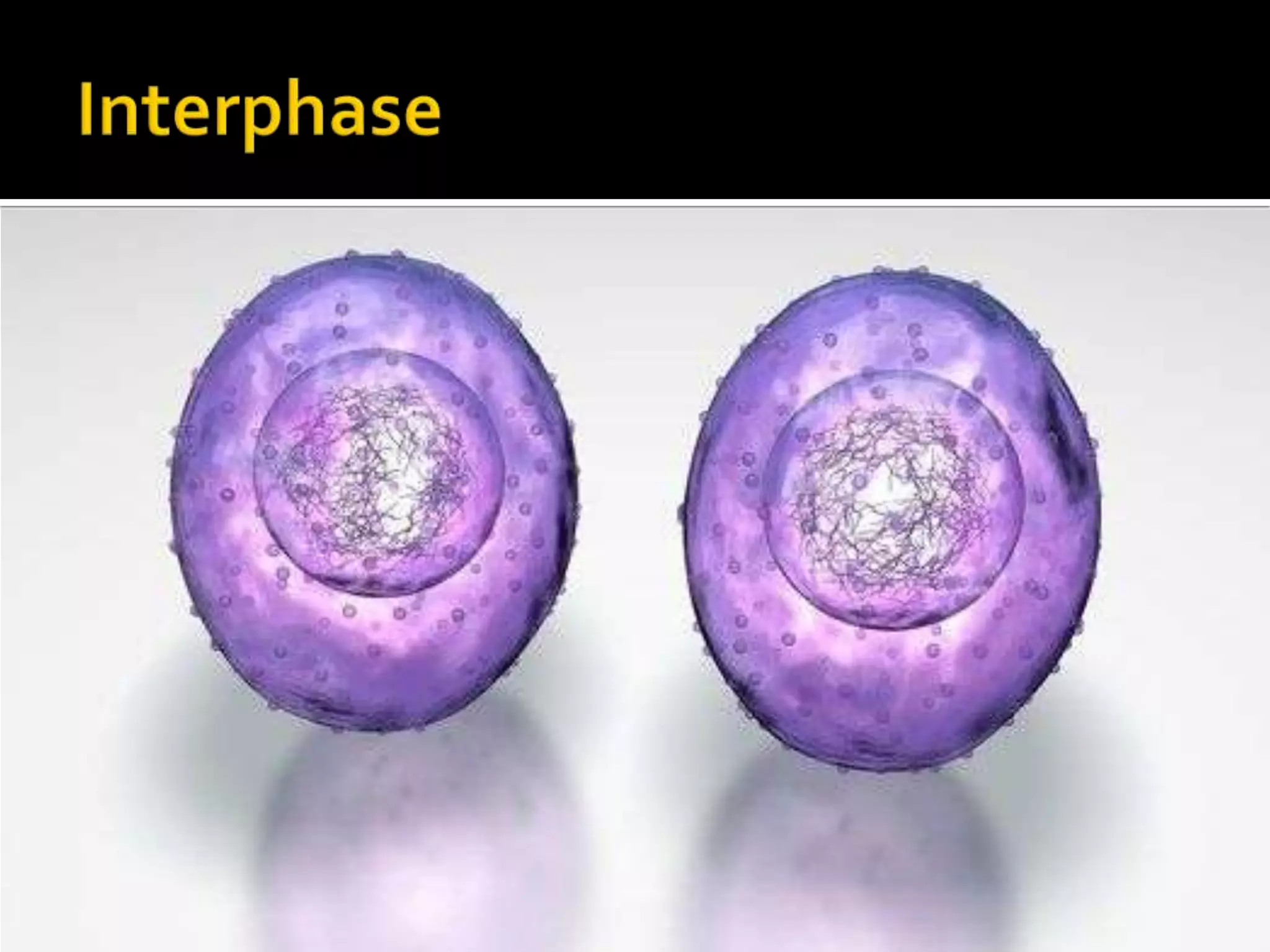
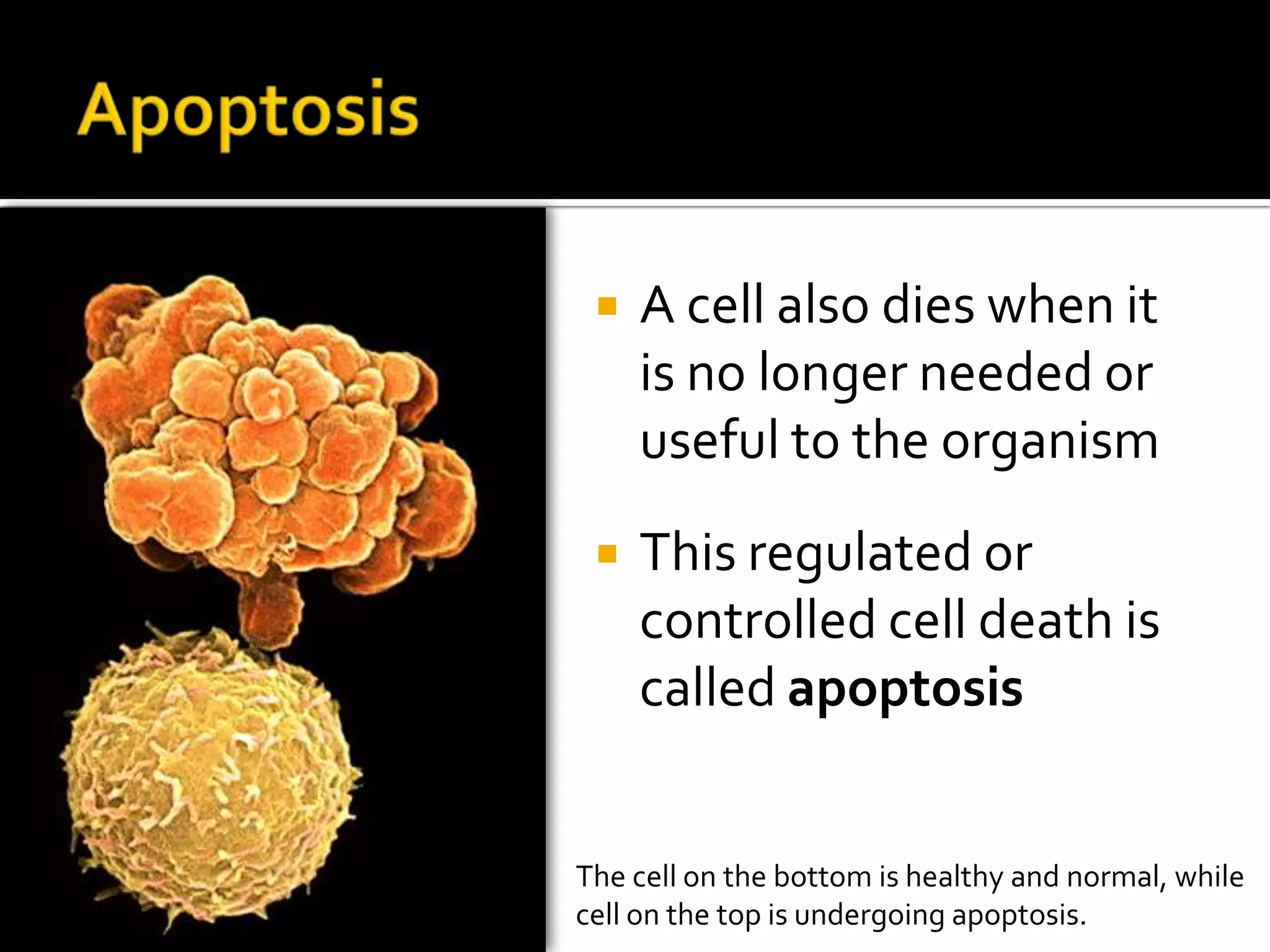
The cell cycle is the repeating series of growth and division that produces new cells. It consists of interphase, where the cell grows and DNA is replicated, and mitosis, where the cell divides into two daughter cells each with identical DNA. Chromosomes, made of DNA and proteins, condense during cell division and separate into each new cell, ensuring genetic continuity. The cycle controls cell growth, division, and death through regulated phases.